Karaikal
Why in the News?
- Karaikal, an enclave of the Union Territory of Puducherry, will soon host a first-of-its-kind state-of-the-art fisheries processing cluster under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- The project, with an estimated cost of ₹348.89 crore (including ₹298.34 crore Central grant), aims to modernize fisheries infrastructure and boost socio-economic development for the fishing community.
- This initiative will create an integrated fisheries cluster with backward and forward linkages, benefiting fishers through higher incomes, employment generation, and market access.
About the Place
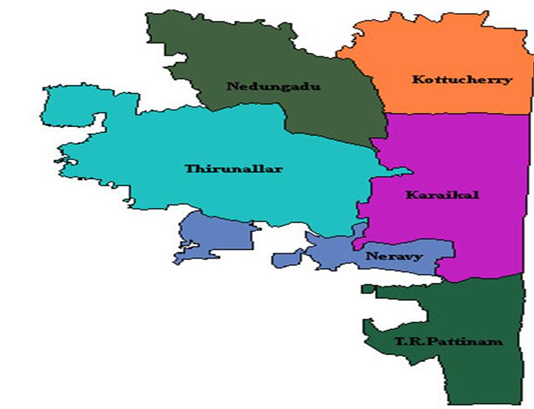
- Location: Karaikal is one of the four districts of the Union Territory of Puducherry, situated on the eastern coast of India along the Bay of Bengal.
- Geography: It is an enclave surrounded by Tamil Nadu and lies about 132 km south of Puducherry city and 150 km from Chennai.
- Area: Covers about 160 sq. km, making it the second-largest region in the UT after Puducherry district.
- Rivers: The district is irrigated by the Cauvery River and its distributaries, making it agriculturally fertile.
- Economy: Predominantly agriculture-based with paddy cultivation and fisheries as key economic activities.
- Culture: Known for its temples, including the famous Sri Saneeswara Temple at Thirunallar, attracting thousands of pilgrims.
- Transport: Well-connected by road and rail, with the nearest airport at Tiruchirappalli (Trichy).
- Special Feature: Hosts a major port project (Karaikal Port) and is being developed as a marine trade and fisheries hub under central government initiatives.
Dibru-Saikhowa National Park
Why in the News?
- A new study titled “Grasslands in Flux” has found that two native species — Bombax ceiba (Simalu) and Lagerstroemia speciosa (Ajar) — have joined invasive species in altering the riverine ecosystem of Dibru-Saikhowa National Park (DSNP).
- The study reveals a substantial decline in grasslands and an increase in degraded forest and shrubland between 1999 and 2024, posing a serious threat to grassland-dependent species.
About Dibru-Saikhowa National Park
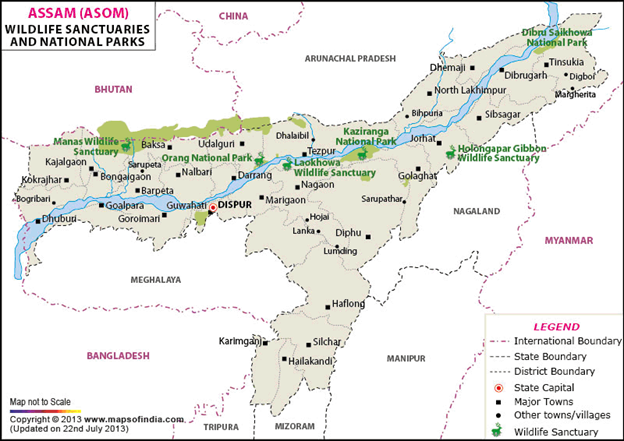
- Location: Situated in eastern Assam, between the Brahmaputra River (north) and the Dibru River (south).
- Area: Covers about 425 sq. km.
- Habitat Type: Known for its grassland-dominated riverine ecosystem, semi-evergreen forests, and wetlands.
- Unique Feature: The only habitat of feral horses in India — around 200 horses, descendants of military horses from World War II.
- Biodiversity: Home to rare and endemic species like Bengal Florican (Houbaropsis bengalensis), hog deer (Axis porcinus), and swamp grass babbler (Prinia cinerascens).
- Conservation Status: Designated as a National Park in 1999; also a Biosphere Reserve.
- Major Threats: Grassland shrinkage, invasive species, frequent floods of Brahmaputra, and human pressure from forest villages.
- Recent Study Findings: Grassland cover has reduced from 78% in 2000 to much less now, replaced by shrubland and degraded forest — impacting wildlife and increasing climate vulnerability.