- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 7th APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 7th APRIL 2025
Cabinet Approves "Vibrant Villages Programme-II (VVP-II)" for 2024-25 to 2028-29
- The Cabinet has approved the Vibrant Villages Programme-II (VVP-II) for the financial years 2024-25 to 2028-29. This new phase builds on the foundation established by the first phase, VVP-I, which focused on border villages along India’s northern frontier.
- The initiative underscores India's commitment to the vision of a Viksit Bharat by 2047, aiming to ensure that the country’s land borders are safe, secure, and self-sufficient.
Why Border Populations Are a Strategic Asset
1. Source of Local Knowledge: Border populations, especially those in remote areas, possess valuable knowledge about local environmental conditions and cross-border activities. They maintain informal networks that provide critical information on security concerns, enhancing national defense efforts.
2. Surveillance & Early Warning Systems: Local nomads and shepherds often act as the first line of defense, providing early warnings for potential border transgressions. One example of this was Tashi Namgyal during the Kargil War, whose vigilance contributed to national security.
3. Logistical Support: Border villages play a vital role in supporting patrol forces by providing food, shelter, and labor, especially in difficult terrains. These communities act as logistical backbones, enabling effective border management.
4. Reinforcing Territorial Claims: Settled populations in disputed border areas help fortify territorial claims. For example, Article 7 of the 2005 India-China Agreement emphasizes the importance of settled populations in reinforcing India’s territorial integrity.
Previous Development Efforts: Over the years, various initiatives have been launched to improve the conditions of border areas:
- 1986-87: Border Area Development Programme
- 2005-06: Model Village Initiative
- 2015: Smart/Model Village Development
Key Features of Vibrant Villages Programme-II (VVP-II)
1. Scheme Type and Coverage: VVP-II is a Central Sector Scheme, fully funded by the Centre. Unlike VVP-I, which was a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, VVP-II aims to cover strategic villages along India’s international land borders (ILBs) across 17 states and Union Territories. It excludes northern border blocks already covered under VVP-I (2023-24).
2. Objectives of VVP-II: The core objectives of the programme are:
- Improvement of living conditions in border villages.
- Provision of livelihood opportunities for local communities.
- Control of trans-border crimes.
- Integration of local populations as vital contributors to national security, acting as ‘eyes and ears’ for the government.
3. Key Components of VVP-II
- Infrastructure Development: Investments will be made in essential infrastructure, including roads, housing, sanitation, drinking water, and SMART classrooms. All-weather road connectivity will be prioritized under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (MGSY-IV).
- Value Chain & Livelihood Development: VVP-II will support cooperatives, Self-Help Groups (SHGs), and border-specific outreach initiatives to create sustainable livelihoods in these villages.
- Welfare Scheme Convergence: The programme will ensure the implementation of existing welfare schemes in the identified villages, ensuring full coverage under the convergence model.
- Cultural & Tourism Promotion: The programme will also focus on promoting local heritage and tourism through organizing fairs, festivals, awareness camps, and national day celebrations.
- PM Gati Shakti: The PM Gati Shakti initiative will be utilized to ensure the effective implementation and smooth execution of the VVP-II projects.
Kazakhstan Discovers Largest Rare Earth Metal Deposit

- Kazakhstan has announced the discovery of its largest rare earth metal deposit in the Karaganda region, containing an estimated one million tonnes of essential rare earth elements, including cerium, yttrium, neodymium and lanthanum.
- This discovery could significantly impact the global market, especially in the fields of green energy and high-tech industries.
Key Points:
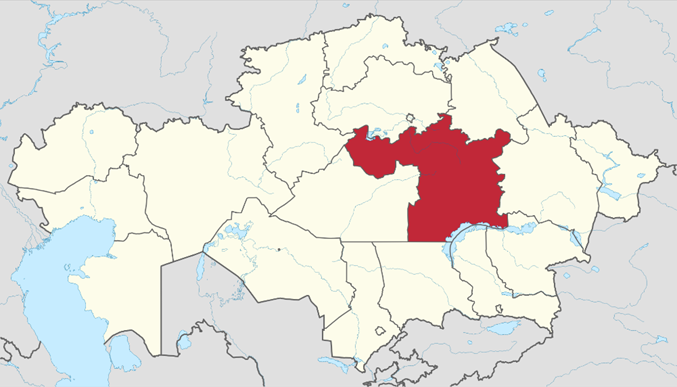
Location of Karaganda Region in Kazakhstan, shown in red.
