Bolivia
Why in the News?
- Bolivia is headed for a presidential run-off after no candidate secured the required majority in the recent elections.
- The results signal the end of over two decades of dominance by the Movement Toward Socialism (MAS) party.
- Centrist candidate Rodrigo Paz secured the highest share of votes, followed by former President Jorge ‘Tuto’ Quiroga.
- The election outcome reflects public discontent amid economic challenges, including high inflation, dollar shortages, and concerns over the existing economic model.
About Bolivia
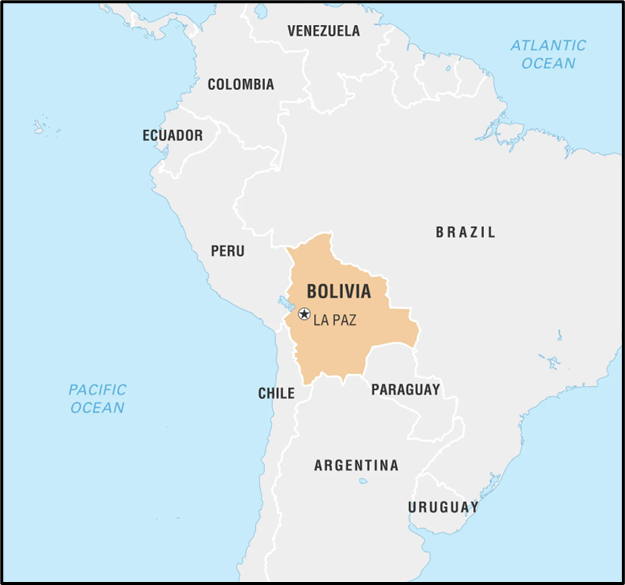
- Location: Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked nation in western-central South America, named after independence leader Simón Bolívar.
- Geography:
- Situated in the Andes Mountains with a mix of highland plateaus and Amazon basin lowlands.
- About one-third of its area lies within the Andean range.
- Shares control of Lake Titicaca, the world’s highest navigable lake (12,500 ft).
- Borders: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, and Peru.
- Capital: Sucre is the constitutional capital; La Paz is the seat of government and executive capital.
- History:
- Once part of the Inca Empire (15th–16th centuries).
- Conquered by the Spanish in 1538.
- Gained independence in 1825.
- Experienced frequent coups and countercoups until the last in 1978; democratic rule restored in 1982.
- Government:
- A republic, with the constitution defining it as a “Social Unitarian State.”
- The President serves as both head of state and head of government.
- Economy: A mixed system, combining private enterprise with state regulation and planning.
- Other Facts:
- Currency: Bolivian Boliviano.
- Languages: 37 official languages, including Spanish.
Myanmar
Why in the News?
- Myanmar’s military junta has announced the start of long-promised elections even as the country remains engulfed in a civil war.
- The elections are being held under conditions where large parts of the territory are controlled by pro-democracy groups and ethnic armed organisations, who have pledged to block polling in their areas.
- Observers and international monitors have described the exercise as a move to rebrand military rule, with opposition leaders jailed or boycotting the process.
- The announcement comes amid worsening humanitarian conditions, with thousands killed, millions displaced, and over half the population pushed into poverty.
About Myanmar
- Official Name & Location
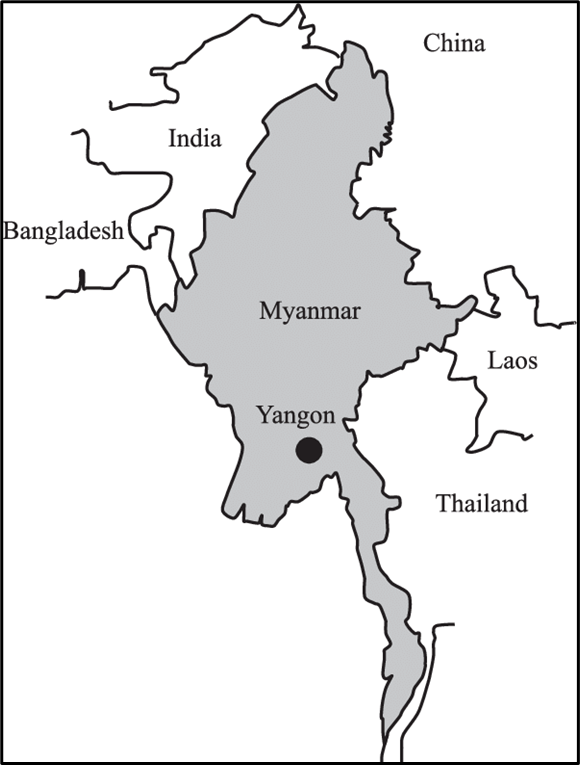
- Myanmar, formally the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, lies in mainland Southeast Asia.
- It shares borders with Bangladesh, India, China, Laos, and Thailand, and has coastlines along the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal
- Area & Geography: Covering approximately 676,553 km², Myanmar features diverse terrain—from mountain ranges in the north through the central Irrawaddy basin to southern coastal plains
- Burmese is the official language, serving as the first language for many and a second language for other groups.
- Economy
- The economy is largely agrarian, with significant contributions from agriculture, forestry, and fishing.
- The country possesses substantial natural resources—including timber, oil, natural gas, and minerals—though political instability and limited infrastructure hamper growth.
- Strategic Location:
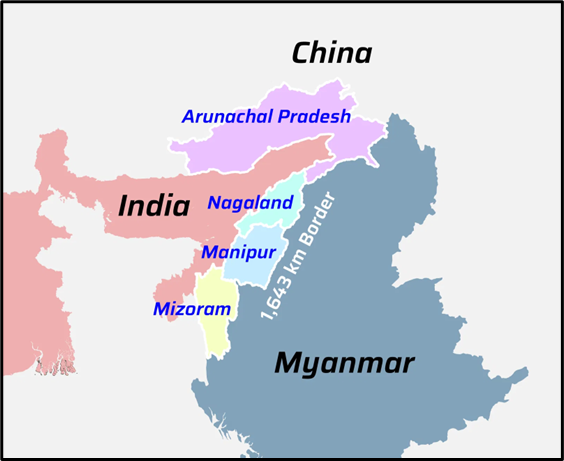
- India and Myanmar share a 1,643 km land border along with a maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal.
- Myanmar serves as India’s gateway to Southeast Asia, crucial for connectivity initiatives like Act East Policy.
- Countering China:
- To balance Chinese influence in the region, India developed the Sittwe Port in Rakhine State under the SAGAR vision, countering China’s development of the Kyaukpyu Port.
- Internal Security:
- Myanmar shares borders with India’s insurgency-prone northeastern states.
- Cooperation with Myanmar is vital for border security, counter-insurgency operations, and maintaining regional stability.
- Economic Cooperation:
- India is among Myanmar’s key trading partners with investments in energy, infrastructure, and agriculture.
- Connectivity projects like the India–Myanmar–Thailand Trilateral Highway highlight the deepening economic linkages.
- Cultural & Historical Ties: Civilizational and religious linkages—especially Buddhism, which spread from India to Myanmar—form the foundation of people-to-people connections and enduring cultural ties.