- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India-Brazil strategic partnership deepened and diversified over years
India-Brazil strategic partnership deepened and diversified over years
09-09-2024
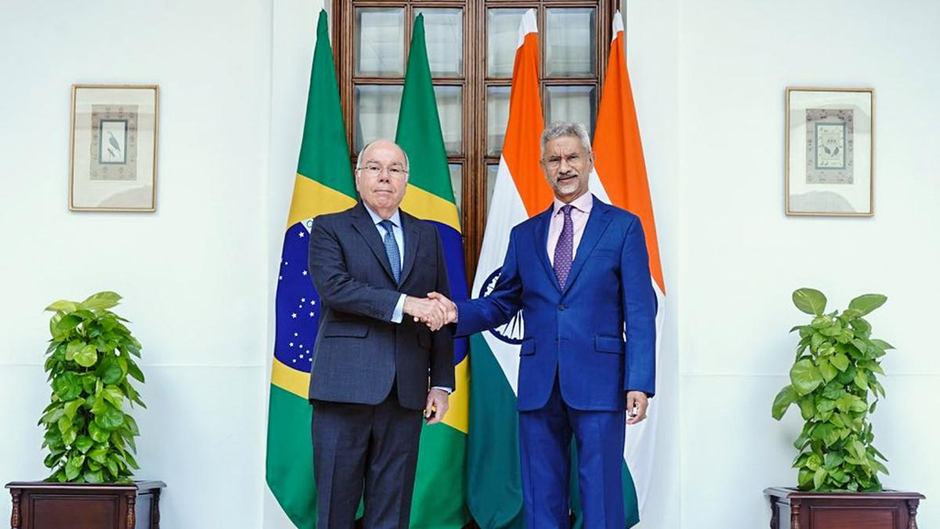

The strategic partnership between India and Brazil has grown and diversified significantly over the years, including areas like defence, space, security, technology, and people-to-people relations. External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar said on 28th Aug.
- In his opening remarks at the 9th India-Brazil Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) in Delhi, Mr. Jaishankar congratulated the Latin American country for conducting the G20 meetings successfully and, also on the first Ministerial consensus document released during a key meeting.
- A notable development in their bilateral ties is the resolution of their World Trade Organization (WTO) trade dispute over sugar subsidies, which aligns with their expanding collaboration in ethanol technology and addresses global sugar surplus issues affecting prices.
What is the India-Brazil Sugar Subsidies Issue?
- Background:
- WTO Challenge (2019): Brazil, along with Australia and Guatemala, challenged India's sugar subsidy measures at the WTO. They claimed these subsidies were inconsistent with the WTO’s Agreement on Agriculture.
- US and Australia’s Concern: They highlighted that India had not included sugarcane or its derivatives in domestic support notifications since the marketing year 1995-96.
- India’s Stand:
- Defence: India argued that sugarcane procurement is managed by private mills rather than the government, aligning with fair trade practices.
- Clarification: India noted that the US-Australia analysis incorrectly included total sugarcane production, regardless of whether it was processed by sugar mills, in calculating subsidies.
Major Areas of Cooperation Between India and Brazil
-
Institutional Level Engagements:
- Multilateral Forums: India and Brazil collaborate in various forums such as BRICS, IBSA, G4, G20, BASIC, International Solar Alliance (ISA), WTO, UNESCO, and WIPO.
- Bilateral Forums:
- Strategic Dialogue: Led by National Security Advisors (NSA), focusing on key regional and global issues.
- India-Brazil Business Leaders Forum: Concentrates on trade, investment, and economic cooperation.
- Trade Monitoring Mechanism (TMM): Resolves issues in bilateral trade.
- Economic and Financial Dialogue: Covers investment, trade, and monetary policy.
- Joint Defence Commission: Facilitates defence cooperation including joint exercises, equipment procurement, and intelligence sharing.
- Joint Committee on Science & Technology: Promotes cooperation in research, development, and knowledge exchange.
