- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Bitcoin Trading in India and Hawala: A Rising Parallel? – Supreme Court Remarks
Bitcoin Trading in India and Hawala: A Rising Parallel? – Supreme Court Remarks
08-05-2025

- The Supreme Court, during a bail hearing, observed that Bitcoin (cryptocurrency) trading in India resembles a sophisticated version of the hawala system.
- The Court highlighted the lack of a clear regulatory regime governing virtual currencies in India.
What is Cryptocurrency?
- Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency based on blockchain technology and built using a unique software code.
- Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.
- Blockchain is an open-source, decentralized public ledger that records transactions permanently across a computer network.
- Key features of cryptocurrency:
- It is non-fiat, meaning it operates independently of government or central bank control.
- It has no intrinsic value, relying purely on market demand.
What is Hawala?
- Hawala is an informal money transfer system used to move funds from one location to another using hawaladars (agents).
- The system is trust-based and operates without actual cash movement, as debts are settled between hawaladars.
- Transactions are off-the-record, with no formal documentation or bank involvement.
Why Are Cryptocurrency and Hawala Being Compared?
- In blockchain networks, nodes (computers maintaining the network) function like hawaladars, operating through mutual trust and consensus.
- Both systems facilitate fund transfer outside the traditional banking system, making them vulnerable to illicit use.
- Both are considered unregulated and often unreported, making detection of misuse difficult.
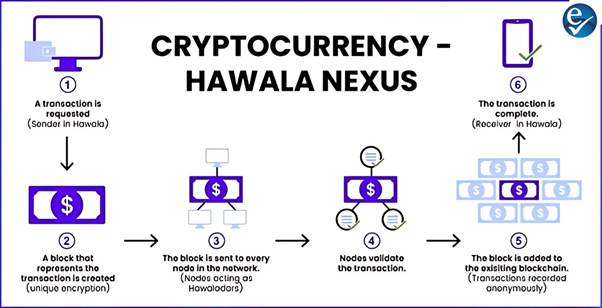
Why Is Their Nexus Increasing?
- Unregulated and Outside Banking Channels: Both systems operate outside conventional financial frameworks, attracting those seeking anonymity.
- Lower Costs: Unlike banks, both systems avoid heavy commissions and currency conversion charges.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Cryptocurrency records transactions anonymously on public ledgers,
- Hawala transactions are done in cash without paper trails.
- Encryption and Passcodes:
- Cryptocurrency uses unique encryption keys for access,
- Hawala relies on shared passcodes between the sender and receiver for verification.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




