- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India Opens Demchok for Civilian Visitors Under Battlefield Tourism Initiative
India Opens Demchok for Civilian Visitors Under Battlefield Tourism Initiative
21-03-2025

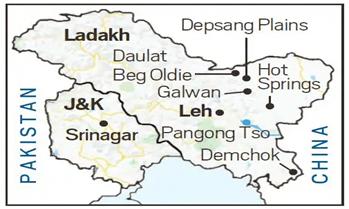
- India has officially opened Demchok, a key friction points along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China, for civilian visitors under the newly launched Battlefield Tourism initiative.
- The move comes just months after the disengagement process was completed in the Demchok and Depsang Plains regions of Eastern Ladakh.
Overview of the Battlefield Tourism Initiative:
- The initiative is jointly led by the Ministry of Defence, Ministry of Tourism, and respective state governments.
- Aims to offer citizens access to forward border locations of strategic and historic importance while promoting tourism and socio-economic development in these regions.
- Total of 77 forward sites included in the initiative: 21 in Arunachal Pradesh, 14 in Ladakh, 11 in Jammu and Kashmir, and 7 in Sikkim
- Total of 77 forward sites included in the initiative: 21 in Arunachal Pradesh, 14 in Ladakh, 11 in Jammu and Kashmir, and 7 in Sikkim
Significance of Demchok Opening:
- Demchok was one of the key friction points in the India-China border standoff post-2020.
- Chinese troops had occupied areas near Charding Nullah, leading to restrictions on Indian troop movement.
- The recent disengagement, part of an agreement between India and China announced on October 21, 2024, has allowed Indian troops to resume patrolling in the Demchok area.
- The agreement came two days before PM Narendra Modi and President Xi Jinping met during the BRICS Summit 2024 in Kazan, Russia (in October) to ease bilateral tensions.
Key Locations under Battlefield Tourism:
- Arunachal Pradesh: Tawang, Bum La, Gorsam, Lohit, Kameng Region, Walong.
- Ladakh: Demchok, Galwan (site of 2020 clashes), Pangong Tso (location of multiple stand-offs since 1962).
- Jammu & Kashmir: Includes various strategic forward posts.
- Sikkim: Key border areas added to promote high-altitude tourism.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