-
Trade and Investment:
- Trade Growth:
- 2021: India became Brazil's 5th largest trading partner with bilateral trade increasing from USD 7.05 billion in 2020 to USD 11.53 billion.
- 2022: Trade grew to USD 15.2 billion.
- 2023: India’s exports to Brazil were USD 6.9 billion, and imports from Brazil were USD 4.7 billion.
- Major Exports and Imports:
- Exports: Agrochemicals, synthetic yarns, auto components and parts.
- Imports: Crude oil, gold, vegetable oil, sugar, and bulk minerals.
- Investment: Both countries have invested in sectors like automobiles, IT, mining, energy, biofuels, and footwear.
- Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA): Signed with MERCOSUR (Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay) in 2004.
- Trade Growth:
-
Defence & Security Cooperation:
- Defence Agreement (2003): Established a framework for collaboration.
- Strategic Dialogue (2006): Facilitated by India's NSA.
- Cyber Security MoU: Signed between CERT-In and its Brazilian counterpart in January 2020.
-
Cooperation in Science and Technology:
- Space Collaboration (2004): Includes data sharing and satellite tracking.
- Amazonia-1 Satellite: Brazilian Minister visited India in 2021 for the launch.
- Ayurveda and Yoga: Recognised in Brazil’s health policy. An MoU on Traditional Medicine and Homeopathy was signed in January 2020.
-
Energy Security:
- MoU (January 2020): Between Indian Oil Corporation and Brazil’s CNPEM to establish a research institution in India for bioenergy.
- Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA): Launched in 2023 to enhance biofuel output and demand.
- Ethanol Blending Programme:
- Brazil’s Leadership: Brazil, a pioneer in ethanol production since 1975, has supported India’s ethanol technology, aiming to boost India's biofuel production.
- Blending Rates: Brazil achieved 27% ethanol blending in gasoline. India’s ethanol blending rate reached 15.83% as of July 2024, with a target of 20% by the 2025-26 supply year.
Challenges in India-Brazil Relations
-
Trade Deficit and Competition:
- Trade Imbalance: India consistently has a trade deficit with Brazil, primarily due to Brazil’s dominance in agricultural products and India’s reliance on imports of commodities like soybeans and sugar.
- Protectionist Measures: Both countries have implemented tariffs and subsidies to protect domestic industries, creating trade frictions.
-
Diverging Interests in International Forums:
- Climate Change: India focuses on emission intensity reduction, economic development, and energy access, while Brazil prioritizes Amazon deforestation reduction.
- Multilateral Institutions: Their priorities often diverge in forums like the UN and WTO.
-
Limited People-to-People Contact:
- Interaction Deficit: There is relatively low engagement in business, cultural, and educational exchanges.
-
Role of China:
- China’s Influence: Brazil’s status as China’s largest trading partner raises concerns about the potential influence on India-Brazil relations.
Way ahead:
-
Economic Cooperation:
- Diversification: Expand trade to include value-added products, services, and technology.
- Investment Environment: Foster a favorable investment climate and promote joint ventures.
- Infrastructure: Invest in infrastructure projects like transportation and logistics to enhance trade and connectivity.
-
People-to-People Exchanges:
- Cultural Diplomacy: Increase cultural and student exchanges and promote tourism to strengthen ties and economic benefits.
-
Strategic Cooperation:
- Defence Collaboration: Enhance joint defence exercises and technology sharing.
- Global Forums: Collaborate in global forums like the UN and G20 to advance shared interests.
-
Technology and Innovation:
- R&D Collaboration: Jointly invest in research and development in renewable energy, biotechnology, and IT.
- Skill Development: Focus on skill development and training to boost workforce competitiveness.
Conclusion
The deepening of India-Brazil relations represents a significant evolution in their strategic partnership. By addressing existing challenges and leveraging opportunities in trade, defence, science, and technology, both countries can enhance their bilateral ties and contribute to global stability and growth.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus



