- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Swell Waves Likely to Hit Coastal Areas
Swell Waves Likely to Hit Coastal Areas

The swell waves, known locally as 'Kallakkadal', caused flooding in coastal areas of southern and central Kerala.
- As noted by the fishing community, this phenomenon is not common at this time of year.
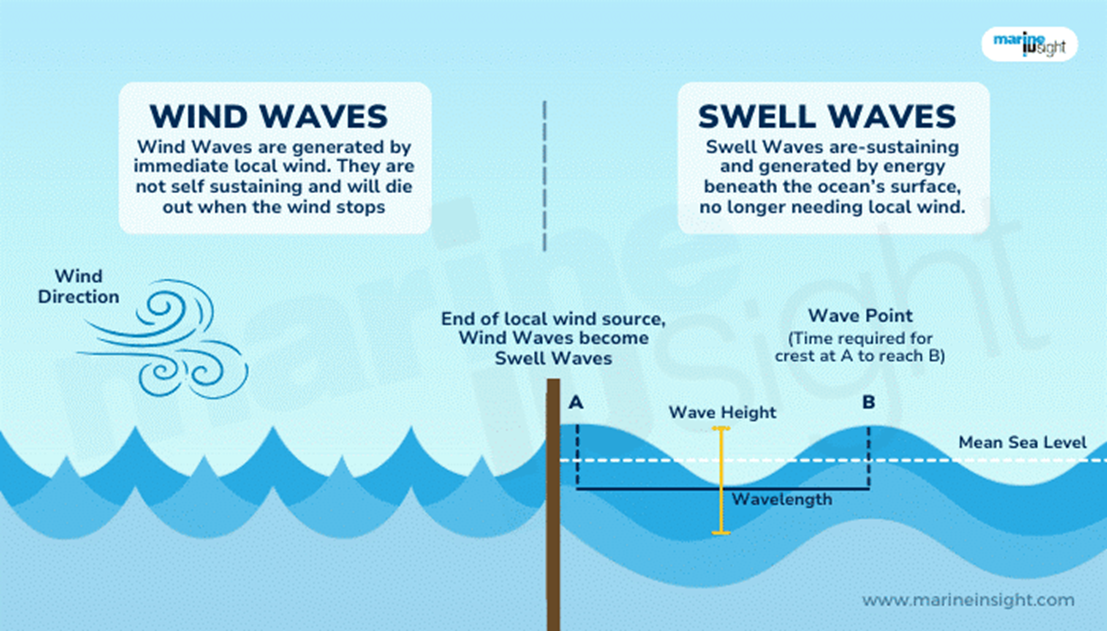
What are the Swell waves ?
- Swell waves are a type of ocean wave that travel long distances from their origin. They are also known as ground swells.
- Swell waves are a series of surface gravity waves that are not affected by local winds. They are caused by distant storms, hurricanes.
- Swell waves can travel thousands of kilometers across the ocean without breaking.
- Swell waves can be a significant factor in shaping coastal areas. When they reach the shore, they can cause erosion and inundation.
What is Kallakkadal?
- Kallakkadal is essentially coastal flooding during the pre-monsoon (April-May) season by swell waves on the southwest coast of India.
- The term Kallakkadal, used by local fishermen, is a combination of 2 Malayalam words, including Kallan and Kadal. “Kallan means thief and Kadal means sea.
Swell waves and P-waves and S-waves are entirely different types of waves with very distinct characteristics:
Swell Waves
- Medium: Swell waves travel across the surface of the ocean.
- Type of Wave: A type of mechanical wave where water particles move in a roughly circular motion.
- Formation: They are generated by wind out in the open ocean and travel long distances.
- Relevance: Important for surfers, coastal shaping, and ocean circulation patterns.
P-Waves and S-Waves
- Medium: P-waves (primary waves) and S-waves (secondary waves) travel through the Earth's interior.
- Type of Wave: Body waves, a type of seismic wave formed during earthquakes.
- Formation: Generated by sudden shifts and ruptures within the Earth's crust.
- Relevance: Used by scientists to study the Earth's internal structure and locate the origin of earthquakes.
Feature |
Swell Waves |
P-Waves |
S-Waves |
|
Medium |
Ocean surface |
Earth's interior |
Earth's interior |
|
Type of Wave |
Surface wave (mechanical) |
Body wave (compressional) |
Body wave (shear) |
|
Motion of Particles |
Circular |
Compressions and expansions (longitudinal) |
Side-to-side motion (transverse) |
|
Speed |
Relatively slow |
Fastest seismic wave |
Slower than P-waves |
|
Travel through liquids |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
What are P-waves and S-waves ?

- P-waves and S-waves are types of seismic waves, the energy waves released during an earthquake or volcanic eruption.
P-waves (Primary Waves)
P-waves, also known as primary or compressional waves, are the fastest seismic waves and travel in the same direction as the ground shaking.
- Type of motion: Compressional, like an accordion being squeezed and stretched. The ground particles move back and forth, parallel to the direction the wave travels.
- Speed: The fastest seismic waves.
- Travel through: Solids, liquids, and gases.
- Effect: Create a push-pull motion on the ground.
S-waves (Secondary Waves)
S-waves, also known as secondary or shear waves, travel more slowly and shake the ground perpendicularly to the direction of propagation.
- Type of motion: Shear or transverse, like shaking a rope up and down. The ground particles move perpendicular to the direction the wave travels.
- Speed: Slower than P-waves.
- Travel through: Only solids.
- Effect: Create a shaking, side-to-side, or rolling motion of the ground.
|
|
P-waves |
S-waves |
|
Speed |
1.5–8 kilometers per second in the Earth's crust |
60–70% of the speed of P-waves |
|
Motion |
Similar to a slinky |
Similar to shaking a rope |
|
Arrival |
First to arrive at a seismograph |
Second to arrive at a seismograph |
|
Mediums |
Can travel through solid, liquid, or gas |
Can only travel through solids |
|
Shaking |
Shakes the ground in the direction of propagation |
Shakes the ground perpendicularly to the direction of propagation |
|
Destruction |
Less destructive than S-waves |
More destructive than P-waves |



