- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
United States and the Paris Agreement
United States and the Paris Agreement

- In January 2025, the White House has confirmed that President Donald Trump will once again withdraw the United States from the Paris climate agreement. The withdrawal will become official one year after the submission of the letter.
- He has repeatedly referred to climate change as a “hoax” and seeks to free US oil and gas industries from environmental regulations.
- By withdrawing, the United States will join Iran, Libya and Yemen as the only four countries not party to the agreement
- Interestingly, Trump had previously pulled the US out of the Paris Agreement during his first term, but his successor, President Joe Biden, rejoined the agreement, four years later.
Paris Agreement
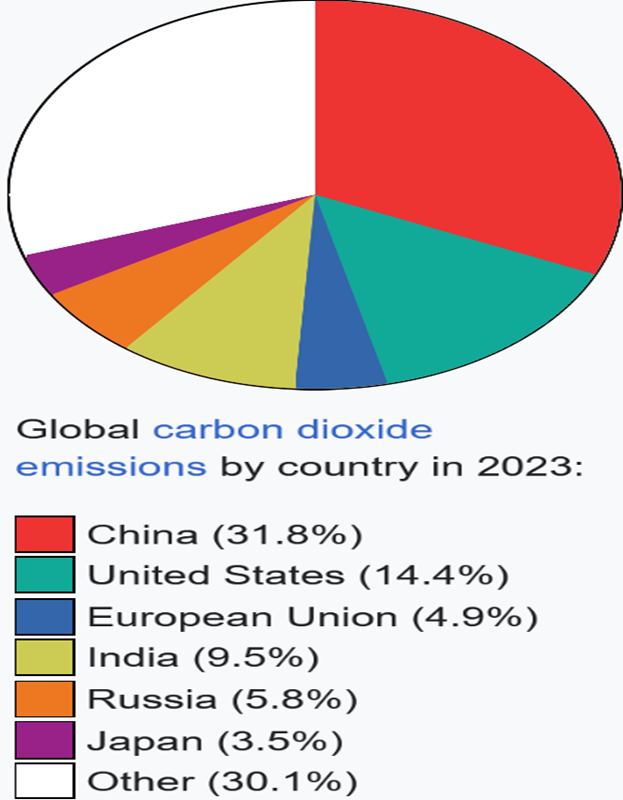
1. The Paris Agreement is an international accord that was adopted by nearly every country in 2015 to address climate change and its adverse effects.
2. Its primary goal is to substantially reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in a bid to limit global warming in this century to “well below” 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels while pursuing the means to curb warming to 1.5 degrees.
Greenhouse Gases |
|
3. The agreement mentions the safer limit of 1.5 degrees based on a fact-finding report which found that breaching the threshold could lead to “some regions and vulnerable ecosystems” facing high risks, over an extended, decades-long period.
4. The treaty also requires all Parties (countries which have joined the agreement) to state every five years what they are doing to tackle climate change — what is known as their nationally determined contribution (NDC). Each successive NDC is meant to reflect an increasingly higher degree of ambition compared to the previous version, according to the website of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
What is the process for a country to withdraw from the Paris Agreement?
1. Article 28 of the Paris Agreement outlines the process and timeline for a country to withdraw from the treaty. It says, “at any time after three years from the date on which this Agreement has entered into force (this happened in 2016) for a Party, that Party may withdraw from this Agreement by giving written notification to the Depositary”.
2. The Article also states, “any such withdrawal shall take effect upon expiry of one year from the date of receipt by the Depositary of the notification of withdrawal, or on such later date as may be specified in the notification of withdrawal.”
3. If a member state wants to withdraw from the treaty, it has to submit the notification of a withdrawal to the Office of Legal Affairs of the UN, based at UN Headquarters in New York.
4. Once the withdrawal notification has been received, it only becomes effective after one year (or later if the member state so says in the notification). Until the withdrawal comes into force, the member state remains in the Paris Agreement and has to fully participate in all activities under it, according to the UNFCCC website.
|
Conference of the Parties (COP) The Conference of the Parties (COP) is the annual meeting of the members of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), an international agreement established in 1992 that serves as the foundation for climate negotiations. Currently, there are 198 parties to the UNFCCC, which includes 197 countries and the European Union, representing almost universal membership.
COP 29 was held in Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan, from 11-22 November 2024.Key Milestones from Previous Conference of the Parties
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
|
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
UPSC Monthly Mgazine |
CSAT Foundation Course |
Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims |
UPSC Test Series |
ENSURE IAS NOTES |
Our Booklist |