- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSIOLOGY OR MEDICINE 2023
NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSIOLOGY OR MEDICINE 2023
03-10-2023
Latest Context
Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman have received the 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on the development of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
What are mRNA vaccines?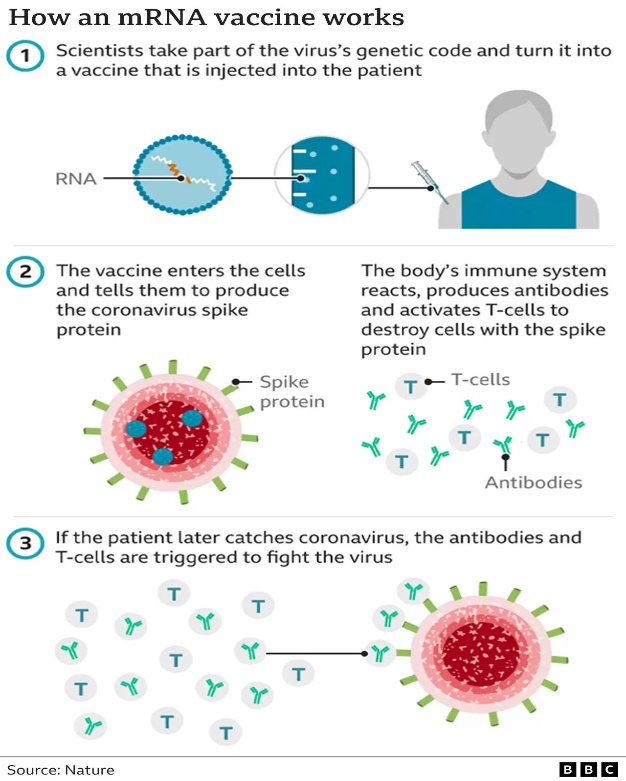
- mRNA stands for messenger RNA. It is a form of nucleic acid which carries genetic information.
- The mRNA vaccine makes an effort, like other vaccines, to stimulate the immune system to develop antibodies that aid in preventing an infection from a live virus.
- However, mRNA vaccines only introduce a portion of the genetic information that matches to a viral protein, unlike conventional vaccines that inject weak or dead bacteria or viruses to stimulate the immune system. Spike protein is a common name for this protein, which is often located on the viral membrane. As a result, the mRNA vaccination spares users exposure to the virus itself.
- But one major issue with mRNA vaccines is that they have to be frozen between -90 and -50 degrees Celsius. They need to be thawed between 2 and 8 degrees Celsius, where they can stay for up to a month. They can be kept frozen for up to two weeks in industrial freezers.
Advantages of mRNA vaccine
- It is not contagious and cannot integrate into host DNA.
- Scaling up and designing mRNA can be done quickly.
- produce a higher immune response than conventional vaccines.
What work did Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman do for mRNA vaccines?
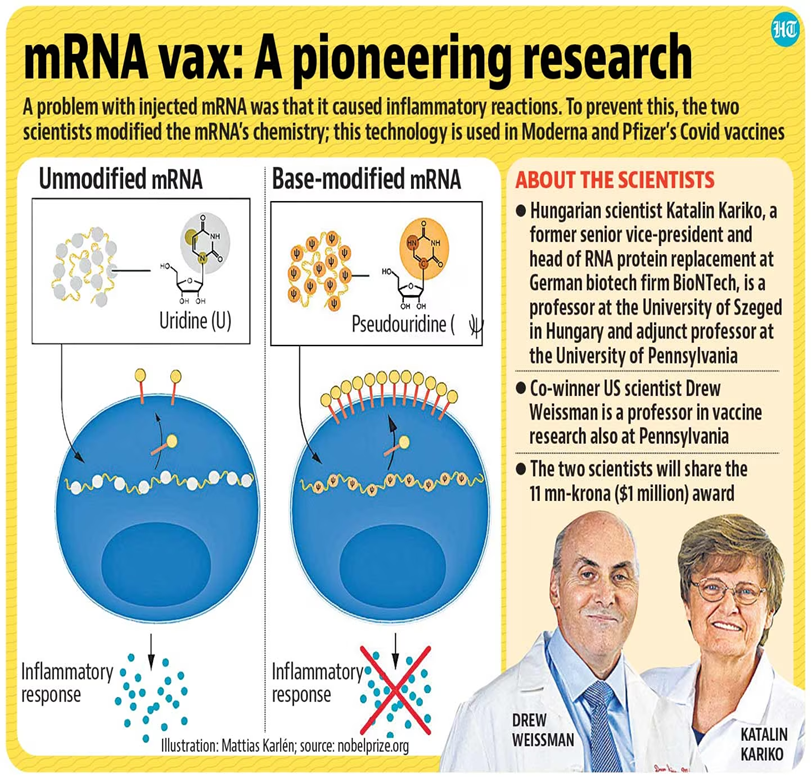
- Early synthetic mRNA prototypes that caused inflammatory reactions made them inappropriate for use in medicine, which posed a substantial barrier to the development of mRNA vaccines.
- Karikó and Weissman discovered a way to stop these inflammatory responses and dramatically increase the production of the target protein by making small chemical changes to the mRNA molecules.
- This discovery served as the foundation for the creation of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
What is the potential of mRNA technology beyond Covid-19?
- Early research indicates that mRNA technology has promise as a cancer treatment, particularly for pancreatic and melanoma.
- Investigating a fresh method to treat autoimmune illnesses is one of the other mRNA research directions now being pursued.And for untreatable illnesses like sickle cell disease, mRNA technology is being investigated as a potential substitute for gene therapy.