- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
The Role of E-fuels in Decarbonising Transport
The Role of E-fuels in Decarbonising Transport
10-01-2024
Introduction:
The report named ‘The Role of E-fuels in Decarbonising Transport’ has been prepared by IEA (International Energy Agency) to access the role of E-Fuels as a promising solution in decarbonize the transport sector.
What are E-Fuels?
- E-fuels, or electro fuels, are synthetic fuels produced through electrolysis
- Example of E-Fuels are e-kerosene, e-methane etc.
- E- fuels are made by combining green hydrogen with captured CO2 to create a synthetic hydrocarbon fuel.
Benefits from E-Fuels
- Carbon Neutrality: E-fuels can be produced using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, thus they have the potential to be carbon-neutral.
- Energy Storage: E-fuels can serve as a means of storing renewable energy in a chemically stable form.
- Decarbonizing Hard-to-Electrify Sectors: In some sectors, such as aviation, heavy industry, and long-haul transportation, E-fuels can be a potential solution to decarbonise these hard-to-electrify sectors.
- Infrastructure Compatibility: E-fuels can potentially be integrated into existing fuel distribution systems and used with current combustion engines.
Carbon Neutrality of E-Fuels:
- E-fuels offer potential carbon neutrality by using renewable electricity (solar, wind, etc.) in the electrolysis process and capturing CO2 from sustainable sources.
- The carbon emissions from combustion of traditional fuels can be balanced out by the captured CO2.
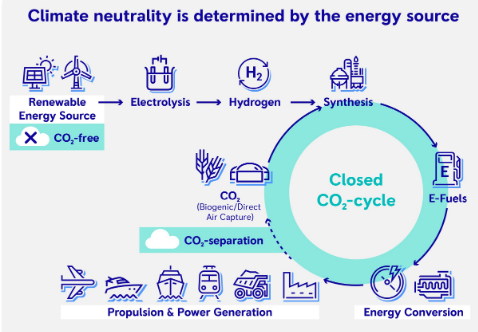
Key Points from the IEA Report:
- 10% E-fuels Share by 2030: The report sets the ambitious target of achieving 10% share of e-fuels in aviation and shipping sectors by 2030.
- Technology Assessment: The report assesses the emerging e-fuel technologies and evaluates their technological and economic aspects.
- Cost Reduction: Emphasis is placed on cost reduction in E-Fuel production, which is necessary for achieving ambitious 10% target.
- Resource and Infrastructure Investments: The report outlines the resources and infrastructure investments essential for achieving the set goal.
Government’s initiatives to promote e-Fuels
- National Green Hydrogen Mission with target of 5 MMT annual green hydrogen/ ammonia production by 2030
- Subsidies for petrol and diesel were removed in the early 2010s, and subsidies for electric vehicles were introduced in 2019.
- Import substitution of around INR 17,500 Cr every year, and Impetus to Research & Development to achieve higher efficiency in solar PV modules.
Challenges and solutions
SR No. |
Challenges |
Solutions |
|
1 |
High Cost of E-fuel Production |
|
|
2 |
Difficulty in altering current Legislation and Policies |
|
|
3 |
Wider acceptance by the general public will be a challenge. |
|
|
4 |
It is difficult for E-fuels to replace traditional fuels like petrol, diesel, etc. |
|
Conclusion:
Overcoming cost and efficiency challenges, coupled with policy support and investments, could position e-fuels as a key player in sustainable transport for the future.