- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary - 3rd APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary - 3rd APRIL 2025
Standing Committee on External Affairs Report on Indian Diaspora Overseas
- The Indian Diaspora refers to people of Indian origin who have migrated to foreign countries, either several generations ago or more recently, often on long-term visas issued by those countries.
- This group includes Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and Non-Resident Indians (NRIs).
- As of January 2024, the Indian Diaspora population stands at approximately 35.42 million, with 15.85 million NRIs and 19.57 million PIOs and OCIs.
Issues and Recommendations:
Must Read: Death Sentence Given To Nimisha Priya in Yemen
Must Read: Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers: ILO Report 2022
The Standing Committee on External Affairs highlighted several key concerns regarding the Indian Diaspora and provided the following recommendations:
|
Area |
Concern |
Recommendation |
|
Conversion of PIO Cards to OCI Cards |
Slow response to the OCI Card Scheme, leading to an inadequate number of OCI cards issued. |
Undertake concerted efforts through social media and Diaspora organizations to complete the conversion of all PIO cards to OCI cards by December 2025. |
|
Voting Rights for NRIs |
NRIs who are enrolled in the voter list must be physically present to cast their votes. |
Consider implementing the Electronically Transmitted Postal Ballot System (ETPBS) to extend voting rights to NRIs. |
|
Transfer of Sentenced Persons from Foreign Jails |
Only 8 Indian prisoners were transferred from foreign jails to India in the past three years. |
Enhance diplomatic efforts to streamline the prisoner transfer process and ensure fair treatment for Indian nationals in foreign jails. |
|
Status of the Emigration Bill |
Delay in finalizing the Emigration Bill, despite issues with illegal emigration. |
Prioritize a comprehensive legislative overhaul, replacing the Emigration Act of 1983 with the Overseas Mobility (Facilitation and Welfare) Bill, 2024. |
|
Working Group on Welfare Schemes/Programmes for Diaspora |
No meetings have been held since 2021 to review the progress of various welfare schemes. |
Ensure biannual meetings of the Working Group to assess the objectives, progress, and challenges of various diaspora-related schemes and initiatives. |
Must Read: Dunki Routes and Illegal Migration
Must Read: Prayas: Empowering Indian Diaspora
India-Chile Bilateral Talks
During the visit of the Chilean President to India, the Indian Prime Minister and the Chilean President held productive bilateral discussions. These talks led to several significant agreements and collaborations between the two countries.
Key Outcomes:
- Antarctica Cooperation: A Letter of Intent was signed to enhance cooperation in Antarctica, with Chile positioning itself as India’s gateway to the region.
- Cultural Exchange: Chile announced the celebration of November 4 as its National Yoga Day, marking a significant step in strengthening cultural ties between the two nations.
- Disaster Management Collaboration: An MoU was signed between Chile’s National Service for Disaster Prevention and Response (SENAPRED) and India’s National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) to bolster disaster response and management cooperation.
- Mining Partnership: An agreement for cooperation and information exchange was established between Chile’s National Copper Corporation (CODELCO) and India’s Hindustan Copper Limited, paving the way for future collaboration in the mining sector.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): Both nations agreed to initiate discussions on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to enhance bilateral trade and economic relations.
India’s Defence Exports Reach Record High of ₹23,622 Crore in 2024-25
- India's defence exports have reached a record ₹23,622 crore in 2024-25, reflecting a growth of 12.04% compared to the previous year.
- This growth underscores the increasing global acceptability of Indian defence products and India's growing integration into the global supply chain.
Significance of Rising Defence Exports:
- Promoting Indigenous Defence Production: India's defence production has grown by 174% from 2014-15 to 2023-24, fostering greater self-reliance in defence manufacturing.
- Policy Targets: India aims to achieve ₹3 lakh crore in defence production and ₹50,000 crore in defence exports by 2029.
- Catering to International Demand: In 2024-25, 92% of the global contracts signed by the Ministry of Defence were awarded to Indian domestic industries.
- Boosting Private Sector Participation: The private sector contributed ₹15,233 crore to India's defence exports in 2024-25, playing a significant role in the sector’s growth.
- Diversified Export Portfolio: India's defence export portfolio includes a variety of products, such as bulletproof jackets, Dornier (Do-228) aircraft, and Chetak helicopters, helping to reduce dependency on imports.
Key Challenges in Defence Exports:
- Slow Growth in Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs): While DPSUs saw a 42.85% rise in exports in FY 2024-25, their actual production levels still lag behind the private sector.
- Lack of Technological Depth: Despite advances, India still imports critical components, systems, and raw materials due to a lack of technological depth in certain areas of defence manufacturing.
- Lag Between Policy Announcement and Implementation: Bureaucratic hurdles continue to impact the timely implementation of policies designed to boost defence exports.
Key Initiatives Driving India’s Defence Exports:
- Indigenous Production: Initiatives like Make in India, strengthening the defence industrial base (including DPSUs and MSMEs), and the Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS) aim to boost domestic production capacity.
- Advancing Self-Reliance: Programs like SRIJAN (Self-Reliant Initiatives through Joint Action) and the development of Defence Industrial Corridors are driving self-reliance in defence manufacturing.
- Innovation and Research: The development of innovative technologies is being supported through initiatives like IDEX (Innovative Defence Excellence) and the MAKE projects, which focus on advancing indigenous production.
- Policy Reforms: The government has implemented liberalized policies such as allowing 74% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) through the automatic route, as well as measures to ease the process of doing business, like extending the validity of export authorization for parts and components.
Cape Town Convention and Protocol
The Rajya Sabha has recently passed The Protection of Interests in Aircraft Objects Bill, 2025, which aims to align India's legal framework with the Cape Town Convention (Convention on International Interests in Mobile Equipment) and the Protocol on Matters Specific to Aircraft Equipment.
