- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Parliamentary Functioning
Parliamentary Functioning
25-12-2023
Context: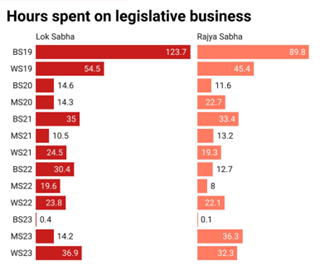
- Winter Session of Parliament saw the highest operational hours this year despite a significant number of MPs being suspended, setting a new record.
What is the role of Parliament?
- Providing a platform for elected representatives to express public concerns and aspirations.
- Enacting laws related to items in the Union List and Concurrent List.
- Scrutinizing government actions through mechanisms like Question Hour, Zero Hour, and debates.
- Controling finances by approving the annual budget and managing public expenditure.
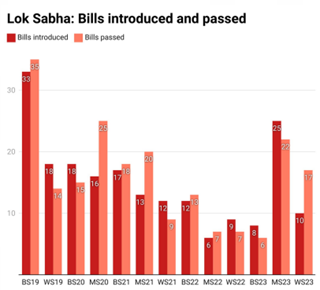
- Serving as a forum for national debates and discussions on crucial issues, influencing public opinion.
What are the challenges in functioning of Parliament?
- Disruptions and adjournments: MPs often use unconventional methods to gain attention, causing frequent disruptions and pauses in discussions. As a result, the Speaker frequently adjourns the session
- Lack of substantive debate: Superficial discussions, driven by politics, distract from the main points and weaken the quality of arguments.
- Limited working hours: Parliament doesn't meet often, and when they do, they spend only around 10-20 hours on actual work during each session (as per PRS Legislative Research).
- Dominance of government agenda: The time taken to pass Bills is getting shorter. This implies that lesser time is being spent on discussion and debates. Hence, one group's strong influence in
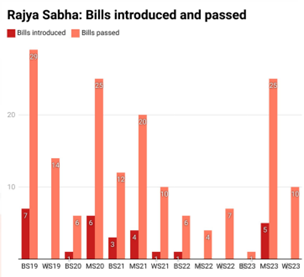 parliament is visible.
parliament is visible. - Underrepresentation of diverse groups: Not all groups and sections of society have enough say in parliament such as women, LGBTQ+, persons with disabilities, etc.
- Inadequate research and expertise: Opposition MPs proposing private bills often lack funds or staff for adequate research.
- Erosion of parliamentary decorum: Decline in respectful behavior during discussions.
Way Forward
- Role of Committees: They carefully review bills, conduct thorough research to bring a comprehensive bill.
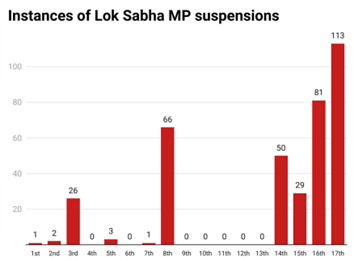
- Intellectual Shortage: The Chief Justice of India has highlighted the lack of legal experts in the Parliament, leading to laws with loopholes needing subsequent amendments.
- Suspensions/Expulsions Issue: More than 100 suspensions in the last session of Parliament, mostly of opposition members, can degrade parliamentary discussions by instilling fear.
- New Legislation Committee: A dedicated committee can be established to look after legislation process.
- Shadow Cabinet: Modeled on the line of UK, it is a group formed by the opposition in the parliament, mirroring the government's structure. It consists of opposition leaders who take on roles similar to the government's cabinet ministers to propose alternative policies and decisions.



