1. Syria
Why in the News?
- Israeli PM Benjamin Netanyahu confirmed talks with Damascus on demilitarisation of southern Syria.
- Focus areas of discussions:
- Protection of the Druze community in Sweida and beyond.
- Creation of a demilitarised zone from the Golan Heights to Sweida, south of Damascus.
- Establishment of a humanitarian corridor for aid delivery.
- Syria’s official news agency (SANA) reported a meeting in Paris (Aug 19) between Syrian FM Asaad al-Shaibani and an Israeli delegation led by Ron Dermer.
- Damascus confirmed indirect contacts with Israel with the aim of returning to the 1974 disengagement agreement that created the buffer zone.
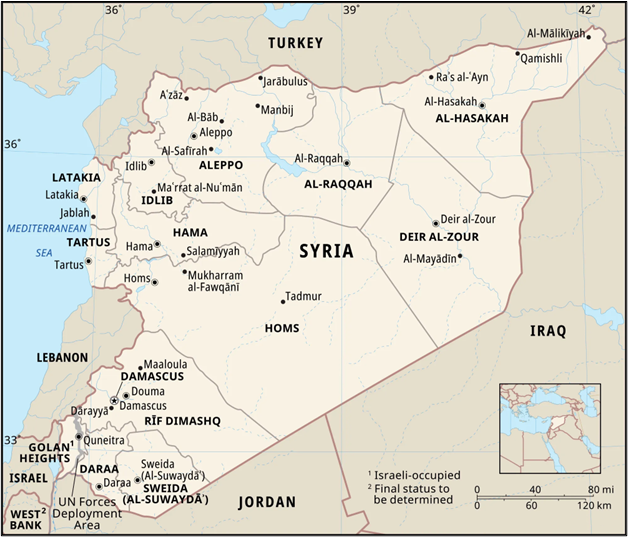
About Syria
- Location & Borders:
- West Asian country.
- Borders Turkey, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, and Israel.
- Has a Mediterranean Sea coastline on the west.
- Ethnic Composition:
- Home to Syrian Arabs (largest group), Turkmen, Kurds, Assyrians, Circassians, Armenians, Greeks, and Mandaeans.
- Religious Groups:
- Includes Sunnis (largest group), Alawis, Shiites, Christians, Jews, Mandaeans, Druze, Salafis, Ismailis, and Yazidis.
- Historical Significance:
- Historically refers to the Levant region of the ancient world.
- Modern Syria includes territories of several ancient kingdoms and civilisations.
- Damascus and Aleppo are among the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities.
- In Arabic, Syria is also called “Al Sham”.
- Modern Political History:
- Became a parliamentary republic in 1945 after the French mandate ended.
- Was earlier under centuries of Ottoman rule.
- 1963: A Ba’athist coup d’état brought the Ba’ath Party to power.
- 1963–2011: Syria remained under a state of Emergency, curtailing citizens’ constitutional rights.
2. Lebanon
Why in the News?
- The UN Security Council voted unanimously to terminate the UN peacekeeping force (UNIFIL) in southern Lebanon at the end of next year, after nearly five decades.
- The decision came after pressure from the United States and Israel, which argued for reducing or ending the mission.
- UNIFIL was originally deployed in 1978 to oversee Israeli withdrawal and later expanded after the 2006 Israel-Hezbollah war.
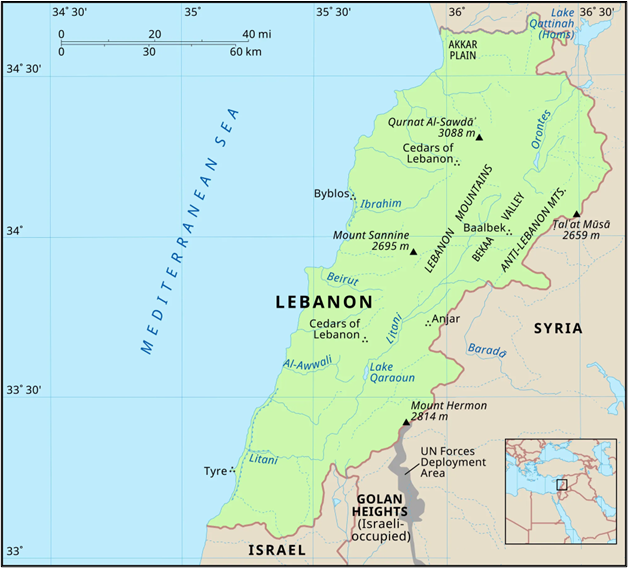
About Lebanon
- Location: Lebanon is a small country in Western Asia, located on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, bordered by Syria to the north and east, and Israel to the south.
- Capital: Beirut, a major cultural and financial hub in the Middle East.
- Geography: Features a narrow coastal plain, Lebanon Mountains, and the fertile Beqaa Valley.
- Population: Around 6 million people, with a significant Lebanese diaspora worldwide.
- Government: Parliamentary Republic with a unique power-sharing system among religious communities.
- Economy: Traditionally based on banking, tourism, and agriculture, but currently faces a severe economic crisis and hyperinflation.
- Religion: Known for its religious diversity, including Christians, Sunni Muslims, Shia Muslims, and Druze.
- Recent Issues: Struggles with political instability, refugee influx from Syria, and periodic conflicts involving Hezbollah and Israel.