- Deposit Size: Initial estimates suggest one million tonnes, with the potential to grow to over 20 million tonnes after further research.
- Strategic Importance: The rare earth metals found are crucial for technologies like electric vehicles, wind turbines, and defense systems.
- Global Competition: Countries like China, Russia, the US, and Europe are competing for access to these resources, with the EU showing particular interest due to its carbon neutrality goals by 2050.
India-Thailand Sign Strategic Partnership Declaration
- India and Thailand have recently signed a Joint Declaration aimed at establishing a Strategic Partnership between the two nations.
- While not overly formal, this partnership is rooted in shared objectives, particularly in the areas of security, trade, economy, and technology.
Significance of the India-Thailand Strategic Partnership
- Shared Interests: Both nations are committed to a free, open, transparent, and rules-based Indo-Pacific. They also emphasize ASEAN centrality, which highlights ASEAN’s role as a driving force in the region's geopolitics and geo-economics.
- Strategic Location: Thailand, as India’s maritime neighbor, plays a crucial role in maintaining regional peace.
- Complementary Policies: India’s "Act East" policy and Thailand’s "Act West" policy align well, supporting stronger regional cooperation.
- Regional Groupings: Thailand is a vital partner for India in several regional and sub-regional groupings, including ASEAN and the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC).
Key Agreements Signed
- Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs): Several agreements were signed covering various areas of cooperation, such as the development of the National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) at Lothal and the development of the North Eastern Region.
- People-to-People Ties: A new India-Thailand Consular Dialogue will be established to enhance diplomatic and cultural exchanges.
- Trade Facilitation: Both countries are exploring mechanisms to enable local currency-based trade settlements.
Overview of India-Thailand Relations
- Diplomatic Relations: India and Thailand have maintained diplomatic ties since 1947.
- Economic Ties: Bilateral trade between the two nations reached approximately USD 15 billion in 2023-24.
- Defense Cooperation: Both countries engage in joint defense activities, including exercises like Exercise Maitree and INDO-THAI CORPAT (Coordinated Patrol).
SC Orders Probe into Violations of Forest and Wildlife Laws in Tamil Nadu's Agasthyamalai Landscape
- The Supreme Court has directed an investigation into the violations of forest and wildlife laws concerning encroachments in the Agasthyamalai Landscape in Tamil Nadu.
- The case specifically addresses the encroachment of lands in the Singampatti Zamin forests, which were cleared for plantation cultivation, including tea, coffee, and rubber.
- These lands were declared part of the Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Reserved Forest in 1978, and subsequently, a Core Critical Tiger Habitat in 2007, as well as a Wildlife Sanctuary and Tiger Reserve in 2012. This designation led to the eviction of tea estate workers.
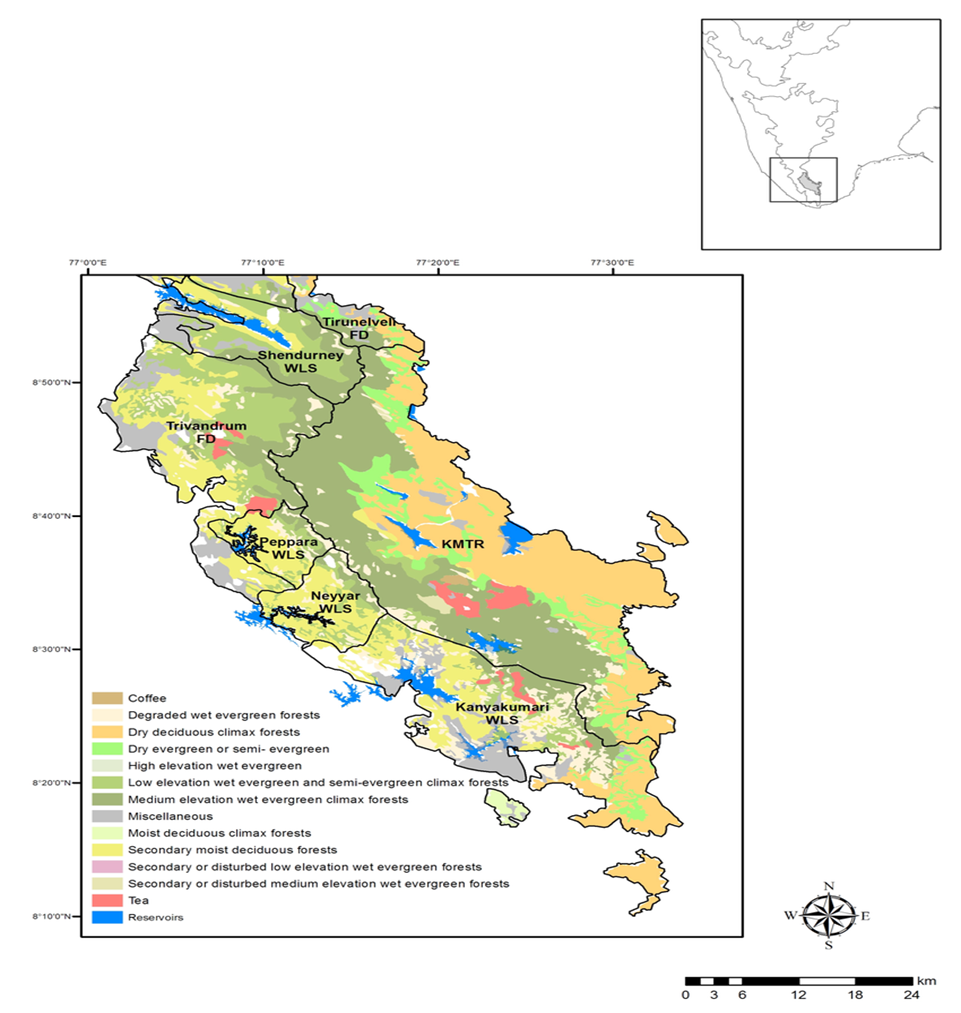
Map showing the Agasthyamalai landscape consisting of the Kalakad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve (KMTR) and adjoining areas and different vegetation types in the landscape. Inset map shows Western Ghats with the study area (KMTR) at the southern tip of India
Key Observations from the SC Order in the Case of A. John Kennedy v. State of Tamil Nadu & Others
- Forests as Vital Ecosystems:
- The court emphasized that forests are the "lungs of the ecosystem," and their depletion has direct and severe consequences on climate change and biodiversity.
- It highlighted that approximately 13,000 sq. km of forest land in India is under encroachment (according to the Ministry of Environment).
- Role of Tigers in Ecosystem Balance: The court referred to the landmark T.N. Godavarman case, stating that tigers are critical for maintaining the balance of ecosystems. It asserted, "The tiger perishes without the forest, and the forest perishes without its tigers."
- Endorsement of an Ecocentric Approach: The Supreme Court endorsed the ecocentric approach (focusing on ecosystems rather than human-centered concerns) as outlined in the State of Telangana v. Mohd. Abdul Qasim case (2024).
Forest and Wildlife Protection Laws in India
1. Forest Classification: Under the Indian Forest Act, 1927, forests are classified into different categories, each with varying degrees of protection:
|
Type of Forest |
Protection Level |
|
Reserved Forest |
Full protection; all activities prohibited unless permitted. |
|
Protected Forest |
Limited protection; all activities permitted unless prohibited. |
|
Unclassed Forest |
Areas recorded as forests but not categorized as reserved or protected; ownership status varies by state. |
2. Forest Conservation Act, 1980: Any use of forest land for non-forestry purposes requires the prior approval of the Government of India.
3. Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: This Act lays down the framework for the protection of wildlife and establishes Tiger Reserves. These reserves are classified into:
- Core or Critical Tiger Habitat: Areas where the habitat is preserved without disrupting the rights of scheduled tribes or other forest dwellers.
- Buffer or Peripheral Area: Areas that allow limited human activity, promoting coexistence between wildlife and people.
About the Agasthyamalai Landscape
The Agasthyamalai Landscape spans across both Tamil Nadu and Kerala. It is an ecologically significant area known for its rich biodiversity. The landscape includes several important wildlife sanctuaries and reserves, such as:
- Periyar Tiger Reserve
- Srivilliputhur Grizzled Squirrel Wildlife Sanctuary (WLS)
- Meghamalai WLS
- Thirunelveli WLS
In addition to these reserves, the Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve is a part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Program. The landscape is also home to 14 rivers, including the Thamirabarani River.
The reserve includes several Wildlife Sanctuaries (WLS) and Tiger Reserves, such as:
- Shendurney WLS, Peppara WLS, and Neyyar WLS in Kerala.
- Kalakkad-Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu.
The Supreme Court’s order to probe violations in the Agasthyamalai Landscape underscores the critical need for protecting forests and wildlife in India. This case highlights the importance of preserving ecosystems, ensuring the survival of species like tigers, and enforcing laws that safeguard natural habitats from encroachment and degradation. The landscape itself is of immense ecological value, and any threat to its integrity can have far-reaching consequences for biodiversity and environmental health.
Article 311: Key Points and Clarification by the Supreme Court
- The Supreme Court in the case of State of Jharkhand vs. Rukma Kesh Mishra clarified that Article 311(1) does not require the appointing authority's approval to initiate disciplinary proceedings against a state employee.
- However, it was emphasized that Article 311(1) does mandate the appointing authority's approval for dismissal.
About Article 311
Article 311 of the Indian Constitution deals with the dismissal, removal, or reduction in rank of individuals employed in civil capacities under the Union or State government. It ensures the protection of civil servants from arbitrary actions by the government.
- Article 311(1):
- This clause protects civil servants from being dismissed or removed by any authority subordinate to the appointing authority.
- Key Point: It mandates the appointing authority's approval for dismissal or removal, but it does not require approval to initiate disciplinary proceedings.
- Article 311(2):
- This clause outlines that a civil servant cannot be dismissed, removed, or reduced in rank without being given a reasonable opportunity to be heard after a proper inquiry.
- Key Point: It ensures procedural fairness by granting the employee the right to a hearing before any major action is taken against them.
One Health Approach: Key Information
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has launched a study to detect zoonotic spillover in bird-human interaction settings using the One Health approach.
- Zoonotic spillover refers to the transmission of pathogens from vertebrate animals to humans, which is a critical area of focus for global health.
About the One Health Approach
- Definition: The One Health approach is an integrated and unifying strategy aimed at optimizing and balancing the health of people, animals, and the environment. It recognizes that the health of each of these domains is interconnected.
- Purpose:
The One Health approach helps in:- Preventing, predicting, and detecting health threats that affect humans, animals, and the environment.
- Responding effectively to global health challenges, such as zoonotic diseases, which can be transmitted between animals and humans.
- India's National One Health Mission:
India has launched the National One Health Mission to:- Coordinate and support existing One Health activities across various sectors in the country.
- Integrate efforts from different health disciplines (human, animal, and environmental health) to better address emerging health threats.
Tulips: Key Information and Indigenization Efforts
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM), in collaboration with the Field Station Bonera in Jammu, are working on indigenizing tulips.
- This initiative aims to enhance the growth and cultivation of tulips in India, leveraging the country’s rich agricultural potential.
About Tulips
- Origin: Tulips are native to Central Asia and Turkey, where they have been cultivated for centuries for their beauty and vibrant colors.
- Physical Characteristics:
- Tulips are bulbous herbs, belonging to the lily family.
- They are popular garden flowers, known for their wide variety of colors.
- The flowers are typically erect, with long, broad, parallel-veined leaves.
- Growing Conditions:
- Climate:
- In colder climates, tulips are planted before the ground freezes, ensuring they grow properly during the next blooming season.
- In warmer climates, they are usually planted annually as part of seasonal gardening.
- Soil: Tulips thrive best in well-drained loam soil, which helps prevent waterlogging and supports healthy bulb growth.
- Climate:
Significance of Tulips in India
Indira Gandhi Memorial Tulip Garden in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, is Asia's largest tulip garden. This garden showcases the beauty and potential of tulip cultivation in India, and the ongoing efforts to indigenize tulips aim to make their cultivation more widespread across the country.
Koch-Rajbongshi Community

Koch Rajbongshi Largest Ethnic Group Of South Asia
The Assam Cabinet recently decided to drop cases against the Koch-Rajbongshi community in various Foreigners’ Tribunals (FTs), which is a significant development for this community.
About the Koch-Rajbongshi Community
- Historical Background:
- The Koch-Rajbongshi people trace their roots to the Kamata Kingdom, which was ruled by the Koch Dynasty.
- The Kamata Kingdom was located in parts of what is now Assam, West Bengal, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- The kingdom emerged in the 13th century, following the fall of the Pala Dynasty in the older Kamarupa kingdom, which was located in the same region.
- Language:
- The community primarily speaks Rajbongshi or Rajbanshi, also known as Kamtapuri.
- According to the 2001 Census, there are approximately 1 crore speakers of this language.
- Cultural Practices:
- The Koch-Rajbongshi community initially practiced animism.
- Over time, they largely adopted Hinduism, although a minority of the community members have embraced Christianity.
Hansa-3 (NG): India's Indigenous Trainer Aircraft
- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), in collaboration with the National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), has signed a technology transfer deal with a private firm to manufacture the HANSA-3 trainer aircraft in India.
- This marks a historic achievement as the HANSA-3 is the first aircraft to be fully designed and developed indigenously in India and will be manufactured based on this local technology.
Key Features of HANSA-3 (NG)
- Engine: The aircraft is powered by the Rotax 912 iSc3 Sports engine, which is known for its fuel efficiency, contributing to lower operational costs and environmental sustainability.
- Performance:
- Range: The aircraft has a range of 620 nautical miles, making it suitable for various training requirements.
- Endurance: It boasts an impressive 7 hours of endurance, ensuring long-duration training sessions.
- Speed: The aircraft achieves a maximum cruise speed of 98 Knots Calibrated Airspeed (KCAS), suitable for its role as a trainer.
Significance of HANSA-3 (NG)
- Flying Training Ecosystem: The HANSA-3 contributes to the creation of a world-class flying training ecosystem in India, enhancing the quality and capacity of aviation training.
- Strengthening India's Aviation Industry: By manufacturing this trainer aircraft locally, India takes a significant step toward self-reliance in its aviation sector, boosting both the industry and the economy.
- Indigenous Technology:
The HANSA-3 aircraft is a testament to India's growing capabilities in aerospace technology, marking a new chapter in the development of indigenous aviation solutions.
Quad Partnership on Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR)

QUAD nation’s Flag
- The Quad countries—Australia, India, Japan, and the United States—have been collaborating under the Quad Partnership on Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) to address natural disasters and humanitarian crises across the Indo-Pacific region.
- Recently, they released a joint statement to assist in the aftermath of the earthquake in Myanmar.
About Quad HADR
- Background:
- The Quad partnership, which traces its origins back to the Indian Ocean Tsunami of 2004, aims to strengthen cooperation among these four countries in areas like disaster relief and humanitarian aid.
- The Guidelines for the Quad Partnership on HADR in the Indo-Pacific were officially announced in Tokyo in 2022, outlining the framework for cooperation in such areas.
- Objectives of Quad HADR:
- Addressing Regional Vulnerabilities: The initiative seeks to respond to the region's various vulnerabilities, particularly in the wake of natural disasters like tsunamis, earthquakes, and cyclones.
- Enhancing Capacity and Capability: Quad countries work together to augment their collective capacity and operational efficiency to respond to humanitarian emergencies.
- Interoperability and Synergy: The partnership focuses on improving interoperability and creating operational synergy among the four countries to ensure effective disaster relief operations.
Adjournment Sine Die: Understanding the Concept
The Lok Sabha was adjourned sine die, ending the Budget session.
What is Adjournment Sine Die?
The term “Sine Die” is derived from Latin, meaning "without assigning a day for a further meeting." In the context of parliamentary procedures, Adjournment Sine Die refers to the conclusion of a session of Parliament with no fixed date for its reconvening.
Key Aspects of Adjournment Sine Die
-
Process:
-
The Presiding Officer of the House announces the adjournment sine die.
-
Following this, the President of the country issues a notification to prorogue the House, officially bringing the session to an end. This process is carried out in accordance with Article 85 of the Indian Constitution.
-
-
Effect on Pending Business:
-
Bills: All bills that are pending in the House remain unaffected. They will be taken up in the next session.
-
Notices: Most notices (including questions, motions, and resolutions) lapse once the session ends and need to be resubmitted in the following session, unless specifically exempted.
-
Wat Pho Temple: A Cultural and Spiritual Landmark

PM Modi & Thailand PM Paetongtarn Shinawatra at Wat Pho Temple, Thailand
In April 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited the Wat Phra Chetuphon Wimon Mangkhalaram Rajwaramahawihan, or Wat Pho Temple.
Location:
Wat Pho Temple, officially known as Wat Phra Chetuphon Wimon Mangkhalaram Rajwaramahawihan, is situated in Rattanakosin Island, in the heart of Bangkok, Thailand.
Key Features of Wat Pho Temple
- Famous Reclining Buddha:
The temple is renowned for housing the **46-meter-long gold-plated Reclining Buddha. This statue represents the Buddha as he enters a state of complete spiritual enlightenment. - Cultural and Historical Significance:
- Wat Pho is officially classified as a first-class royal temple.
- It is widely regarded as the birthplace of traditional Thai medicine and massage, and is also considered the first university of Thailand, where many important subjects, including medicine and art, were taught.
- Historical Importance:
- The temple gained prominence during the reign of King Rama I from the Chakri Dynasty.
- King Rama III further expanded and renovated the temple, enhancing its grandeur and architectural significance.
Kannadippaya Receives Geographical Indication (GI) Tag

kannadippaya tribal handicraft product from Kerala
The Kannadippaya (literally meaning mirror mat) , a traditional tribal handicraft from Kerala, has been awarded the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, marking it as the first tribal handicraft product from the state to receive this prestigious recognition.
Key Details:
- Craft Preserved By: The Oorali, Mannan, Muthuva, Malayan, and Kadar tribal communities, along with Ulladan, Malayarayan, and Hill Pulaya artisans from Idukki, Thrissur, Ernakulam, and Palakkad districts.
- Materials Used: The finest Kannadippaya is woven from reed bamboo (Teinostachyum wightii) and other bamboo species such as Ochlandra sp. (varieties include Kareetta, Pereetta, Velleeta, etc.).
- Historical Significance: Historically, Kannadippaya was presented to kings as a mark of honor by the tribal communities.
- The GI tag will empower tribal artisans, enabling them to become independent entrepreneurs and market their products more effectively.
Amalsad Chikoo Awarded Geographical Indication (GI) Tag

Amalsad Chikoo
The Amalsad Chikoo, a fruit renowned for its sweetness, fine texture, and long shelf life, has been awarded the Geographical Indication (GI) tag. This recognition is attributed to its unique characteristics and deep-rooted connection to the Amalsad village in Gujarat’s Navsari district.
Key Details:
- Valsad Navsari Jilla Fal Ane Shakbhaji Sahakari Sangh Ltd (Navsari district fruit and vegetables co-operative).
- The Amalsad Chikoo is the third fruit from Gujarat to receive a GI tag, joining the Gir Kesar Mango and Kutchhi Kharek (date).
- Gujarat produces 98% of India's chikoo, with Navsari district being the largest producer. The Amalsad Chikoo accounts for 30% of the state’s chikoo production.
- The GI tag will provide legal protection, ensuring higher economic benefits for local farmers and better access to global markets. Key export destinations for Indian chikoo include the UAE, UK, and Bahrain.
BHEL Bags 2x660 MW Supercritical Power Plant Order from CSPGCL
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) has received a major order from Chhattisgarh State Power Generation Company Limited (CSPGCL).
- The order is for setting up a 2x660 MW Supercritical Thermal Power Plant at Hasdeo Thermal Power Station (HTPS), Korba West, Chhattisgarh.
- The order was secured through domestic competitive bidding.
Scope of Work
BHEL’s responsibilities under this project include:
- Design, engineering, manufacturing, and supply of key equipment, such as: Supercritical Boiler, Turbine and Generator
- Complete erection, testing, and commissioning of the thermal power station.
- Supply of state-of-the-art Flue Gas Desulphurization (FGD) equipment to control SOx emissions from the plant.
Strategic Role in Energy Security
- BHEL’s Role: As India’s leading power equipment manufacturer, BHEL has installed over 1,72,000 MW of utility power capacity across the country.
- Energy Security: BHEL continues to contribute significantly to India’s energy security and supports the vision of self-reliance in the power sector.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




