Perito Moreno Glacier
Why in the News?
- The Perito Moreno Glacier in Argentina, long known for its unusual stability compared to other shrinking glaciers, is now showing signs of accelerated thinning.
- Scientists observed a sudden speed-up in August 2019, which could indicate a shift toward instability.
- New research suggests changes in the glacier’s floating ice tongue and its interaction with bedrock may be driving this threat.
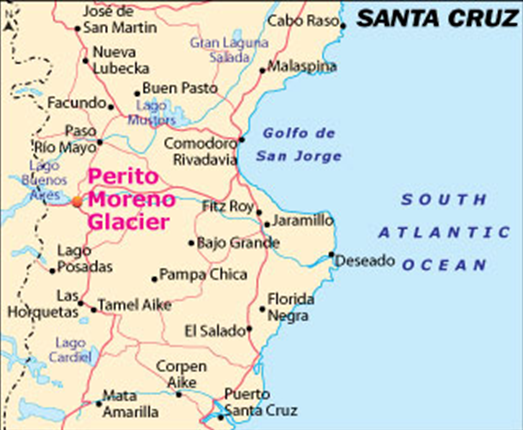
About Perito Moreno Glacier
- Location – Situated in Los Glaciares National Park, in the southwest of Santa Cruz Province, Argentina.
- Type – One of the world’s largest freshwater glaciers and among the few that have remained relatively stable in size for decades.
- Size – Stretches about 30 km in length with an average height of 74 meters above the surface of Lake Argentino.
- Unique Feature – Known for periodic rupture events when ice dams form and then collapse, releasing water dramatically into Lake Argentino.
- Tourism – A major tourist attraction in Patagonia, drawing visitors for its spectacular ice formations and dynamic calving events.
- UNESCO Status – Part of Los Glaciares National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1981.
- Climate Context – Historically resisted the rapid retreat seen in most other glaciers, making its new instability especially concerning.
- Scientific Importance – Studied as a benchmark for understanding glacier dynamics, climate change impacts, and freshwater storage.