Why in the News?
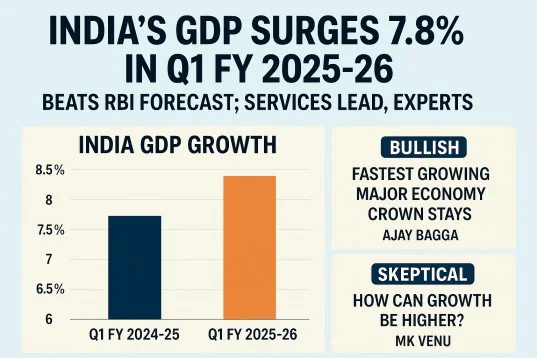
- India’s GDP growth rate for the first quarter of FY2025 (April–June) accelerated to 8%, the fastest pace in the last five quarters, as per government data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- The growth was driven mainly by manufacturing, construction, and services sectors, even as some sectors like utilities saw a slowdown.
- The announcement comes amid concerns about the impact of U.S. tariff hikes (50%) on imports from India and its possible effect on exports and domestic demand.
Key Highlights
- Overall GDP Growth
- Q1 FY2025 growth was 8%, higher than the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) recent forecast of 6.5%.
- It marks the strongest growth since Q1 FY2024 (January–March 2024).
- Government’s Position
- Chief Economic Adviser Anantha Nageswaran emphasized that the growth momentum is expected to continue.
- The government retained its full-year growth estimate, showing confidence in domestic demand.
- Lower indirect tax rates are expected to cushion any adverse effects on demand.
- Sectoral Performance
- Manufacturing grew 7%, better than 4.8% in the previous quarter and on top of 7.6% last year.
- Construction expanded by 6%, though slower compared to 10.1% in Q1 last year.
- Utilities (Electricity, Gas, Water) slowed sharply to 5%, compared to 10.2% last year.
- Services sector as a whole grew 3%, higher than 6.8% last year and 7.3% in the previous quarter.
- Sub-sectors within Services
- Public Administration, Defence, and Other Services grew at 8%, the highest in three years.
- Financial, Real Estate, and Professional Services recorded 5%, a two-year high.
- Trade, Hotels, Transport, and Communication saw 6%, also a two-year high.
- External Concerns
- The U.S. tariffs are expected to impact export-oriented units, particularly those exposed to the American market.
- This could temporarily affect domestic spending and employment decisions in these sectors.
- However, the government expects the demand impact to be modest and believes festival season consumption will boost recovery.
Implications
- For the Economy
- Strong Q1 performance indicates resilience despite external trade challenges.
- Domestic demand continues to be the key growth driver, supported by government policies.
- For Sectors
- Manufacturing and services are emerging as pillars of growth.
- Utilities slowdown signals the need for investments in infrastructure and energy efficiency.
- For Exports
- Tariffs by the U.S. may weaken India’s export competitiveness in certain goods.
- Export-dependent industries may cut costs, affecting jobs and wages.
- For Policy-making
- Indirect tax rate reductions are likely to boost consumption.
- The government may need to consider export diversification to reduce dependency on the U.S. market.
- For the Future Outlook
- If domestic demand holds up, India may remain one of the fastest-growing major economies
- A good festival season could further push consumption-led growth in Q2 and Q3.
Challenges and Way Forward
| Challenges | Way Forward |
| Impact of U.S. tariffs on Indian exports. | Diversify export markets and strengthen trade with ASEAN, Africa, and Europe. |
| Slowdown in utilities sector (electricity, gas, water). | Encourage renewable energy investment and infrastructure upgrades. |
| Possible dip in domestic consumption due to export uncertainty. | Boost domestic demand through tax cuts, welfare measures, and festive season incentives. |
| High base effect may moderate growth in upcoming quarters. | Focus on productivity improvements in manufacturing and services. |
| Dependence on global economic trends. | Build stronger internal economic resilience through Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat policies. |
Conclusion
India’s Q1 FY2025 GDP growth at 7.8% reflects a robust start to the year, driven by strong performance in manufacturing and services. While concerns remain over U.S. tariffs and a slowdown in the utilities sector, the government’s confidence in domestic demand, tax reforms, and the upcoming festival season provide optimism. Going forward, sustaining growth will require sectoral balancing, export diversification, and steady domestic consumption support, ensuring India remains a global growth leader.
| Ensure IAS Mains Question
Q. India’s GDP growth in Q1 FY2025 has accelerated to 7.8%, led by strong performances in manufacturing and services, but concerns remain over U.S. tariffs and sectoral imbalances. Discuss the implications of this growth for India’s economy, and suggest policy measures to sustain the momentum. (250 words) |
| Ensure IAS Prelims Question
Q. Consider the following statements regarding India’s Q1 FY2025 GDP growth: 1. India’s GDP grew by 7.8% in April–June 2025, the fastest in the last five quarters. 2. Manufacturing and services were the major contributors, while the utilities sector slowed sharply. 3. The Reserve Bank of India had projected the Q1 growth at 8.5%. 4. Public Administration, Defence, and Other Services recorded their highest growth in three years. Which of the above statements are correct? a) 1, 2 and 3 only b) 1, 2 and 4 only c) 2 and 3 only d) 1 and 4 only Answer: b) 1, 2 and 4 only Explanation: Statement 1 is correct: India’s GDP growth for Q1 FY2025 (April–June) was 7.8%, as per data from the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. This was the fastest in the last five quarters, showing strong recovery momentum. Statement 2 is correct: The growth was mainly driven by manufacturing (7.7%) and services (9.3%), which performed strongly. However, the utilities sector (Electricity, Gas, Water) slowed sharply to just 0.5%, compared to 10.2% a year ago. Statement 3 is incorrect: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had projected Q1 growth at 6.5%, not 8.5%. Statement 4 is correct: The Public Administration, Defence, and Other Services sector grew at 9.8%, marking its highest growth in three years, surpassing even the 9% growth recorded in Q1 of the previous year. |