- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Nalanda University: An Ancient Centre of Learning
Nalanda University: An Ancient Centre of Learning
25-07-2024
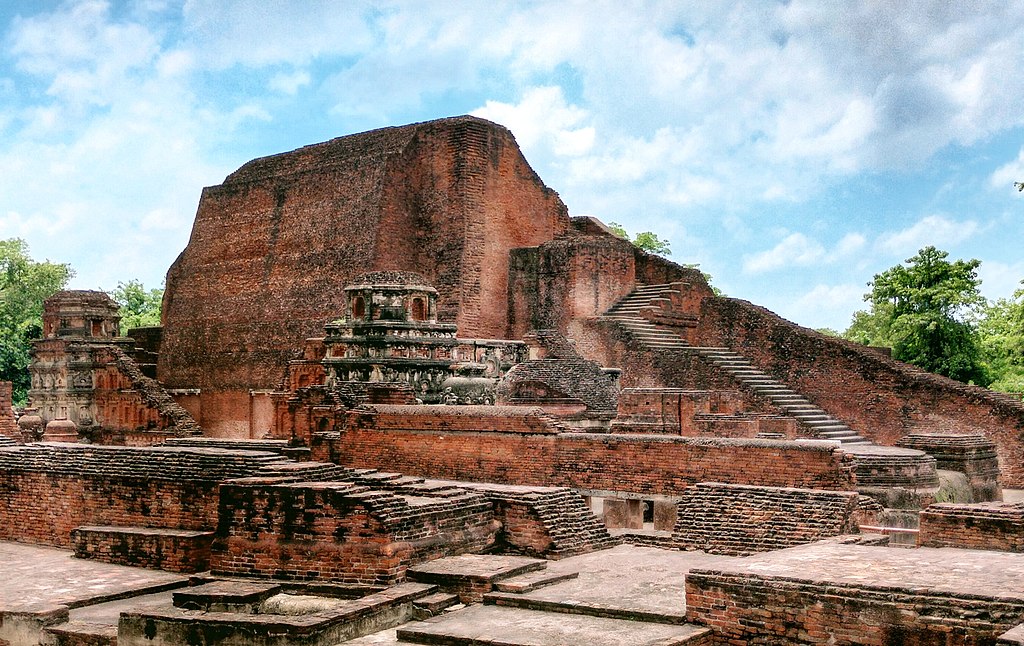

In June 2024, Prime Minister Narendra Modi inaugurated the new campus of Nalanda University, marking a significant step in the revival of this ancient seat of learning.
History and Revival Efforts of Nalanda University
A. History:
- Founding: Established in the 5th century CE, possibly with earlier origins, and expanded under the patronage of Gupta Emperor Kumaragupta I (and potentially other Gupta rulers).
- Global Appeal: A renowned center of Buddhist learning and scholarship for over 700 years, from the 5th to the 12th century CE. Attracted students and scholars from across Asia, including China, Mongolia, Tibet, Korea, and other countries.
- Famous Visitors: Notable Chinese scholars like Xuan Zang and I-Tsing studied at Nalanda.
- Attacks:
- First Attack: Nalanda was likely first attacked by the Huns under Mihirakula in the 5th century CE.
- Second Attack: It was then attacked again in the 7th century CE, possibly by the Gauda ruler Shashanka.
- Final Destruction: Primarily destroyed by Turkic Muslim invaders in the late 12th century, with the most devastating attack attributed to Bakhtiyar Khilji in 1193 CE.
- Rediscovery: Rediscovered in the 19th century by European explorers and archaeologists.
B. Revival
- The idea for the revival of Nalanda University did emerge in the early 2000s, with several key figures and organizations advocating for its return.
- A.P.J. Abdul Kalam: In 2006, then-President Kalam proposed the revival of Nalanda University in a speech to the Bihar Legislative Assembly.
- Singapore Government: The Singapore government also expressed interest in supporting the project.
- East Asia Summit (EAS): Leaders of the EAS countries endorsed the idea during their summits in 2007 and 2009.
- Nalanda University Act: The Indian Parliament passed the Nalanda University Act in 2010, providing a legal framework for the new institution.
- Collaborative Effort: Nalanda University is envisioned as a collaborative effort between India and other East Asian nations, symbolizing a renewed focus on regional knowledge exchange.
- Campus: The university has a 455-acre campus near the ancient ruins, designed by architect B.V. Doshi, and features modern amenities like a solar plant, domestic and drinking water treatment plant, and water recycling plant.
The New Campus
- Location: The campus is situated in Rajgir, Bihar, about 90 km east of Patna.
- Design and Amenities: The 455-acre campus, designed by architect B.V. Doshi, features modern amenities like a solar plant, water treatment plants, smart classrooms, a state-of-the-art auditorium, and a fully equipped sports complex. Only 8% of the campus is built up, preserving the natural environment.
- Courses: The university offers Post Graduate and Doctoral programmes in Buddhist studies, philosophy and comparative religions, languages and literature, ecology and environmental studies, sustainable development and environment, and international relations and peace studies.
Significance and Importance
- Cultural Heritage: Nalanda University is a symbol of India's rich cultural heritage and its historical contribution to education.
- Global Hub of Learning: As a center of research and learning, the university offers a platform for students from around the world to engage in intellectual discussions and debates.
- International Cooperation: The involvement of 17 countries in its establishment showcases Nalanda as a model of international cooperation.
Challenges
- Funding: The university faces challenges in terms of funding, with the need for sustained investment to maintain its infrastructure and facilities.
- Faculty Recruitment: The university faces challenges in recruiting and retaining faculty members, particularly in specialized fields.
- Infrastructure: The university faces challenges in terms of infrastructure, with the need for continued investment in its facilities and amenities.
UNESCO's Heritage Sites Related to Buddhism:
- Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara: Declared as a UN Heritage Site in 2016.
- Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi: Located in Madhya Pradesh.
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex: Located in Bodh Gaya, Bihar.
- Ajanta Caves: Located in Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
- Buddhist Chanting of Ladakh: Included in UNESCO’s Representative List of Humanity's Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2012.
Conclusion
The revival of Nalanda University is a significant milestone in India's educational landscape, and a testament to the country's rich cultural heritage. The university's commitment to providing a platform for intellectual discussions and debates, and its focus on international cooperation, make it an important institution in the field of education.