- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
UK-Mauritius Treaty on Chagos Archipelago
05-10-2024
- In October 2024, the United Kingdom has announced the transfer of sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius which marks a significant move for post-colonial justice.
|
An Archipelago is a group of small islands or an area of sea in which there are many small islands. |
- This decision follows years of legal battles and diplomatic efforts led by Mauritius, aiming to reclaim the islands that were separated from it in the 1960s.
- While the treaty is yet to be finalized, both nations have committed to completing the process swiftly.
- UK’s decision comes after substantial international pressure, including a 2019 ruling by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and a UN General Assembly resolution, both of which declared the UK’s control over the islands illegal.
- The handover marks an important phase in Britain’s decolonization, as the Chagos Islands are among the last of its colonial territories.
- The US military base on Diego Garcia which is the part of the archipelago will remain operational with the UK retaining control over the base for an initial 99-year period.
- Both countries reaffirmed their commitment to ensuring the long-term, secure operation of the US military base on Diego Garcia as the base is seen as vital to regional and global security.
- The new treaty will establish a framework for economic, security, and environmental collaboration between the UK and Mauritius.
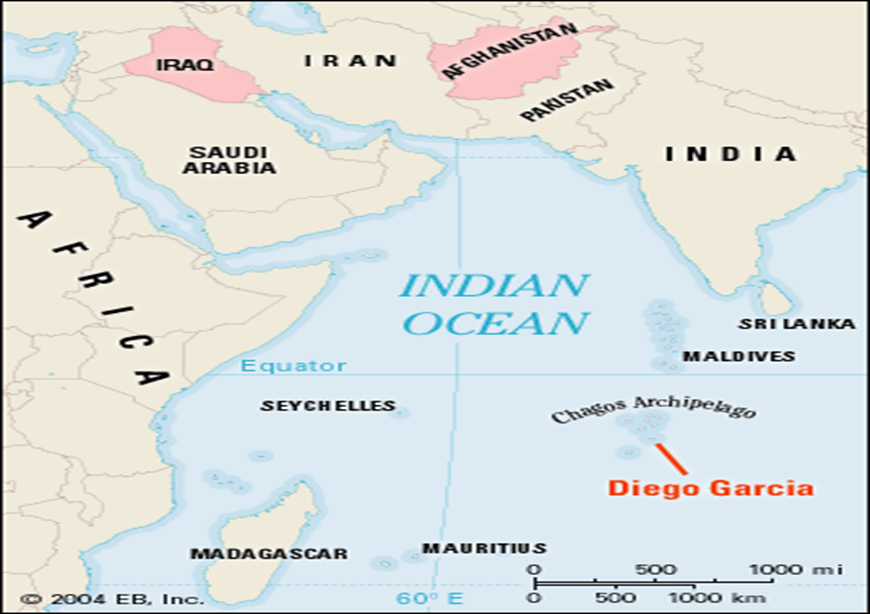
What is the Chagos Archipelago?
- Geographical Location: The Chagos archipelago consists of 58 islands located approximately 500 km south of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean.
- Historical Background:
- Initially uninhabited until the late 18th century when the French established coconut plantations using slave labor from Africa and India.
- The islands were ceded to the British in 1814 after the Napoleonic Wars.
- In 1965, the UK formed the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), which included Chagos. Following Mauritius's independence in 1968, Chagos remained under British control despite Mauritius’s claims.
What is Diego Garcia?
- Military Significance: Diego Garcia is the largest island in the Chagos archipelago and hosts a vital military base.
- Strategic Use:
- An agreement with the US in 1966 allowed for the establishment of a military presence, making Diego Garcia a crucial location for military operations, especially during the Gulf War and post-9/11 conflicts.
- It serves as a monitoring outpost for the Malacca Strait, crucial for global trade routes, particularly concerning China.
Why did Mauritius seek Sovereign Rights over Chagos?
- Legal Claims: Mauritius has consistently claimed that the UK illegally occupies Chagos. The issue has been raised in various international forums.
- UN Actions:
- In 2017, the UN General Assembly requested the International Court of Justice (ICJ) to assess the legal status of the Chagos archipelago.
- The ICJ ruled that the detachment from Mauritius was not conducted with the genuine consent of the local population, which has led to calls for the UK to withdraw.
Significance of the UK-Mauritius Treaty:
- Sovereignty Transfer: The treaty allows Mauritius to implement resettlement programs on the Chagos Islands (excluding Diego Garcia), marking a shift in control.
- Trust Fund: The UK will establish a trust fund for the benefit of the Chagossians, supporting those displaced by earlier policies.
- Continued Military Presence: Diego Garcia will remain under UK sovereignty for an initial period of 99 years, maintaining its military operations.
Implications of the Treaty:
- Geopolitical Balance: The resolution of the dispute is critical for Western commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific. An unresolved issue could push Mauritius to engage with alternative partners like China.
- India's Position: As a former British colony, India has supported Mauritius’s claims over Chagos. It voted in favor of Mauritius at the UNGA and has strengthened ties with Mauritius amid China's rising influence in the Indian Ocean. Recent developments include India's construction of infrastructure in Mauritius, enhancing bilateral relations.
Why Did India Support Mauritius in Its Claim Over the Chagos Archipelago?
- India has consistently supported Mauritius in its claim over the Chagos Archipelago, aligning with its broader foreign policy principles focused on decolonization, sovereignty, and solidarity with developing nations.
- This stance was evident in May 2019, when India was among 116 nations voting in favor of a UN General Assembly resolution.
- Alignment with India’s SAGAR Policy: Mauritius has become a key partner in India's Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR) policy, which aims to enhance economic and security cooperation with maritime neighbours.
- Through SAGAR, India works with its partners to improve maritime security by exchanging information, conducting coastal surveillance, developing infrastructure, and strengthening capabilities.
India-Mauritius RelationsStrategic Infrastructure Development
Defence Cooperation with Mauritius
Strategic Importance of Mauritius
|
Conclusion:
The UK-Mauritius treaty on the Chagos Archipelago represents a crucial step in resolving a long-standing territorial dispute, with significant implications for regional geopolitics and international relations. The agreement not only addresses historical grievances but also underscores the importance of the Chagos Islands in global security dynamics, particularly concerning US military strategy and the influence of China in the Indian Ocean region.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus



