- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 21st DECEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 21st DECEMBER 2024
21-12-2024

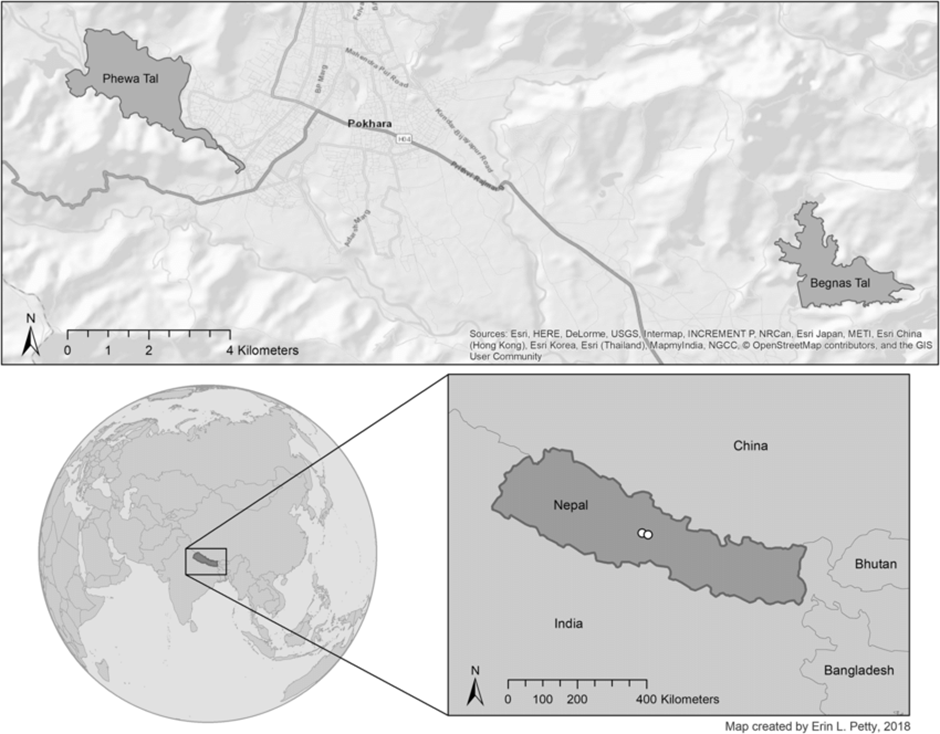
Phewa lake
Why in news?
Nepal and China jointly launched the “Phewa Dialogue” series in Pokhara, aiming to foster regional prosperity and peace policies. Named after the iconic Phewa Lake, the two-day event was inaugurated by former Nepalese President Bidya Devi Bhandari.
About Phewa Lake:
- Geography
- Phewa Lake, located in Pokhara, Nepal, is the second-largest lake in the country and a vital natural resource in the region.
- It lies at an altitude of 742 meters above sea level, covering an area of approximately 4.43 square kilometres, with an average depth of about 8.6 meters.
- The lake rests in a valley surrounded by the lush greenery of the Annapurna range foothills, creating a stunning landscape that attracts both locals and tourists.
- Phewa Lake features Rani Tal, a small island that houses the Tal Barahi Temple, a site of religious and cultural significance.
- Ecological and Economic importance
- Ecologically, the lake plays a crucial role in maintaining the region's biodiversity.
- It supports a variety of aquatic species, including fish, birds, and amphibians, and serves as an important stopover for migratory birds.
- The dense forests around the lake act as a natural buffer, protecting the water body from erosion and sedimentation while providing habitat for diverse flora and fauna.
- The wetlands associated with Phewa Lake help regulate the local climate by storing water and releasing moisture into the atmosphere.
- The lake contributes significantly to Pokhara's economy by sustaining livelihoods through activities like fishing, tourism, and irrigation.
- It supports traditional farming practices in the surrounding areas by providing a reliable water source.
- As a tourism hub, it offers recreational activities such as boating, kayaking, and sightseeing, boosting the region's cultural and economic vibrancy.
- However, rapid urbanisation and increasing human activities pose threats to Phewa Lake’s ecological balance. Efforts to preserve its water quality and biodiversity are essential to sustain its ecological and economic importance.
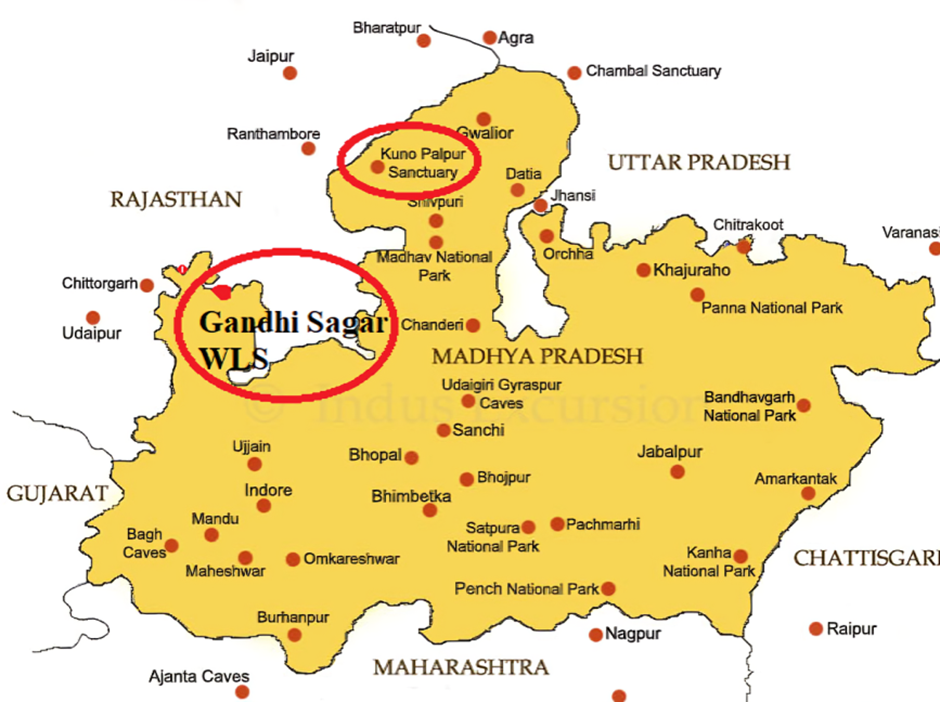
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- The Cheetah Action Plan for Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh aims to establish a sustainable cheetah population by introducing 6-8 cheetahs into a predator-proof enclosure and augmenting prey species like chital and blackbuck.
About Gandhi Sagar Sanctuary:
- Geography
- Gandhi Sagar Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary situated on the northern boundary of Mandsaur and Nimach districts in Madhya Pradesh, India. It is spread over an area of 368.62 km² (142.32 sq mi) adjoining Rajasthan state in India.
- It is situated along the Chambal River, which flows through the sanctuary, creating a unique ecosystem of riverine forests and savannah grasslands.
- The terrain includes dry deciduous forests, open grasslands, and rocky outcrops, providing diverse habitats that support a wide range of species.
- The climate is semi-arid, with temperatures ranging from scorching summers to cool winters, influencing the seasonal dynamics of vegetation and wildlife.
- Flora
- The sanctuary boasts a rich diversity of flora, including species like teak, dhok, babul, and kadaya.
- These forests are interspersed with grasslands that serve as grazing grounds for herbivores.
- Riverine patches feature dense evergreen trees and shrubs, adding to the ecological complexity of the sanctuary.
- Fauna
- Fauna in Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary is equally diverse, making it an important biodiversity hotspot.
- Large herbivores like nilgai, chinkara, chital, and blackbuck thrive here, supported by the ample grasslands.
- Carnivores such as leopards, hyenas, wolves, and jackals dominate the food chain, creating a balanced predator-prey dynamic.
- The sanctuary is also home to smaller mammals like wild boars, hares, and porcupines, contributing to its ecological richness.
- Birds such as peafowls, partridges, and numerous migratory species find refuge in the varied habitats, enhancing its avian diversity.
- The sanctuary’s proximity to the Chambal River makes it a crucial habitat for aquatic and semi-aquatic species, including crocodiles and turtles.
- Efforts to introduce cheetahs underline their ecological importance, as the sanctuary’s grasslands and prey base offer a promising habitat for their reintroduction.
- Gandhi Sagar serves as a critical natural reserve, contributing to regional conservation and ecological balance.
About Cheetah Reintroduction Plan:
- India’s Cheetah Reintroduction Plan aims to reintroduce cheetahs to their historic range after the species became extinct in the country over 70 years ago.
- The project, led by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) in collaboration with the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), focuses on restoring ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity.
- The plan involves importing cheetahs from African nations, selecting genetically diverse and predator-wary individuals to ensure a strong foundation.
- The first phase began with the introduction of cheetahs into Kuno National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh. Twenty cheetahs, including males and females, were brought from Namibia and South Africa in 2022 and 2023. The project ensures their acclimatisation through enclosures before releasing them into the wild.
- Currently, 24 cheetahs, including 12 cubs born in India, reside in KNP. However, challenges such as disease and competition with leopards have prompted cautious management.
- To expand the program, Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh is being prepared for another batch of cheetahs, with efforts underway to secure habitats and relocate leopards.
- The initiative is part of a decade-long strategy to stabilise the cheetah population, contributing to ecological balance and serving as a global model for species reintroduction.
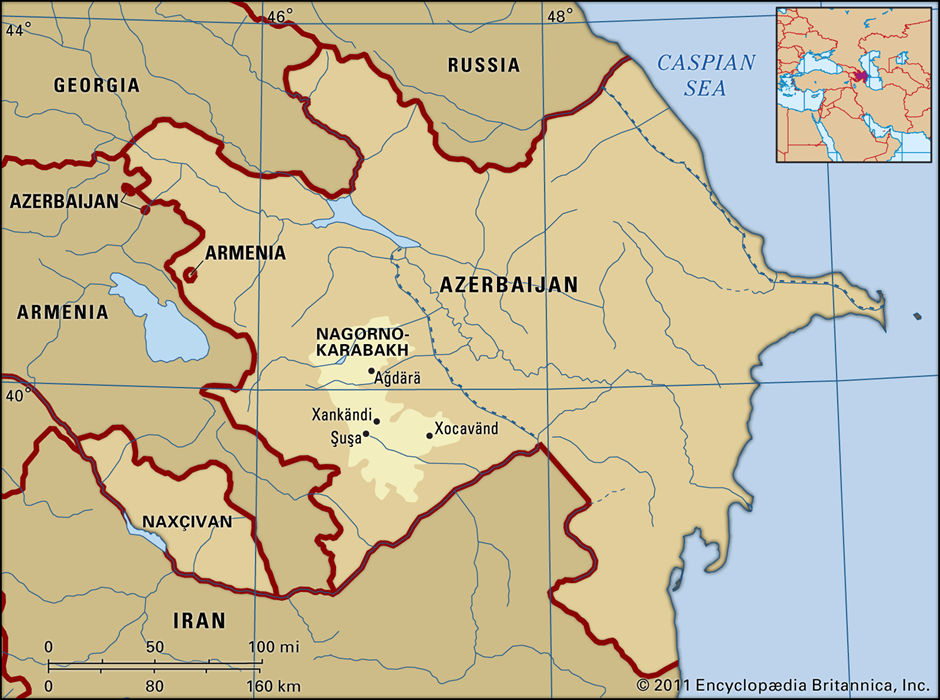
Nagorno-Karabakh region
Why in news?
- US State Department Deputy Spokesman Vedant Patel reaffirmed Washington's belief in achieving peace in the Nagorno-Karabakh region.
About Nagorno-Karabakh region:
- The Nagorno-Karabakh region is a mountainous enclave located in the South Caucasus, within the borders of Azerbaijan but predominantly populated by ethnic Armenians.
- It spans approximately 4,400 square kilometres and is characterised by rugged terrain, forests, and a temperate climate, making it strategically significant and ecologically rich.
- The region is surrounded by seven Azerbaijani districts, creating a geographical buffer that has been central to the ongoing territorial dispute.
Regional Conflict:
- The conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh stems from historical, ethnic, and political factors.
- In the early 20th century, the region was integrated into Azerbaijan by the Soviet Union, despite its Armenian-majority population, fuelling grievances among Armenians.
- With the collapse of the Soviet Union in the late 1980s, ethnic tensions escalated as Nagorno-Karabakh sought independence and closer ties with Armenia.
- A full-scale war erupted between Armenia and Azerbaijan from 1988 to 1994, leading to significant casualties and displacement on both sides.
- Armenian forces gained control of Nagorno-Karabakh and adjacent Azerbaijani territories, creating a de facto Armenian administration.
- In 2020, Azerbaijan launched a military offensive, reclaiming parts of Nagorno-Karabakh and surrounding areas.
- A Russia-brokered ceasefire ended the conflict but left tensions unresolved, with periodic skirmishes continuing.
- The region remains disputed, with Armenia advocating for self-determination for Nagorno-Karabakh’s residents and Azerbaijan asserting sovereignty over its internationally recognised territory.
- Efforts by global powers, including the US, Russia, and the OSCE Minsk Group, aim to mediate a peaceful resolution.
- However, deeply rooted mistrust, ethnic divides, and competing geopolitical interests complicate long-term stability in the region.
- Nagorno-Karabakh remains a flashpoint, reflecting the complexities of post-Soviet statehood and unresolved ethnic conflicts.
Essequibo region
Why in news?
- Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro has warned of U.S. military activities in the Essequibo region, a disputed territory between Venezuela and Guyana.
About Essequibo region:
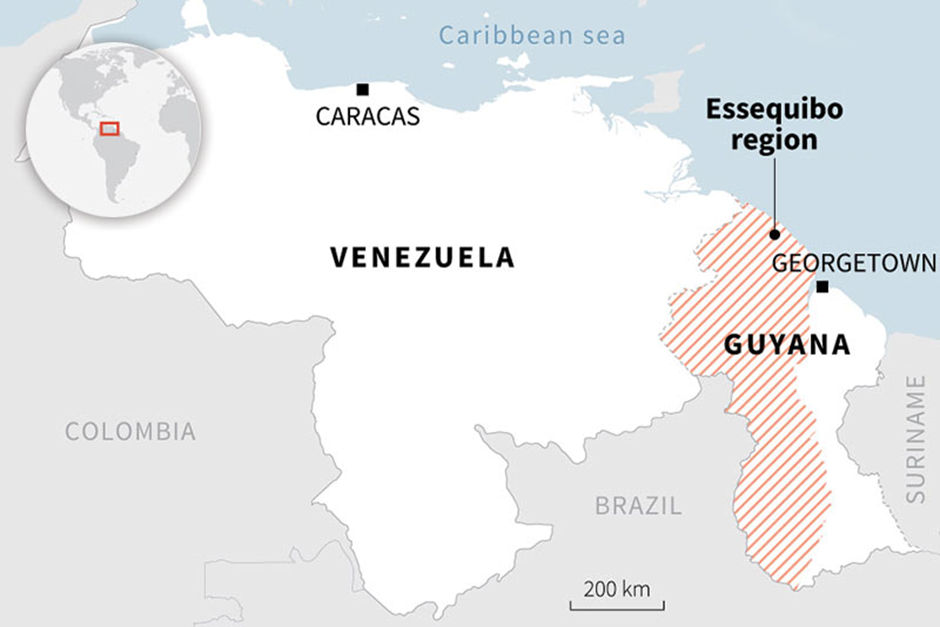
- The Essequibo region is located in the north-eastern part of South America, spanning approximately 159,500 square kilometres.
- It accounts for nearly two-thirds of Guyana’s total landmass and is bordered by Venezuela to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the north.
- The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, gold, and timber. Its rivers, such as the Essequibo River, serve as key waterways, making it strategically and economically significant for both Guyana and Venezuela.
Regional Dispute:
- The dispute over Essequibo dates back to the 19th century when Venezuela challenged Britain’s claim over the territory as part of British Guiana.
- In 1899, an arbitration tribunal in Paris ruled in favour of Britain, granting Essequibo to British Guiana. Venezuela later rejected the decision, claiming it was influenced by undue pressure.
- When Guyana gained independence in 1966, Venezuela renewed its claim, asserting that the region historically belongs to its territory.
- The discovery of offshore oil in 2015 further heightened tensions, as Exxon Mobil’s operations in Guyana’s waters are seen as a threat to Venezuela’s interests.
- Venezuela contends that Essequibo’s resources and geography are vital to its economy and security, especially in light of its declining oil revenues.
- Guyana, supported by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and international partners like the United States, asserts its sovereignty over Essequibo based on legal precedents and international recognition.
- The region’s importance lies not only in its resource wealth but also in its geostrategic position, providing access to crucial shipping routes and maritime boundaries.
- The dispute remains unresolved, with both countries advocating their claims through legal channels, referendums, and diplomatic manoeuvres, reflecting broader regional and international interests.
Dharavi Slum
Why in news?
- The Bombay High Court upheld the Maharashtra government's decision to award the Dharavi Redevelopment Project to the Adani Group, dismissing SecLink Technologies’ petition.
- SecLink had challenged the scrapping of its 2018 bid and the issuance of a new tender in 2022, which Adani won with a ₹5,069 crore bid.
- The court ruled that there was no arbitrariness in the tender process, noting that multiple bidders participated and met the technical requirements.
About Dharavi Slum
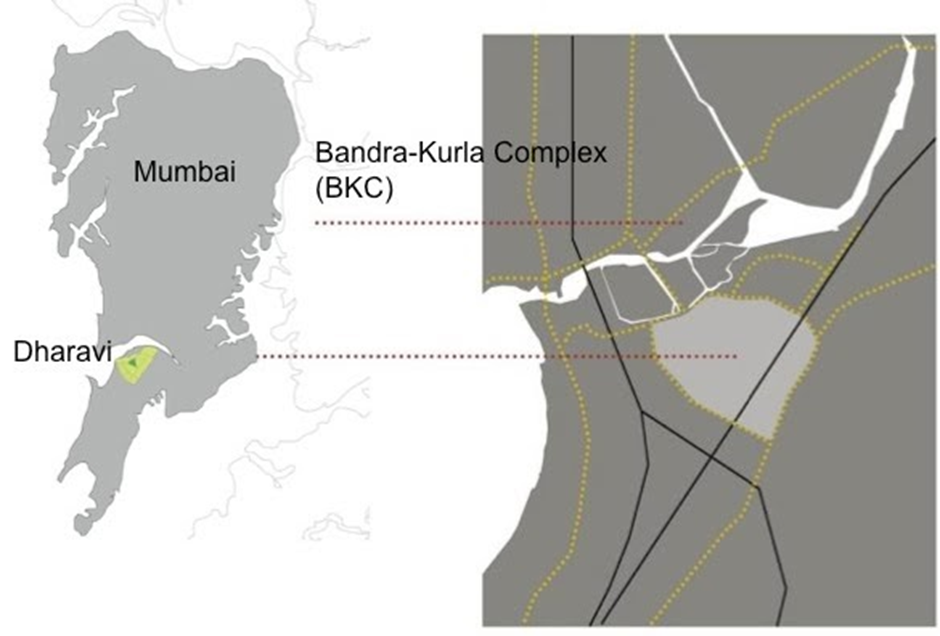
- Dharavi is located in the heart of Mumbai, India, covering an area of 240 hectares (594 acres), making it one of the largest slums in Asia.
- It is home to an estimated 700,000 to 1 million people, though exact figures are difficult to determine due to the densely packed living conditions.
- The population density is extremely high, with over 270,000 people per square kilometre, one of the highest in the world.
- Dharavi is made up of various informal settlements, with narrow lanes and poorly constructed buildings. It is characterised by overcrowded homes, lack of sanitation, open sewers, and limited access to clean water.
- The slum is divided into multiple sectors, including industrial, residential, and commercial areas, making it a complex urban environment.
- Dharavi is a major economic hub, with thriving informal industries including pottery, textiles, recycling, and food processing. It generates an estimated $1 billion in annual economic output, providing livelihoods to many residents.
- It has a thriving recycling industry, where plastic, paper, metal, and electronic waste are processed and repurposed, contributing significantly to Mumbai’s waste management system.
- The area is bordered by the Bandra-Kurla Complex and Mumbai International Airport, providing it strategic significance in the city’s economy.
- Dharavi gained international attention after being featured in the 2008 Oscar-winning film "Slumdog Millionaire."
- The Dharavi redevelopment project, initiated by the Maharashtra state government, aims to transform the area into a modern urban hub. The project covers 259 hectares and will involve the construction of over 70,000 new homes for slum residents.
- The redevelopment is estimated to cost around ₹20,000 crore ($2.5 billion) and aims to improve infrastructure, sanitation, and living conditions while also addressing the challenge of urban poverty and overpopulation in Mumbai.
- Despite the redevelopment plans, many residents face uncertainty regarding displacement and rehabilitation, with concerns over their future livelihoods and community ties.
|
UPSC CSE PYQs Q. Consider the following pairs:
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?(2023)
Explanation: Option D |
| Also Read | |
| UPSC Prelims Result | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Previous Year Interview Questions |
| Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims | UPSC Test Series |
| ENSURE IAS NOTES | Our Booklist |



