Context
India has officially assumed the Chair of the Kimberley Process (KP) for 2026. This international initiative is critical for maintaining the integrity of the global diamond trade.
Overview
- What are Conflict Diamonds: Conflict diamonds are rough diamonds mined or sold to fund armed rebel groups that fight to overthrow legitimate governments.
- Purpose: A global coalition (Governments, Industry, and Civil Society) established to eliminate the trade in “conflict diamonds” (also known as “blood diamonds”).
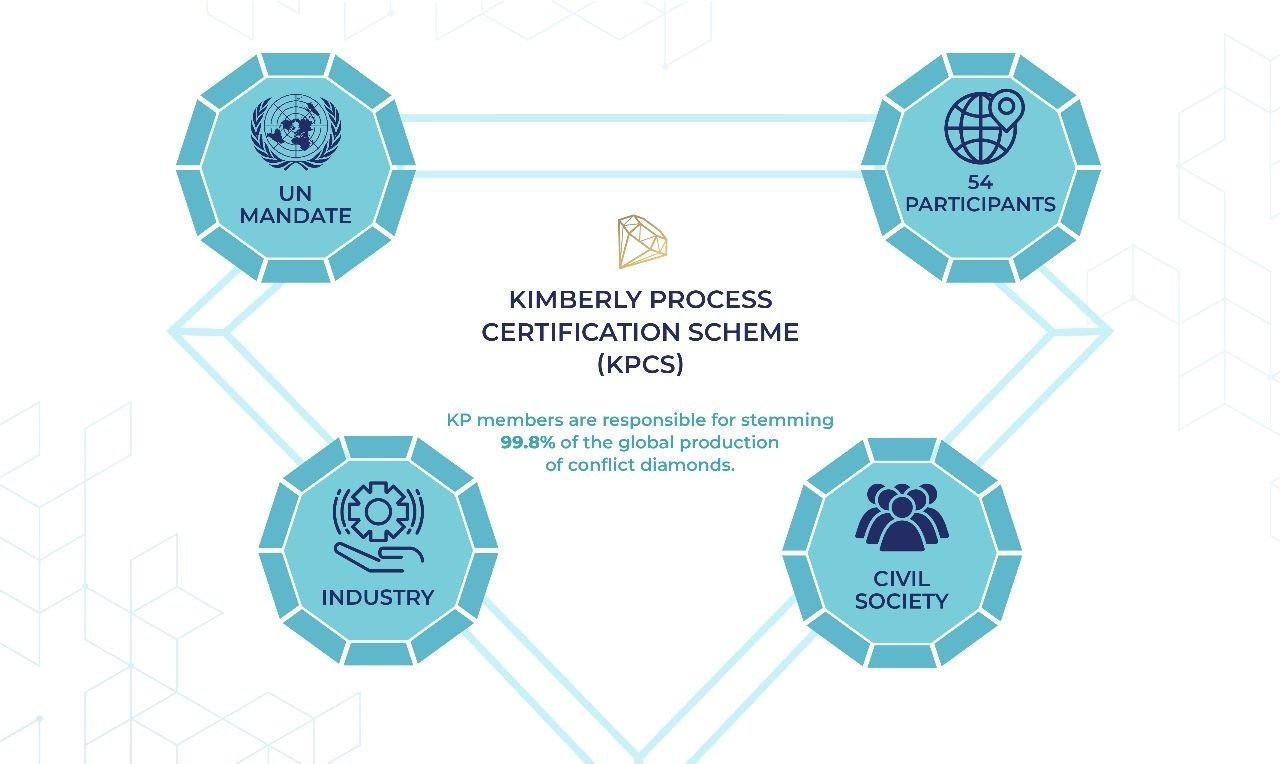
The Certification Scheme (KPCS)
The Kimberley Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) is the primary mechanism to ensure a “conflict-free” supply chain:
- Requirement: Every shipment of rough diamonds must be accompanied by a KP Certificate and transported in a tamper-resistant container.
- Interstate Trade: Participants are strictly prohibited from trading with non-participants.
- Governance: Operates on a consensus-based model and meets twice a year (Intersessional and Plenary).
India and the Kimberley Process
India has been a member since 2003 and plays a pivotal role as a global leader in diamond cutting and polishing.
- Nodal Department: Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Executive Authority: The Gem & Jewellery Export Promotion Council (GJEPC) is the designated Importing and Exporting Authority.
- GJEPC Responsibilities:
- Issuing KP Certificates for exports.
- Acting as the custodian for certificates received with imports.
- Ensuring the authenticity of rough diamonds entering or leaving India.
You Can Also Read |
|
| UPSC Foundation Course | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |
| Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims | UPSC Test Series |
| Best IAS Coaching in Delhi | Our Booklist |