- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
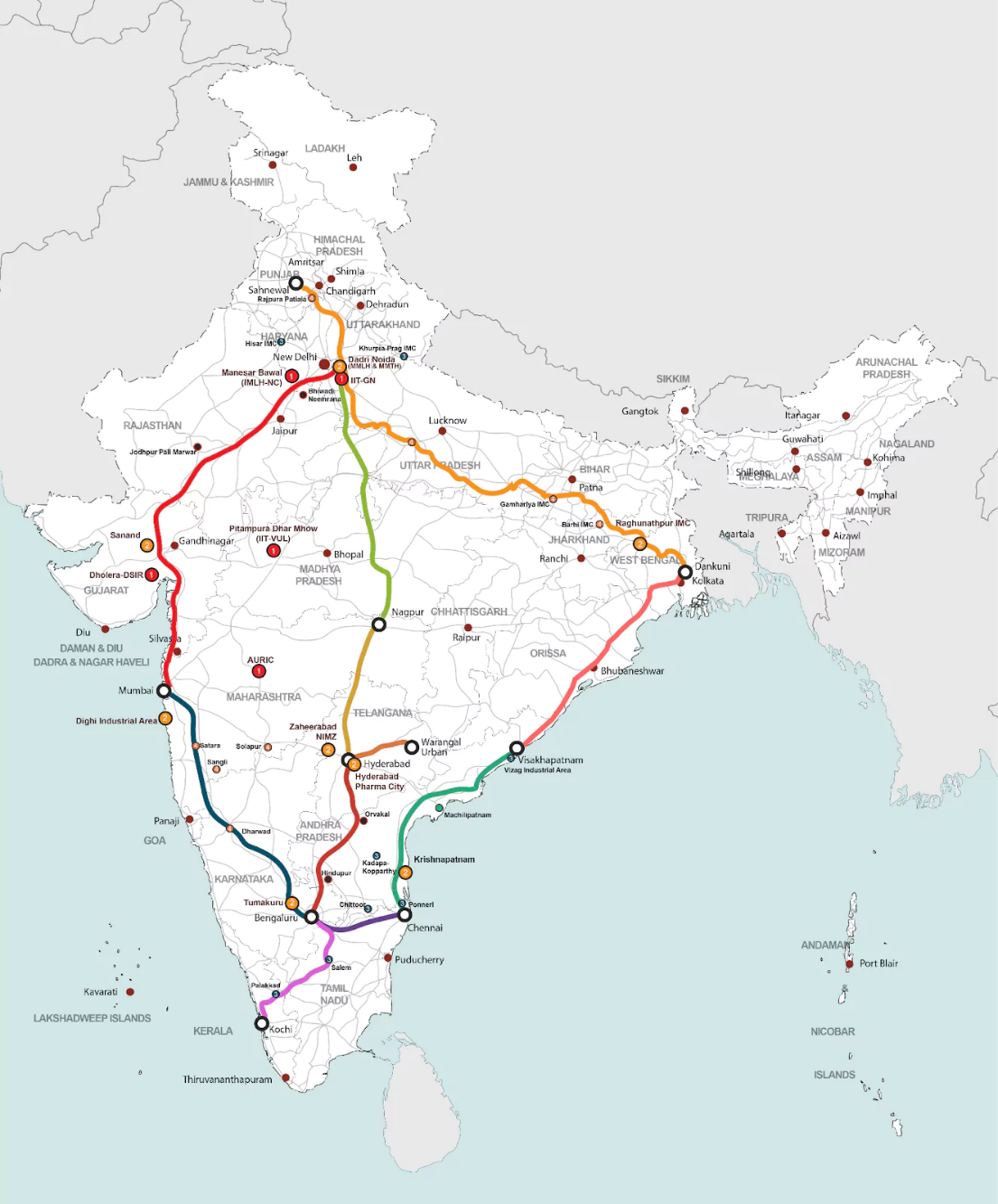
Union Cabinet Approves 12 Industrial Smart Cities
Union Cabinet Approves 12 Industrial Smart Cities
- Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved the establishment of 12 industrial smart cities across 6 major industrial corridors in 10 states with an investment of around ₹28,600 crore as part of the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme.
- The smart cities will be located in: Khurpia (Uttarakhand), Khurpia (Punjab), Dighi (Maharashtra), Palakkad (Kerala), Agra and Prayagraj (Uttar Pradesh), Gaya (Bihar), Zaheerabad (Telangana), Orvakal and Kopparthy (Andhra Pradesh, Jodhpur-Pali (Rajasthan)
What is an Industrial Smart City?
- An Industrial Smart City is a modern urban area that uses advanced technologies and data to improve industrial operations and promote sustainable development.
- These cities aim to attract foreign investment, boost domestic manufacturing, and generate employment.
-
Objectives of Developing Industrial Smart Cities:
- Global Value Chains: The initiative seeks to enhance India's position in global value chains by offering investors ready-to-allot land.
- Modern Urban Concepts: It incorporates concepts like -
- Plug-and-play: Pre-built infrastructure that allows businesses to start operations immediately.
- Walk-to-work: Urban design encouraging people to live close to their workplaces, reducing car usage and promoting walking.
- Development Road Map: These cities are being developed under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP), which aims to create world-class industrial cities.
- NICDP Vision: NICDP is designed to create a vibrant industrial ecosystem, facilitating investments from both large industries and MSMEs.
- Implementation: The programme is carried out by the National Industrial Corridor Development and Implementation Trust (NICDIT) and National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation Limited (NICDC).
- 1st Industrial Corridor: Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor was the 1st such project which was approved in 2007.
- Self-Sustaining Cities: These industrial nodes will integrate residential and commercial spaces, functioning as self-sustaining urban areas.
- Marketing and Implementation: The government will partner with Invest India for project marketing.
- A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) will be set up to implement the parks, aiming for completion within 3 years depending on the cooperation from the state governments.
Key Features of Approved Industrial Smart Cities
Alignment with National Economic Goals & PM Gati-Shakti National Master Plan:
- These smart cities align with India's goal of reaching USD 2 trillion in exports by 2030.
- They will integrate with the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan, which includes multi-modal connectivity infrastructure for seamless movement of people, goods, and services.
- This infrastructure will boost logistical efficiency and improve supply chains across the country.
- The cities will form a 'necklace of industrial cities' along the Golden Quadrilateral, promoting connectivity and industrial growth.
Significance:
- These projects aim to attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) from countries such as Singapore and Switzerland.
- The cities are expected to create around 1 million direct jobs and up to 3 million indirect jobs, with an investment potential of Rs 1.5 lakh crore.
- Developed under the NICDP, these cities will focus on sustainability by using ICT-enabled utilities and green technologies to minimize environmental impact.
- Ready-to-allot land parcels will be available to attract both domestic and international investors, helping India strengthen its position in global value chains.
Challenges in Developing Industrial Smart Cities and solutions
|
Challenges |
Solutions |
|
Upgrading outdated infrastructure for IoT and high-speed internet requires major investment and faces logistical challenges, especially in older cities. |
Create land banks, ensure fair compensation to reduce disputes, and use innovative methods like land pooling to speed up land acquisition processes. |
|
Protecting large amounts of data from smart devices against breaches requires strong security measures and constant monitoring. |
Conduct thorough environmental assessments, promote sustainable practices, and invest in infrastructure that supports sustainable growth. |
|
Attracting financial investments, whether public or private, is challenging. Stakeholders must be convinced of the long-term benefits and return on investment (ROI). |
Promote Public Private partnerships, sharing risks and rewards equitably while maintaining transparency and accountability in governance. |
|
Addressing concerns about privacy, job losses due to automation, and lifestyle changes through effective communication and education is crucial for success. |
Address skill shortages through vocational training, collaborating with industries, and providing incentives for businesses to invest in employee development. |
|
Implementing smart city initiatives involves navigating complex local laws, regulations, and policies, which can be time-consuming and politically sensitive. |
Simplify and digitize administrative processes, harmonize regulations across government levels, and increase transparency to improve efficiency and attract investors. |



