- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Soil Acidification and Its Impacts
Soil Acidification and Its Impacts
23-04-2024
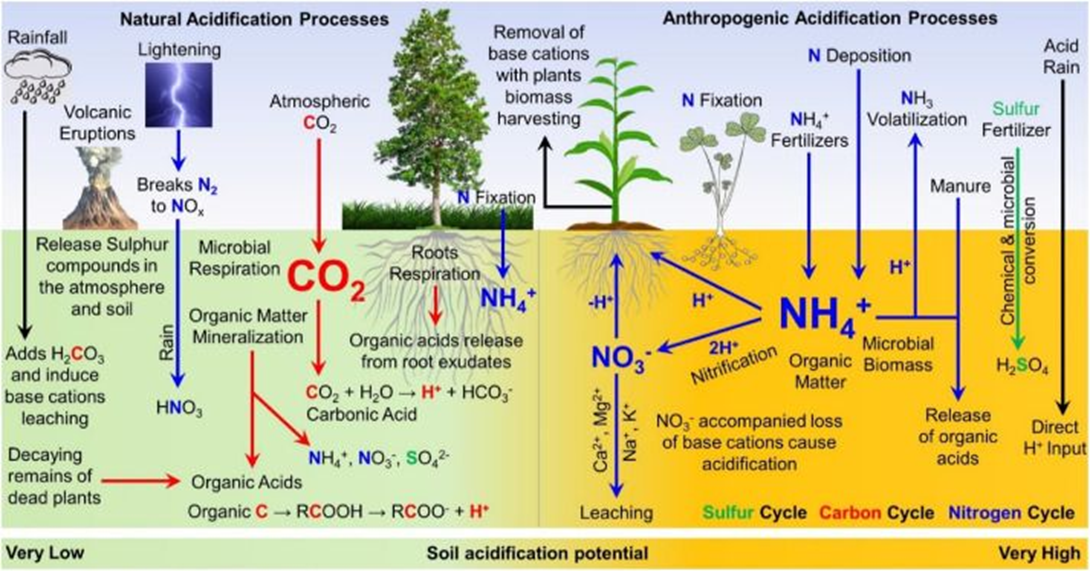
Over 30 per cent of cultivable land in India is said to carry acidic soil, impacting plant growth. Now, a new study highlighted another concern: Loss of soil inorganic carbon, a stable carbon pool. This depletion could hurt the health of soil and its ability to regulate nutrient levels, foster plant growth and store carbon.
- Soils are turning acidic due to industrial activities and intense farming.
- In India, soil acidification might lead to loss of 3.3 billion tonnes of soil inorganic carbon (SIC) from the top 0.3 metres of its soil over the next 30 years, according to the study published in the journal
Soil Acidification:
- Definition: Soil acidification is a gradual decrease in soil pH over time, leading to a more acidic environment.
- Distribution in India: In India, acidic soils are predominantly found in the humid southwestern, northeastern, and Himalayan regions.
- Contributing Factors:
- Excessive use of ammonium-based nitrogen fertilizers, especially in naturally acidic soils.
- Leaching of nitrate nitrogen from fertilizers, initially applied as ammonium-based compounds.
- Removal of plant materials during harvesting, as plant residue acts as an alkaline buffer when returned to the soil.
Impacts of Soil Acidification:
- Depletion of Soil Inorganic Carbon: Acidification depletes soil inorganic carbon, an important component for soil health and ecosystem services.
- Reduced Crop Growth and Productivity: Acidic soils hinder crop growth and yields by limiting the availability of essential plant nutrients and making plants more vulnerable to biotic and abiotic stressors.
What is Soil Inorganic Carbon?
Soil inorganic carbon exists in ores and minerals, unlike organic carbon found in natural sources such as plants and animals.
FAQs:
Q1: What is Pedology?
Soil science is a branch of science that includes the study of all aspects of soils. This includes examining their physical and chemical properties, the function of organisms in soil formation and their impact on soil characteristics, the identification and mapping of soil units, as well as the processes involved in soil origin and development.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



