- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
The Brain-Eating Amoeba: Naegleria fowleri
The Brain-Eating Amoeba: Naegleria fowleri
10-06-2024
- A 15-year-old boy in Kerala's Alappuzha district has died of a rare infection caused by Naegleria fowleri or "brain-eating amoeba".
- He suffered from high fever for a week and his body organs rapidly deteriorated.
- He used to take bath in a drain near his house, the likely source of the amoeba, which is known to thrive in any natural environment, especially in warm water habitats.
- However, it does not survive in salt water and is therefore not found in marine water.
- It survives on bacteria found in sediments in lakes and rivers.
What is Naegleria fowleri?
About:
- Naegleria fowleri, commonly referred to as the "brain-eating amoeba," is a unicellular organism found in warm freshwater environments such as lakes, hot springs, and poorly maintained swimming pools.
- It is a microscopic organism visible only under a microscope.
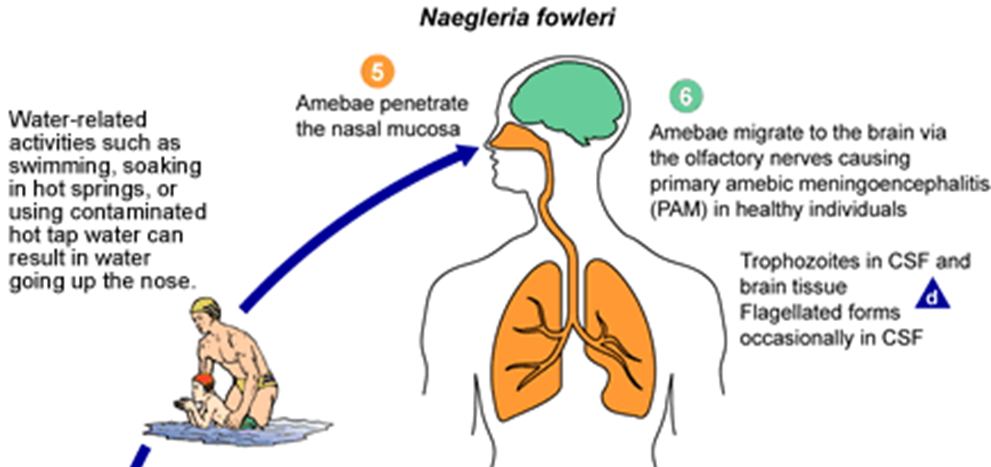
- The amoeba enters the body through the nose and can trigger a severe brain infection known as primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM).
Key points:
Spread in the Human Body:
- The amoeba, Naegleria fowleri, is usually acquired through the nasal passage and mouth when an individual engages in activities like swimming, diving, or participating in religious rituals involving contaminated water.
- Subsequently, the amoeba migrates through the olfactory nerve to the brain, triggering severe inflammation and destruction of brain tissue.
- It is important to note that Naegleria fowleri infection does not spread from person to person.
At-risk Individuals:
- While humans are generally susceptible to Naegleria fowleri, infections are exceptionally rare.
- Specific factors such as a weakened immune system or a history of nasal or sinus problems may increase vulnerability.
- Additionally, activities involving exposure to warm fresh water may also increase the risk of infection.
Symptoms and Prognosis:
- Symptoms usually appear within a week of infection and include severe headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, confusion, seizures, and hallucinations.
- The infection progresses rapidly and can lead to coma and death. The chances of survival are unfortunately low.
Treatment:
- Treatment involves a combination of medications.
- The drug miltefosine has shown efficacy in killing Naegleria fowleri in the laboratory and has been used successfully to treat the few survivors.
- Even with treatment, survival rates from Naegleria fowleri infections are low, with mortality rates as high as 97 percent.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi