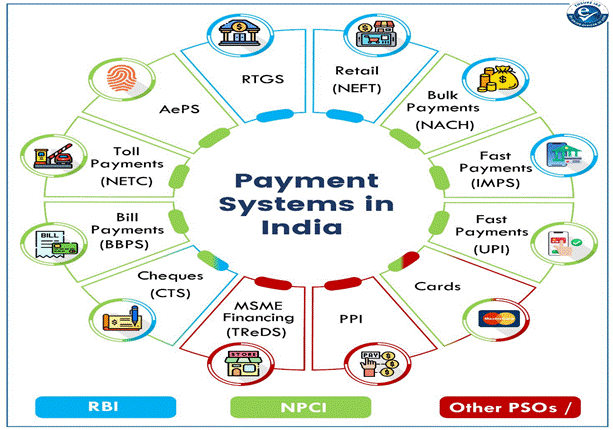
- Recently, Payment Systems Report December 2024 was published by Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- This is a bi-annual publication from the RBI.
- This report reveals a significant shift in India’s payment system, highlighting the growth of credit card usage and digital payments over the past few years.
Key findings/highlights of Payment Systems Report:
1. Credit Card Growth
- The number of credit cards in circulation has more than doubled in the last 5 years.
- As of December 2019, there were 5.53 crore credit cards, which surged to approximately 10.80 crore by December 2024.
- While the growth in credit card usage is striking, the number of debit cards has remained relatively stable, increasing slightly from 80.53 crore in December 2019 to 99.09 crore in December 2024.
2. Exponential Growth of Digital Payments
- Digital transactions in India have grown 94 times in volume and 3.5 times in value from the year 2013 to 2024.
- In 2013, there were 222 crore transactions worth Rs 772 lakh crore, while in 2024, this has escalated to over 20,787 crore transactions valued at Rs 2,758 lakh crore.
- The last five years have seen a 6.7 times increase in volume and 1.6 times increase in value, reflecting a 5-year CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of:
- 45.9% in transaction volume
- 10.2% in transaction value
- The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is the average annual growth rate of an investment or value over a specific period of time, assuming the growth happens at a steady rate
- Retail digital payments have also witnessed a remarkable rise, from 162 crore transactions in FY 2012-13 to 16,416 crore transactions in FY 2023-24, marking a nearly 100-fold increase over 12 years.
- The Digital Payment Index (DPI), a key indicator of payment systems’ growth, has surged by more than four times in the last six years, reaching 445.50 in March 2024 (up from a base of 100 in March 2018).
3. Cross-Border Payment Innovations
- The RBI has been working towards enhancing cross-border payments, particularly by integrating India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the fast payment systems of other countries.
- This effort addresses challenges like high costs, slow processing times, limited access, and lack of transparency in cross-border remittance systems.
- Key Developments:
- In February 2023, the UPI system was linked to PayNow, Singapore’s fast payment system, allowing seamless cross-border transactions between India and Singapore.
- As of now, UPI-enabled payments can be made to merchants via QR codes in Bhutan, France, Mauritius, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and the UAE.
- Project Nexus: The RBI has joined Project Nexus, an international initiative to enable instant cross-border retail payments by linking the domestic fast payment systems of multiple countries.
4. RBI’s Role in Innovation and Payment System Modernization
- The RBI has been proactive in fostering a supportive environment for payment system operators (PSOs) and encourages continuous innovation in the sector.
- According to RBI Deputy Governor, the RBI has prioritized staying ahead of the curve when it comes to developing and modernizing India’s payment systems. With strong regulatory support, India’s payment systems have become globally competitive and modern.
Introduction to India’s Payment SystemsPayments are a critical component of economic activity and are increasingly recognized for driving financial inclusion, ensuring that benefits reach all segments of society, including underserved groups.
Key Factors Driving Growth in Payment SystemsUnified Payments Interface (UPI)
|