Overview of the Cape Town Convention and Protocol:
- Objective: The primary aim of the Cape Town Convention is to standardize transactions involving movable assets, particularly high-value equipment such as aircraft, engines, and helicopters. The Convention provides a legal structure to help creditors enforce their rights in the event of default.
- Adoption: The Cape Town Convention was adopted jointly by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the International Institute for the Unification of Private Law (UNIDROIT) in 2001.
- Global Participation: As of 2016, the Convention has been ratified by 65 parties. India signed the Convention in 2008.
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
In FY 2024-25, India achieved a record of 4,515 child adoptions, with CARA facilitating the introduction of 8,598 newly identified children into the adoption pool.
About CARA:
- Establishment: CARA was established in 1990 to oversee adoption processes in India.
- Legal Status: It functions as a statutory body under the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015.
- Affiliated Ministry: CARA operates under the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Roles and Responsibilities: As the central authority for child adoption, CARA regulates both in-country and inter-country adoptions. It monitors these processes through the Child Adoption Resource Information & Guidance System (CARINGS).
- International Role: CARA is designated as the central authority for inter-country adoptions under the Hague Convention on Inter-country Adoption, 1993, which India ratified in 2003.
Open Market Operations (OMO)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently announced an Open Market Operation (OMO) to inject ₹80,000 crore into the banking system.
About OMOs:
Open Market Operations (OMO) involve the RBI's buying and selling of government bonds in the open market. This is a key monetary policy tool used by the central bank to manage the money supply, control inflation, and maintain economic stability.
- Buying Government Bonds: When the RBI purchases government bonds, it increases the money supply in the economy.
- Selling Government Bonds: When the RBI sells bonds, it reduces the money supply.
Taiwan Strait
China recently initiated new military drills, "Strait Thunder-2025A," in the middle and southern regions of the Taiwan Strait.
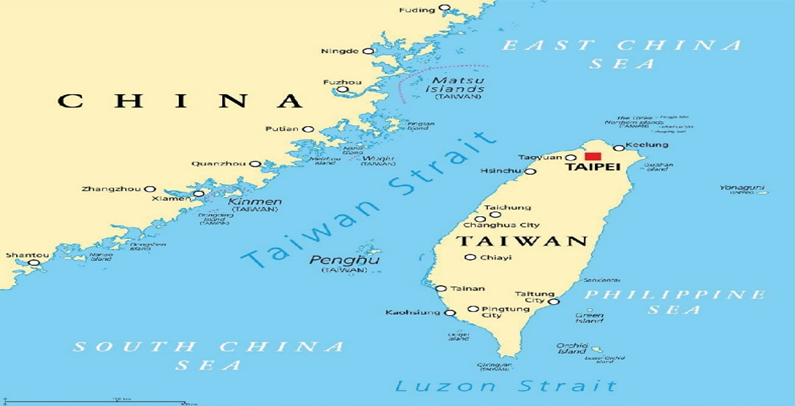
About Taiwan Strait (also known as the Black Ditch):
- Historical Name: The Taiwan Strait was named Formosa ("Beautiful") by Portuguese navigators in the late 16th century.
- Location: It lies between China’s Fukien province and Taiwan.
- Connecting Seas: The Strait extends from the southwest to the northeast, linking the South China Sea and the East China Sea.
- Global Significance: The Taiwan Strait is a crucial global shipping route, with approximately 44% of the world’s container fleet passing through it.
- Median Line (Davis Line): The Strait features a median line running roughly down its center, although China does not recognize this boundary.
Prime Minister's National Relief Fund (PMNRF)
The Prime Minister recently announced an ex-gratia payment from the PMNRF for the victims of the fire factory explosion in Gujarat.
About PMNRF:
- Establishment: The PMNRF was set up by the first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, in 1948 to provide assistance to displaced persons from Pakistan.
- Purpose and Usage: The fund is primarily used to provide immediate relief to families of those affected by natural disasters, including floods, cyclones, and earthquakes. It also offers partial assistance for medical treatments, such as heart surgeries, kidney transplants, cancer treatment, and recovery from acid attacks.
- Funding Source: The PMNRF is entirely funded through public contributions and does not receive any budgetary allocation from the government.
- Tax Exemption: Contributions to the PMNRF are exempt from Income Tax under section 80(G).
NITI NCAER States Economic Forum’ Portal
The finance minister recently launched the NITI NCAER States Economic Forum portal, developed by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER).
About the Portal:
- Content: The portal serves as a comprehensive repository containing data on various so cial, economic, and fiscal parameters. It includes research reports, papers, and expert commentary on state finances, covering a span of approximately 30 years (from 1990-91 to 2022-23).
- Objective: The portal aims to assist states in making informed policy decisions related to public finances, including revenue generation, debt management, and learning from the experiences of other states.
SAMARTH UDYOG BHARAT 4.0 (SAMARTH Centres)
Recently, the Minister of State for Heavy Industries and Steel informed Parliament about the establishment of 4 Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) Centres.
About SAMARTH Centres:
- Initiative: SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 is part of the Ministry of Heavy Industry & Public Enterprises' Industry 4.0 initiative, aimed at modernizing India's manufacturing sector.
- Industry 4.0: This initiative focuses on integrating advanced digital technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics to enhance efficiency, flexibility, and smart decision-making in manufacturing processes.
- Objectives: The SAMARTH Centres are designed to support industries, including MSMEs, by providing workforce training on Industry 4.0 technologies. They offer workshops, consultancy services, and incubation support for start-ups, helping businesses embrace advanced manufacturing techniques and remain competitive.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |