- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Electronic Soil
Electronic Soil
Context
Scientists have created a new electronic soil (E Soil), which was discovered to boost the growth of barley seedlings by 50 % in Hydroponic based setups.
Benefits of E soil over Traditional soils
Enhanced Growth |
E soil has shown to increase plant growth significantly, offering a 50% boost in barley seedlings compared to traditional soils, promoting healthier and faster development. |
Improved Nutrient Absorption |
The E soil facilitates better nutrient absorption by plants (especially nitrogen), ensuring they receive essential elements more efficiently, leading to enhanced overall nutritional value and crop yield. |
Water Conservation: |
E soil's advanced technology enables efficient water use, reducing water wastage and contributing to sustainable farming practices, crucial for areas facing water scarcity or drought conditions. |
Environmental Sustainability: |
E soil's benefits extend to environmental conservation by promoting healthier plant growth with reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers, minimizing environmental impact and fostering sustainable agricultural practices. |
What is Hydroponics?
- Definition: Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to the plant roots.
- Use: It is widely employed in agriculture to cultivate crops such as vegetables, herbs, and flowers, providing precise control over nutrient levels and environmental conditions.
- Advantages:
- Enhanced Growth: Plants in hydroponic systems often grow faster as they receive direct access to nutrients.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponics uses less water compared to traditional soil-based cultivation.
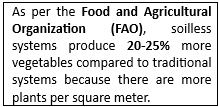
- Space Optimization: Suitable for urban farming, hydroponics maximizes space utilization.
- Reduced Pesticide Use: Controlled environments minimize the risk of pests and diseases.
- Year-Round Cultivation: Independent of seasons, hydroponics allows year-round crop production.
- Disadvantages:
- Initial Cost: Setting up hydroponic systems can be expensive.
- Technical Knowledge: Requires a certain level of expertise in managing nutrient solutions and environmental variables.
- Dependency on Electricity: Some hydroponic systems are energy-dependent.
- Risk of System Failures: Malfunctions in equipment or nutrient imbalances can impact plant health.
- Limited Crop Types: Not all crops may thrive equally well in hydroponic systems.
- Future: With increasing global population and environmental concerns, hydroponics offers a sustainable and resource-efficient approach to food production.


