- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 27 NOVEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 27 NOVEMBER 2024
Bolivia
Why in news?
- Heavy rains after a prolonged drought triggered a landslide in La Paz, Bolivia, early Sunday, destroying over two dozen homes, flooding 40 others, and leaving parts of the city without electricity.
- Torrential rains caused a river to overflow, dislodging mud and debris in the southwestern Bajo Llojeta neighbourhood, where poorly constructed hillside homes collapsed.
- However, Local authorities blamed the illegal construction of hillside homes for destabilizing the area.
- La Paz, situated in a valley prone to floods and landslides, faces heightened risks as the rainy season begins following one of Bolivia's most severe droughts in recent years.
About Bolivia:
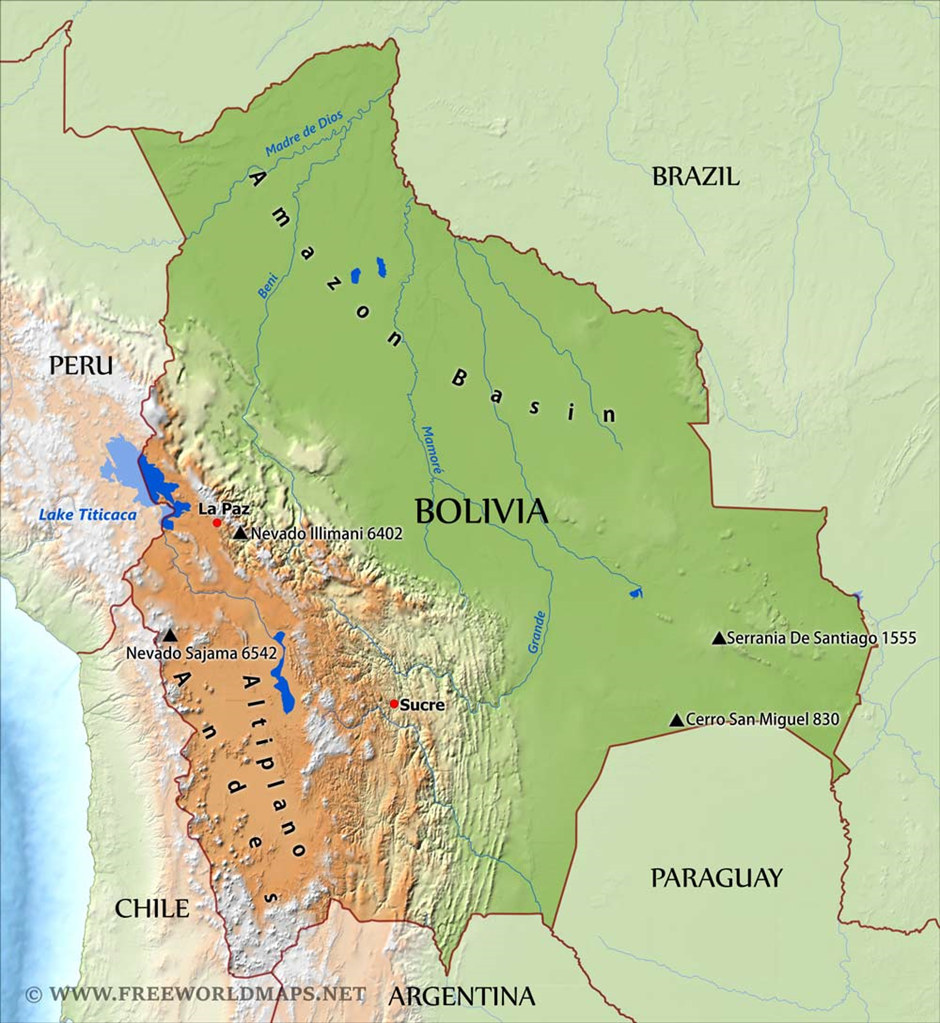
- Bolivia is a landlocked country in central South America, characterized by diverse geophysical features, including the Andes Mountains in the west, the Altiplano high plateau, tropical lowlands in the east, and extensive Amazonian rainforests.
- The Altiplano, situated between the Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Real, includes Lake Titicaca, the world’s highest navigable lake, and the Uyuni Salt Flats, the largest salt flat on Earth.
- Bordering countries are Brazil to the north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the south, Chile to the southwest, and Peru to the northwest.
- Bolivia has a mixed economic geography, with agriculture, mining, hydrocarbons, and tourism being significant sectors. Key crops include soybeans, quinoa, and coffee, while cattle ranching thrives in the lowlands.
- Rich in mineral resources, Bolivia is one of the leading producers of tin, zinc, and silver in the world.
- Bolivia is also part of the "Lithium Triangle," a region encompassing Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile, which contains more than half of the world's known lithium reserves.
- The Salar de Uyuni in Bolivia, the world's largest salt flat, holds a significant portion of these reserves, making the country a potential global leader in lithium production.
- The country is a major exporter of natural gas, particularly to neighboring Brazil and Argentina, and has significant petroleum reserves.
- Its varied climate ranges from arid conditions in the highlands to humid tropical climates in the Amazon basin, influencing agricultural and economic activities.
- Forests and biodiversity-rich ecosystems cover much of Bolivia, making it a key player in global environmental conservation efforts.
Bay of Bengal
Why in news?
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecasted the intensification of a deep depression over the Bay of Bengal into Cyclone Fengal by Wednesday, expected to impact Tamil Nadu and the Sri Lankan coast over the next two days.
- Currently located southeast of Tamil Nadu, the storm is predicted to move north-northwest, bringing heavy to extremely heavy rainfall across Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, and parts of Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, and Karnataka.
- A 'red' alert has been issued for Tamil Nadu on Wednesday, with an 'orange' alert on Thursday.
About Bay of Bengal:
-
Geophysical and geographical Characteristics:
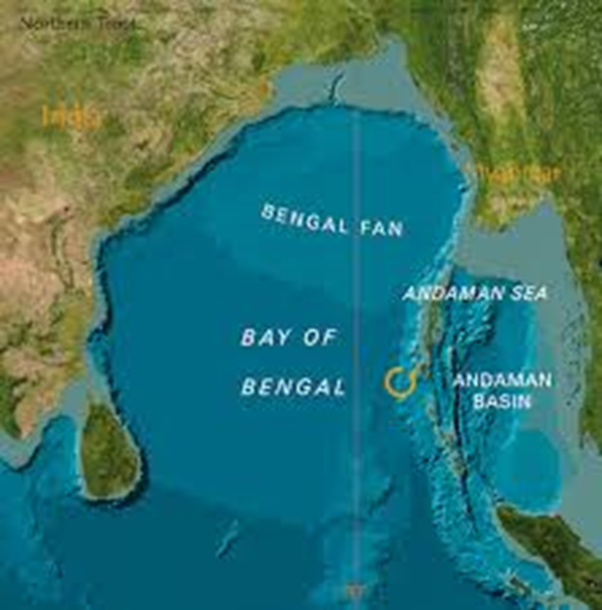
- The Bay of Bengal is a north-eastern arm of the Indian Ocean, bordered by India and Sri Lanka to the west, Bangladesh to the north, Myanmar to the east, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the southeast.
- It is the largest bay in the world, spanning approximately 2.2 million square kilometres.
- The bay is shallow with a continental shelf that supports extensive sediment deposits from major rivers like the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Irrawaddy.
- Submarine canyons and deltas such as the Bengal Fan, the world's largest submarine fan, are prominent features.
- It hosts several important river deltas, including the Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest, shared by India and Bangladesh.
- The Andaman Sea in the southeast connects the bay to the Pacific Ocean via the Strait of Malacca. The region supports diverse marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, seagrasses, and mangroves, and is a hub for biodiversity.
- Climate:
- The Bay of Bengal experiences a tropical monsoon climate, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- The summer monsoon (June to September) brings heavy rainfall and frequent cyclonic activity, while the northeast monsoon (October to December) causes additional rainfall along the south-eastern Indian and Sri Lankan coasts.
- Sea surface temperatures are warm year-round, ranging from 28°C to 30°C, conducive to cyclone formation.
- The region is also influenced by phenomena like El Niño and La Niña, which affect cyclone patterns and rainfall.
other recent cyclones developed in the Bay of Bengal:
|
name |
Description |
|
Cyclone Mocha (2023) |
Mocha was a powerful cyclone that formed in May 2023 and intensified into a Category 5-equivalent storm. It made landfall in Myanmar, causing severe destruction in the Rakhine state. |
|
Cyclone Mandous (2022) |
Mandous formed in December 2022 and made landfall near Mamallapuram, Tamil Nadu. It caused heavy rainfall and wind damage across coastal Tamil Nadu and parts of Andhra Pradesh. |
|
Cyclone Jawad (2021) |
Jawad developed in December 2021 but weakened to a depression before making landfall. It affected Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and West Bengal, causing heavy rains and localized flooding but relatively limited damage compared to more severe cyclones. |
|
Cyclone Yaas (2021) |
In May 2021, Cyclone Yaas hit Odisha and West Bengal. It caused significant damage with storm surges, flooding, and high winds, particularly in coastal areas. It was classified as a Very Severe Cyclonic Storm by the India Meteorological Department (IMD). |
|
Cyclone Amphan (2020) |
Amphan was one of the strongest cyclones in recent years, forming in May 2020. It intensified into a Super Cyclonic Storm and devastated West Bengal and Bangladesh. It caused massive loss of life and property, with damages exceeding $13 billion, making it one of the costliest storms in the region. |
Norway
Why in news?
- Norway’s Parliament recently apologized for its century-long assimilation policies targeting the Sami, Kven, and Forest Finn peoples, addressing historical discrimination.
- The Norwegianisation policies, active from the 1850s to 1960s, suppressed indigenous languages, cultures, and practices while forcibly separating Sami children from families.
- The Truth and Reconciliation Commission (2018-2023) revealed ongoing prejudice, land disputes, and endangered languages despite legal reforms. The Commission's report urged steps like reconciliation centers and preserving minority languages.
- This marks Norway’s first official apology to Kvens and Forest Finns, building on earlier efforts like the 1977 Sami apology.
- However, the challenges persist, including limited healthcare access and continued bullying.
About Norway:
-
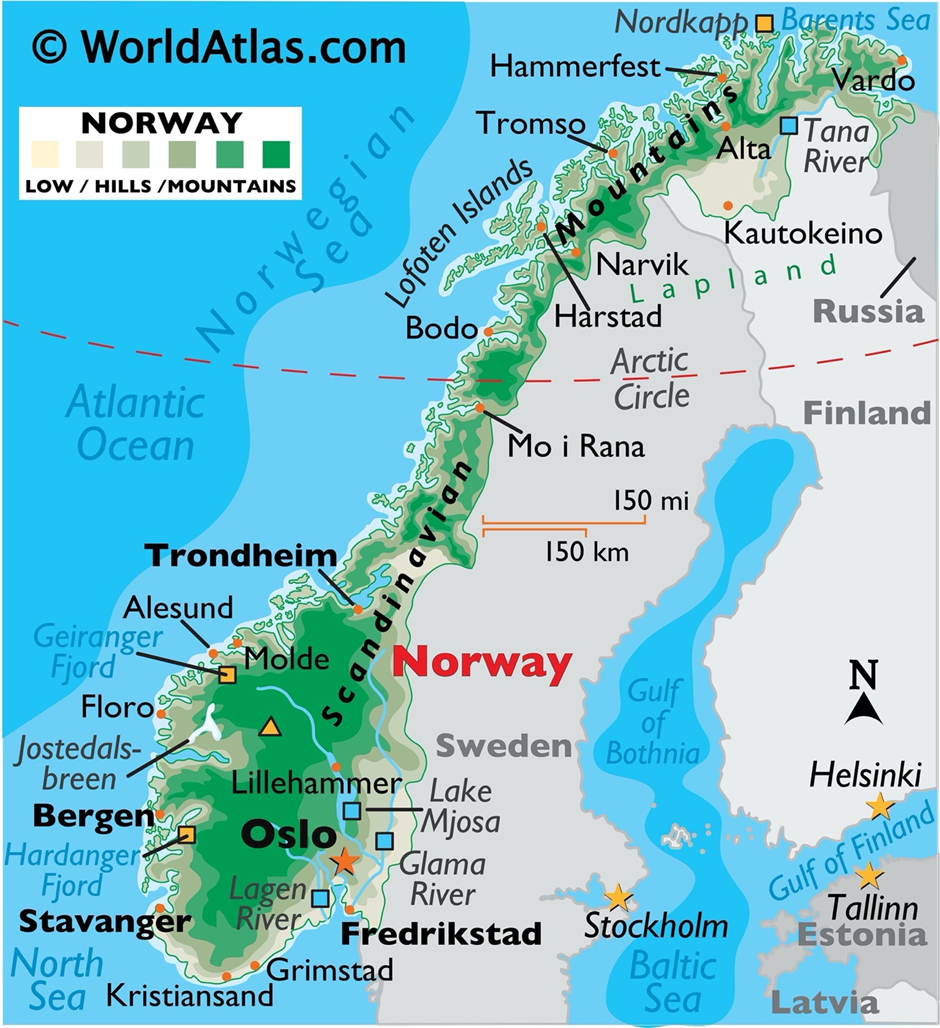
- Norway is located in Northern Europe, part of the Scandinavian Peninsula, with an elongated shape stretching 1,700 km from north to south.
- Norway's capital is Oslo, and its currency is the Norwegian Krone (NOK).
- It is bordered by the North Sea, Norwegian Sea, and Barents Sea, with mountains, deep fjords, and an extensive coastline of over 25,000 km, including islands.
- The Scandinavian Mountains run along the eastern border.
- Norway shares land borders with Sweden, Finland, and Russia.
- The country also controls the Svalbard archipelago and Jan Mayen islands in the Arctic.
- Coastal Norway has an oceanic climate with mild winters and cool summers, while inland and northern regions experience a subarctic or continental climate.
- Northern Norway, within the Arctic Circle, experiences the Midnight Sun and polar nights.
- Western Norway gets heavy rainfall, while the interior and east are drier.
- Natural resources include abundant oil, gas, and hydropower, with 90% of electricity sourced from renewables.
- Norway is a major exporter of seafood, especially salmon, cod, and herring.
- The forestry industry is supported by vast forest cover, and mining includes iron ore, copper, and titanium.
- Tourism thrives, especially with fjords, mountains, and the Northern Lights.
- Norway invests in green technologies, focusing on electric vehicle infrastructure and sustainable industry practices.
Sudan
Why in news?
- Over half of Sudan’s population, approximately 26 million people, are experiencing acute hunger, with 755,000 facing catastrophic conditions, including hunger-related deaths, according to the UN.
- The Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) report highlights a dire situation, marking the first time such severe conditions have been recorded in Sudan.
- Fourteen areas are at risk of famine, as ongoing conflict since April 2023 exacerbates food insecurity.
- The World Food Programme (WFP) is scaling up emergency aid and seeking increased funding to avert famine.
About Sudanese Crisis:
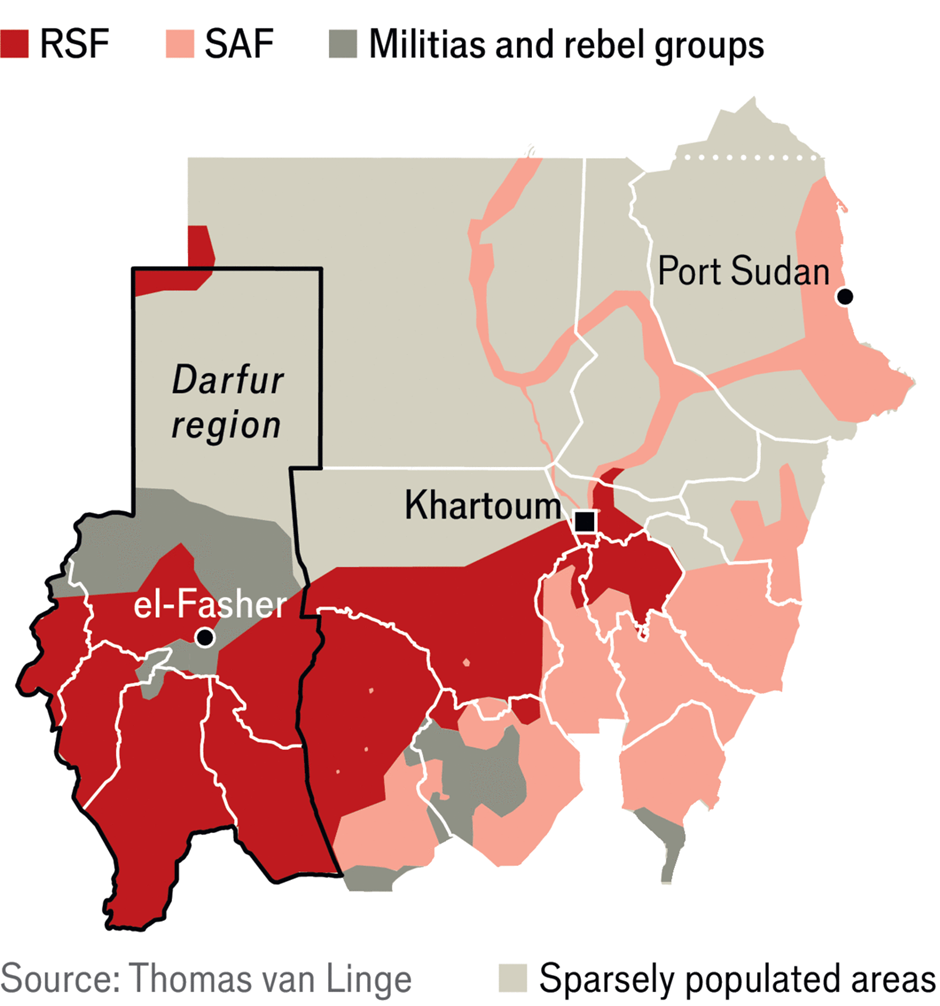
- Sudan's ongoing crisis, which escalated in April 2023, is primarily driven by a violent power struggle between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) led by Abdel Fattah al-Burhan and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) under Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo (Hemedti).
- This conflict emerged after tensions over the integration of the RSF into the national army as part of Sudan's transition to civilian rule. The clashes have resulted in extensive displacement, severe humanitarian crises, and devastating impacts on civilian life.
Key affected regions include:
- Khartoum: A primary battleground and origin of the majority of displaced persons, with large-scale urban fighting.
- Darfur (North, South, and Central): Experiencing widespread violence, with the RSF and militias accused of atrocities.
- Kordofan region: Also affected by conflict and displacement.
- Eastern States (Gedaref, Kassala, and Red Sea): Witnessing refugee movements and indirect impacts of the crisis.
- Aj Jazirah, White Nile, and Northern States: Hosting significant numbers of internally displaced people (IDPs).
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus