- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
4th edition of Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers: ILO Report 2022
4th edition of Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers: ILO Report 2022

- The International Labour Organization (ILO) released its 4th edition of the Global Estimates on International Migrant Workers in December 2024.
- This report talks about the important role of international migrant workers (IMWs) in the world economy.
- IMWs help to fill jobs in host countries which support the economies of both regions.
Who are International Migrant Workers (IMWs)?
What is the International Labour Organization (ILO) ?
The ILO has 8 core conventions. However, India has not ratified two of these conventions:
In 2017, India ratified ILO Conventions No. 138 and 182, showing its commitment to eliminating child labor. Major Publications:
|
Key Findings from the ILO Report:
- The global labor force means all the people in the world who are able and available to work. This includes both those who already have jobs and those who are looking for work.
- In 2022, international migrants made up 4.7% of the global labor force, which is about 167.7 million people. This is an increase of 30 million compared to 2013.
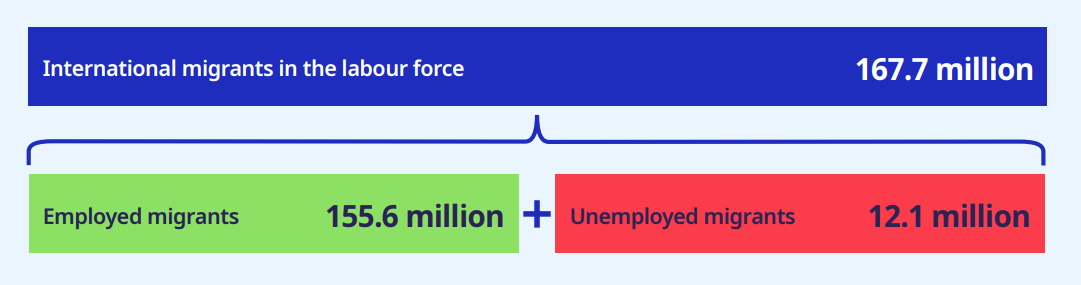
- However, the growth rate in the number of IMWs between 2019-2022 slowed to less than 1% per year, mainly due to the COVID-19 pandemic and other global factors.
- Age and Gender Distribution of IMs: Age Distribution of IMs (2022) shows that prime-age adults (25-54 years) make up the largest group.
Age Group |
Proportion of IMs |
|
Prime-Age (25-54 years) |
74.9% (125.6 million) |
|
Young Workers (15-24 years) |
9.3% (15.5 million) |
|
Older Workers (55-64 years) |
12.5% |
|
Elderly Workers (65+ years) |
3.4% |
- Gender Distribution of IMs (2022): Male IMs are the majority, but the number of female IMs has increased over time. However, female IMs are less likely to be employed compared to male IMs.
|
Gender |
Proportion of IMs (%) |
Employed IMs (%) |
|
Male IMs |
61.3% (102.7 million) |
61.3% |
|
Female IMs |
38.7% (64.9 million) |
38.7% |
- Sectoral Distribution of IMs: International migrants mainly work in the services sector, including healthcare, education, and caregiving, which are growing fields globally.
|
Sector |
Proportion of IMs (%) |
Proportion of Non-Migrants (%) |
|
Services |
68.4% |
Higher than non-migrants |
|
Industry |
24.3% |
24.2% |
|
Agriculture |
7.4% |
24.3% |
-
- Within services, women make up 80.7% and Men 60.8% of the migrant workforce, reflecting the higher number of women in caregiving and healthcare jobs.
- Regional Distribution of IMs (2022) : The distribution of international migrants shows that high-income countries continue to attract the largest number of IMWs, mainly because of economic opportunities and aging populations.
|
Region |
Proportion of IMs (%) |
Comparison (2013-2022) |
|
High-Income Countries |
68.4% |
Consistent trend over the decade |
|
Upper-Middle-Income Countries |
17.4% |
Growing role in attracting IMs |
|
Northern, Southern, Western Europe |
23.3% |
Slight increase over the decade |
|
North America |
22.6% |
Decrease by over 1 percentage point |
|
Arab States |
13.3% |
Decrease by 3 percentage points |
-
- High-income countries continue to host 68.4% of international migrants, mainly in sectors like healthcare and services.
- North America and the Arab states have seen a small decrease in the number of IMWs over the last decade.
- Economic Contributions of IMs: International migrant workers play an important role in the economy in both the countries they work in and the countries they come from.
- IMs help fill labor shortages in important sectors like healthcare, hospitality, and construction.
- They provide essential services in sectors like care, where there is high demand due to aging populations.
- IMs send a large amount of remittances back to their home countries. This money helps support families and contributes to the economies of poorer countries.
- Remittances are money that people send back to their families or friends in their home country. This money is often sent by workers who live and work in a different country.
- They also help increase the income and living standards of families in their home countries through the money they send back.
Challenges Highlighted by the Report
- The report shows that many female migrants work in the care industry, which often has lower pay and fewer rights. Women also face a higher unemployment rate compared to men.
- Migrant workers often face low wages and poor working conditions. Without proper social security, they struggle to cope with unexpected situations, like illness or job loss.
- Many migrants face challenges in finding jobs due to a lack of qualifications or skills and language barriers, which make it harder for them to fit into the workforce of the country they migrate to.
- Migrants often experience xenophobia, racism, and social exclusion, making it difficult for them to integrate into their new communities.
- Migrants sometimes pay high fees to recruiters to find work, leading to debt and financial pressure. This can make workers vulnerable to trafficking and forced labor, as seen in systems like the Kafala system in many Arab countries.
Conclusion
The ILO report highlights how important international migrant workers are to the global economy. Despite challenges like the pandemic, IMWs continue to be a key part of the workforce, filling important jobs and supporting both host countries' economies and their home countries through remittances. High-income countries remain the main destinations for international migrants, especially in sectors like healthcare and caregiving.
UPSC PYQ 2018:
Q. International Labour Organisation’s Conventions 138 and 182 are related to:
- Child labour
- Adaptation of agricultural practices to global climate change
- Regulation of food prices and food security
- Gender parity at the workplace
Answer: 1
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




