- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
INDIA AIMS TO EXPAND SEAFOOD EXPORTS TO 1 LAKH CRORES
INDIA AIMS TO EXPAND SEAFOOD EXPORTS TO 1 LAKH CRORES
06-04-2024
-1712392725938.png)
India is aiming to reach Rs 1 lakh crore in marine product exports in the next two years by increasing its processing capacity, a senior official said on Wednesday.
Current Exports:
- In 2022-23, India's total marine product exports were $8.09 billion (Rs 63,969 crore).
- Andhra Pradesh accounts for around 70 per cent of the country’s aquaculture shrimp production.
- From April to February 2023–24, marine exports from India were $6.8 billion, a 7.5% decline compared to the previous year.
- The reason for this decline is being said to be the decrease in exports to America and Europe.
Export Target:
- The government has set a target of $9.1 billion for marine exports in 2023-24.
India's Position in Fish Production:
- India is the second largest aquaculture shrimp producer after Ecuador.
- India is also the third largest fish producer, contributing 8% to global fish production. In 2021-2022,
Top Export Destinations:
- United States of America ($2.63 billion or Rs 20600.35 crore)
- China ($1.508 billion or Rs 11956.91 crore)
- European Union ($1.26 billion or Rs 10018.38 crore)
- South East Asian countries ($1.19 billion or Rs 9494.02 crore)
About Marine Products Export Development Authority (MPEDA)
- MPEDA is a statutory body established by an act of Parliament in 1972 to promote the marine products industry and boost exports from India.
- It regulates marine product exports and ensures sustained, quality seafood exports from the country.
- It was previously the Marine Products Export Promotion Council, which was set up by the Government of India in September 1961.
Functions:
- Promotion of Marine Products Export: MPEDA's primary task is to promote the export of marine products.
- Regulation of Off-Shore and Deep-Sea Fishing: MPEDA develops and regulates off-shore and deep-sea fishing and undertakes measures for the conservation and management of these fisheries.
- Registration of Fishing Vessels, Processing Plants, and Conveyances: MPEDA registers fishing vessels, processing plants, storage premises for marine products, and conveyances used for the transport of marine products.
- Setting Standards and Specifications: MPEDA fixes standards and specifications for marine products for export purposes.
- Regulation of Marine Products Export: MPEDA regulates the export of marine products and registers marine products exporters.
- Quality Control Laboratories: MPEDA has set up five full-fledged Quality Control Laboratories in Kochi, Nellore & Bhimavaram, Bhubaneshwar, and Porbandar. It also has 15 ELISA Screening Laboratories in maritime states.
- Regional and Sub-Regional Divisions: To reach out to exporters in different parts of the country, MPEDA has set up 18 Regional/Sub-Regional Divisions/Desk offices.
- Headquarter and Trade Promotion Offices: MPEDA's headquarter is in Kochi, Kerala, and it has trade promotion offices in New Delhi, Tokyo, and New York.
Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Commerce and Industry
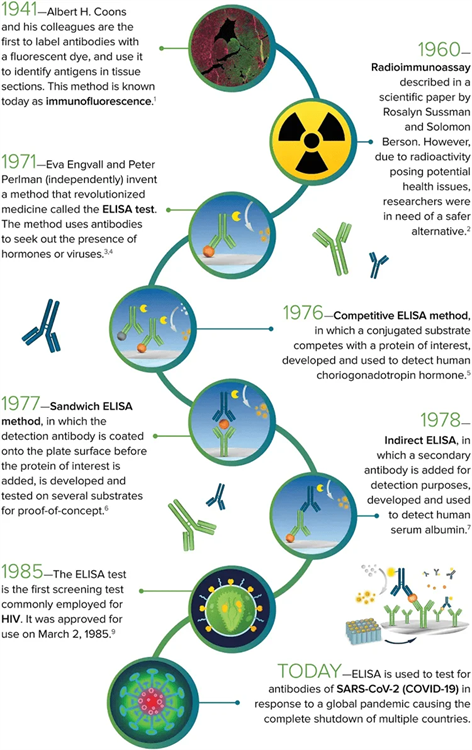
Q1: What is the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) technique?
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a laboratory technique that detects and measures antibodies, antigens, and other substances in bodily fluids. It's often used for diagnosing infections and confirming pregnancy.
ELISA tests can be used to diagnose:
- HIV
- Lyme disease
- Pernicious anemia
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Rotavirus
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Syphilis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Varicella-zoster virus
- Zika virus
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi