- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs-May 20, 2023
Daily Current Affairs-May 20, 2023

25TH ANNIVERSARY OF POKHRAN-II

Latest Context
On May 11, 2023, India marked the 25th anniversary of Pokhran-II, the successful nuclear bomb test explosions that proved a crucial turning point in the country's quest to become a nuclear power.
- The 11th of May is also recognised as National Technology Day to thank the scientists, engineers, and technicians from India who contributed to the growth of science and technology in their nation and made the Pokhran tests successful.

A Nuclear Power's Journey in India
-
Origin: Famous physicist Homi J. Bhaba pushed for the creation of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), which is focused on nuclear physics research, in Bombay in 1945.
- The first research centre in India devoted to the study of nuclear physics was established as TIFR.
- Following India's independence, Bhaba persuaded Jawaharlal Nehru, the prime minister at the time, of the value of nuclear energy. As a result, the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), with Bhabha serving as its director, was established in 1954.
- The DAE functioned independently, shielded from intense public scrutiny.
-
Factors Driving India's Nuclear Weapons Development:
- Indian worries about its sovereignty and security threats from China and Pakistan led to the country's pursuit of nuclear weapons.
- India's need to protect its national security was heightened by the 1962 Sino-Indian War and China's nuclear test in 1964.
- The necessity for self-sufficiency in defence capabilities was further highlighted by the war with Pakistan in 1965, which had Chinese help.
-
Pokhran- I:
- India was able to perform a nuclear bomb test by the 1970s.
- At the Pokhran Test Range in Rajasthan on May 18, 1974, India conducted its first nuclear weapon test, known as Pokhran-I.
- It was officially labelled as a "peaceful nuclear explosion" with "few military implications" and given the code name “Smiling Buddha”.
- India joined the US, the Soviet Union, Britain, France, and China as the sixth nation in the world to be capable of acquiring nuclear weapons.
- The tests were met with almost global criticism and severe sanctions, particularly from the US and Canada.
- It hampered India's nuclear growth and made it more difficult for it to advance in nuclear technology.
- Progress was also hampered by domestic political unrest, such as the Emergency of 1975, and opposition to nuclear weapons.
- Due to Pakistan's prosperity, there was a revival of interest in nuclear weapon development in the 1980s.
- India increased funding for its missile programme and increased the amount of plutonium in its arsenal.
-
Pokhran-II:
- Pokhran-II refers to a series of five nuclear bomb test explosions carried out by India between May 11 and May 13, 1998, in the Pokhran desert of Rajasthan.
- This event, known by the code name “Operation Shakti”, was India's second successful attempt.
- Indian nuclear power status was solidified by Pokhran-II.
- It proved India's capacity to acquire and use nuclear weapons, hence boosting its deterrent capacities.
- Following Pokhran-II, the Atal Bihari Vajpayee-led Indian government formally acknowledged itself as a state with nuclear weapons.
- Although several nations (including the US) threatened sanctions in response to the tests in 1998, there was not the same level of criticism as in 1974.
- India was able to maintain its position and so solidify its standing as a powerful nation state in light of its rapidly expanding economy and market potential.
-
India's Nuclear Doctrine:
- India adopted a credible minimum deterrence policy, vowing to have a robust nuclear arsenal for deterrence but refrain from participating in an arms race.
- India formally released its nuclear doctrine in 2003, which expounded on the 'no first use' policy.
-
India's Current Nuclear Capability:
- Approximately 160 nuclear warheads are now in India's arsenal, according to the Federation of American Scientists (FAS).
- India has successfully developed a functional nuclear triad that enables nuclear weapon launch from land, air, and water.
- Agni, Prithvi, and K series ballistic missiles, fighter jets, and nuclear submarines are some of the triad delivery systems.
What is India's position on the various international nuclear weapons treaties?
-
Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) 1968: India is not a signatory; it rejected to join the NPT because it believed the pact to be discriminatory and there were no commitments for nuclear weapon nations to reciprocate.
-
Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT): India has not ratified the CTBT because it is a strong supporter of a time-bound disarmament commitment from nuclear weapon states (NWS) and may do so for the same reason.
-
The Treaty on the Prohibition of nuclear weapons (TPNW): It becomes effective on January 22, 2021, and India is not a member to this treaty.
-
Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG): India is not a member of the NSG.
-
Wassenaar Arrangement: India became the 42nd member of the agreement in December 2017.

Prelims
Q1. Consider the following countries: (2015)
1.China.
2.France
3.India
4.Israel
5.Pakistan
Which among the above are Nuclear Weapons States as recognized by the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of nuclear weapons, commonly known as Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT)?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q2. What is/are the consequence/consequences of a country becoming the member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’? (2018)
1. It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
2. It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)
Q. Give an account of the growth and development of nuclear science and technology in India. What is the advantage of fast breeder reactor programme in India? (2017)

PHARMACEUTICAL SECTOR IN INDIA

Latest Context
The pharmaceutical sector in India, which is recognised as the world's largest producer of generic medicines, has had severe difficulties with regard to the quality and safety of its products.
- Concerns regarding the regulatory system and the pharmaceutical industry's commitment to guaranteeing high-quality pharmaceutical products have been raised in light of recent occurrences involving contaminated medicines and substandard drugs.
What instances are highlighting poor quality control?
- Twelve children in Jammu died in January 2020 as a result of ingesting contaminated medicine that was later discovered to contain the kidney-damaging compound diethylene glycol.
- Lower quantities of the active chemicals were discovered in Nycup syrup in March 2021.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) issued a notice about a medicinal product in October 2022 that was allegedly responsible for 66 deaths in the small country of Gambia in West Africa and acute kidney injury in children.
- Diethylene glycol and ethylene glycol, both harmful to humans, were identified in unacceptable concentrations in four items manufactured by Maiden Pharmaceuticals, an Indian company.
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) opened an investigation in December 2022 into the deaths of 18 children in Uzbekistan that were allegedly caused by a cough syrup produced by the Indian company Marion Biotech.
- The Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) and the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have recently expressed worry over a drug-resistant bacterium strain that is purportedly connected to eye drops imported from India.
- 48 medicines failed to fulfil quality criteria, according to recent regulatory inspections.
- 3% of medications prescribed for widespread ailments including hypertension, allergies, and bacterial infections were determined to be subpar.
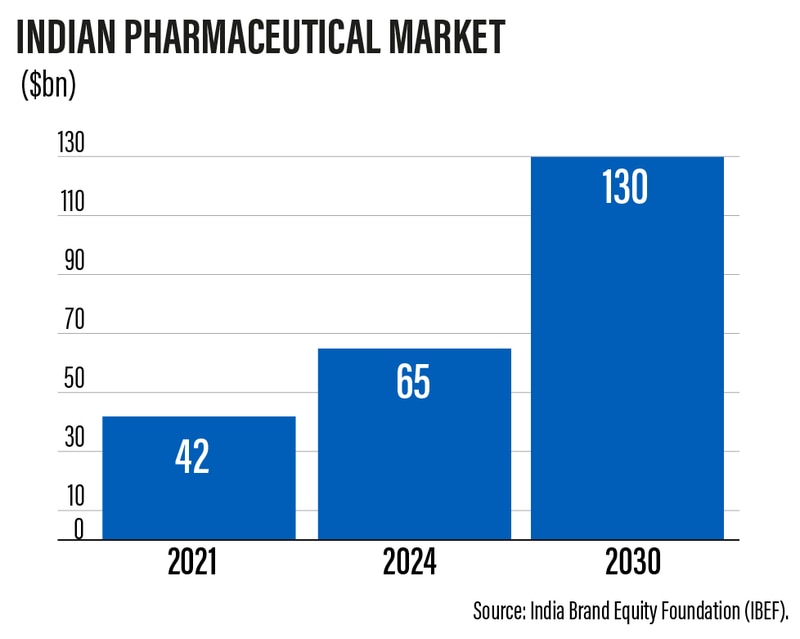
Facts about India's Pharmaceutical Industry
- India is the world's biggest producer of generic medicines. Its pharmaceutical sector contributes significantly to global healthcare by offering generic drugs at reasonable prices that have a positive effect on the lives of the world's poor.
- Being a significant exporter of pharmaceuticals to more than 200 nations, it is presently valued at USD 50 billion.
- It's expected to grow to USD 65 billion by 2024 and USD 130 billion by 2030.
-
Challenges with India’s Pharma industry:
-
Violation of IPR Rules: Legal issues with multinational pharmaceutical companies have resulted from charges that Indian pharmaceutical companies violated Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) laws.
- In one such case, Roche, a Swiss pharmaceutical company, and Cipla, an Indian pharmaceutical company, engaged in 2014.
- By creating a generic version of the cancer medication Tarceva, Cipla was accused by Roche of violating its patent. The argument intensified, resulting in a legal struggle between the two companies.
- The Delhi High Court found in Roche's favour in 2016 and confirmed that Cipla had in fact infringed Roche's patent rights. As a result, Cipla was mandated to compensate Roche.
-
Cost and Affordability: India is renowned for its capacity to produce generic drugs, which has helped to improve access to cheap healthcare throughout the world.
- Pharmaceutical costs in India, however, continue to be a major worry. It is a tough endeavour to strike a balance between the demand for inexpensive medications and pharmaceutical corporations' financial success.
-
Healthcare Infrastructure and Access: Despite the robust pharmaceutical sector in India, many people still struggle to have access to healthcare.
- Access to medications is hampered by problems such a weak healthcare infrastructure, an unequal distribution of medical facilities, and a lack of proper health insurance.
-
Government Initiatives:
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Pharmaceuticals.
- Promotion of Bulk Drug Parks Scheme.
- Strengthening Pharmaceuticals Industry Scheme.
Steps Can be Taken to Reform India's Pharmaceutical Sector
-
Legislative Changes and Centralised Database: It is necessary to update the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940, and the creation of a centralised drugs database can improve surveillance and guarantee efficient control for all manufacturers.
- The danger of regulatory capture and influence networks can be decreased by combining India's 36 regional drug regulators into a single entity.
- In order to maintain uniform product quality, it is also vital to set common quality standards throughout all states.
-
Promote Certification: The WHO's Good Manufacturing Practise accreditation can raise industry-wide quality standards if more pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities pursue it.
-
Transparency, Credibility, and Accountability: In order to improve India's drug regulation system and bring it into line with international norms, the regulator and the industry must work together. Accountability may be ensured by making inspection reports, evaluations of drug applications, and past violations public.
-
Emphasise the use of sustainable manufacturing techniques: green chemistry, waste reduction, and energy efficiency are just a few examples of sustainable manufacturing techniques that may improve industry environmental sustainability while cutting costs. Adopting environmentally friendly practises may also help a brand's reputation and draw in customers who care about the environment.

Mains:
Q. How is the Government of India protecting traditional knowledge of medicine from patenting by pharmaceutical companies? (2019)

INTERNATIONAL CREDIT CARD SPENDING OUTSIDE INDIA UNDER THE LIBERALISED REMITTANCE SCHEME (LRS)

Latest Context
International credit card spending outside of India is now covered under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) thanks to recent changes made to the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) by the Indian Finance Ministry in collaboration with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- This occurs against a backdrop of rising spending on international travel. Between April and February of fiscal 2022–23, Indians spent 12.51 billion USD on international travel, an increase of 104% over the same period the previous year.
- The inclusion permits the imposition of the higher Tax Collected at Source (TCS) rate, which was stated in the Budget for 2022–23 and would take effect on July 1, 2023.

Important Facts and Consequences
-
Inclusion of International Credit Card Spend in LRS: The amendment does not apply to payments for buying foreign products or services from India, but it is likely to make monitoring high-value international transactions easier.
-
Expansion of LRS and Omission of Rule 7: Previously, LRS did not provide coverage for using an international credit card for out-of-country travel costs.
- Rule 7 of the Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transaction) Rules from 2000 has been left out, which exempted these expenditures from LRS.
- This amendment permits the total LRS limit of 250,000 USD per person per financial year to be calculated using foreign credit card transactions.
-
Tax Repercussions:
- Until July 1st, 2023, a 5% TCS charge will be applied on these transactions (with the exception of those related to the medical and educational sectors).
- The TCS rate will rise to 20% for credit card purchases made outside of India starting on July 1st, 2023.
- The new rules have no bearing on payments made for "educational" and "medical" expenses, nor do they alter how citizens of other countries use their international credit cards while they are in India.
- Banks and other financial institutions are faced with compliance issues since the system for levying TCS on purchases made using international credit cards has not yet been made operational.
-
Impact on Compliance and Refunds: These changes may result in a greater compliance burden for banks and other financial organisations.
- Taxpayers may request refunds on the TCS levy when filing tax returns, but doing so may cause cash to be held up until the tax agency starts processing refunds.
Facts about Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS)
- This is the Reserve Bank of India's programme, which was launched in 2004.
- All residents, including children, are permitted under the programme to freely remit up to USD 2,50,000 every fiscal year (April through March) for any permitted current account transaction, capital account transaction, or combination of both.
-
Not Eligible: Corporations, partnership businesses, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF), Trusts, etc. are not eligible for the Scheme.
- Although there are no limitations on the frequency of remittances under LRS, a resident individual would not be entitled to make any future remittances under this scheme after a transfer for an amount up to USD 2,50,000 during the financial year is made.
-
Utilisation of remitted funds:
- Costs associated with travel (personal or professional), medical care, education, presents and contributions, upkeep of close family, etc.
- Investment in shares, debt instruments, and the purchase of real estate abroad.
- Additionally, individuals may create, manage, and hold foreign currency accounts with banks outside of India in order to conduct the authorised transactions under the system.
-
Prohibited Transactions:
- Any activity expressly forbidden by Schedule-I of the Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000 (such as the purchase of lottery tickets, restricted periodicals, etc.), or any item limited by Schedule II.
- Trading in foreign currency overseas.
- Direct or indirect capital account transfers to nations that the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has deemed "non-cooperative countries and territories" on occasion.
- Remittances sent directly or indirectly to people or organisations that have been warned separately by the Reserve Bank to the banks that they pose a serious danger of conducting terrorist activities.
- Requirements: For all LRS transactions carried out by Authorised Persons, it is mandatory for the resident individual to supply his or her Permanent Account Number (PAN).
What is Tax Collected at Source?
- TCS is the tax that the seller must pay and that he must collect from the customer when certain products or services are sold.
- TCS is administered by Section 206C of the Income-tax Act, which details the products and services that are subject to TCS as well as its rates.
- Liquor, lumber, tendu leaves, scrap metal, minerals, automobiles, parking lots, toll booths, mining and quarrying, overseas remittance under LRS, and other products or services are some of those to which TCS is applicable.
- To collect and submit TCS to the tax authorities, the seller needs a Tax Collection Account Number (TAN).
- Within a predetermined timeframe, the seller must provide the buyer with a TCS certificate detailing the amount of tax collected and deposited.
- When completing his income tax return, the buyer may seek a credit for the TCS amount that was subtracted from his income.


SELF-HELP GROUP KUDUMBASHREE

Latest Context
Recently, during her visit to Kerala, the President of India inaugurated the silver jubilee celebrations of Kudumbashree which is the largest self-help group network in India presently. On this occasion, the President also released a book titled Chuvadu (Footsteps). This book codifies the ideas for the movement’s future and its achievement acquired so far.
Kudumbashree
-
Background: It was established in Kerala in 1997 with the objective of poverty alleviation and women empowerment on the recommendations of a government-appointed task force. It was launched with the support of the Government of India and NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development).
-
Meaning: The meaning of Kudumbashree is 'prosperity of the family' in the Malayalam language. It also encourages democratic leadership in addition to providing support structures within the "Kudumbashree family."

Objective
Its motto is to eliminate absolute poverty within a pre-determined time frame of ten years, through active participation of local self-governments. As per its mission, the main objective of this group is to uplift families and women empowerment to improve their socio-economic status and overall well-being.
Operation: There are three-tier structures through which it functions
- Neighborhood Groups (NHGs) at the primary level
- Area Development Societies (ADS) at the ward level
- Community Development Societies (CDS) at the local government level.
Due to its structure, it consists of the largest networks in India.
Significance
- It has become Kerala's biggest social capital, and its members have become elected representatives in local government bodies.
- It has played a very significant role in women’s empowerment by generating employment and eradicating poverty.
- During a severe flood that occurred in Kerala five years ago, Kudumbashree, the self-help group network, donated Rs 7 crore to the Chief Minister's distress relief fund.
- Tech giants like Google and Apple and the organizations which provide social services like the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation are not able to contribute so much in comparison with SHGs regarding money generation.
- Many of the Kudumbashree workers themselves were victims of the flood, but they still wanted to help others by contributing to the relief fund.
Self-Help Group
-
Concept: These are informal groups of people who come together in order to find ways to improve their living standards. It is a self-controlled group of people having similar socio-economic backgrounds who collectively perform a common purpose. It lays emphasis on the notion of “Self Help” in order to perform self-employment and poverty alleviation.

Objectives
- To resolve conflicts by way of collective leadership and mutual discussion.
- To offer collateral-free loans with terms determined by the group at market-driven rates.
- To build the working capacity of the poor and the marginalized in employment and income-generating activities.
- To work as a collective guarantee system for members who want to borrow from organized sources. The poor collect their savings and save it in banks. In return they receive easy access to loans with a small rate of interest to start their micro unit enterprise.
Role of SHGs in Women’s Empowerment and Fighting Poverty
-
Overcoming Social Barriers: These groups play a vital role in challenging negative social norms and empowering women to take decisions independently. By participating in SHGs, women become self-confident, assertive, and develop the leadership skills necessary for challenging gender stereotypes. By involving in these groups, women participate in local governance (e.g., gram sabha) and even contest elections.
-
Socio-economic Status: These groups play a very critical role in improving women's status in society and within their families. In addition, these groups provide better access to education, healthcare, and resources which, in a cumulative sense, improve the socio-economic status of the women. These groups significantly improve the self-esteem and confidence of the women by offering them a platform to voice their opinions and contribute to decision-making processes.
-
Economic Empowerment: In rural areas, they provide women with an occasion to generate independent sources of income. By utilizing their skills and talents, women can start their own businesses and become financially self-reliant. SHGs enable women in providing access to the capital necessary to invest in their ventures and expand their economic activities.
-
Access to Financial Services: These groups are linked with many financial institutes like NABARD. It facilitates easier access to credit for SHGs. Priority Sector Lending norms and definite returns provide incentives to banks to lend to SHGs. Easy access to credit empowers women not to depend upon the traditional moneylenders and non-institutional sources. It led to fairer and more affordable financial services.
-
Alternative Employment Opportunities: The biggest advantage of SHGs is that it provides help in setting micro-enterprises that provide numerous alternatives to agriculture-based livelihoods. By taking the help from SHGs, women can establish personalized businesses such as tailoring, grocery shops, and repair services, diversifying their income sources.
Other Initiatives of Women Empowerment and Poverty Alleviation
- Ujjawala Yojna
- Swadhar Greh
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana
- Pradhan Mantri Mahila Shakti Kendra Scheme
- Mahila e-haat
- Mahila Bank
- Mahila Coir Yojana
- Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP)
- Support to Training and Employment Programme for Women (STEP) Scheme
![]()
Q. Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (2021)

ECL-BASED LOAN LOSS PROVISIONING FRAMEWORK

Latest Context
Lenders have demanded a one-year extension from the Reserve Bank of India for the implementation of the Expected Credit Loss-based (ECL) loan loss provisioning framework. Earlier in the beginning of this year, RBI proposed draft guidelines for the adoption of expected credit loss for credit impairment. According to RBI, one year term will be given to Banks for the implementation of the ECL approach after finalising the guidelines.
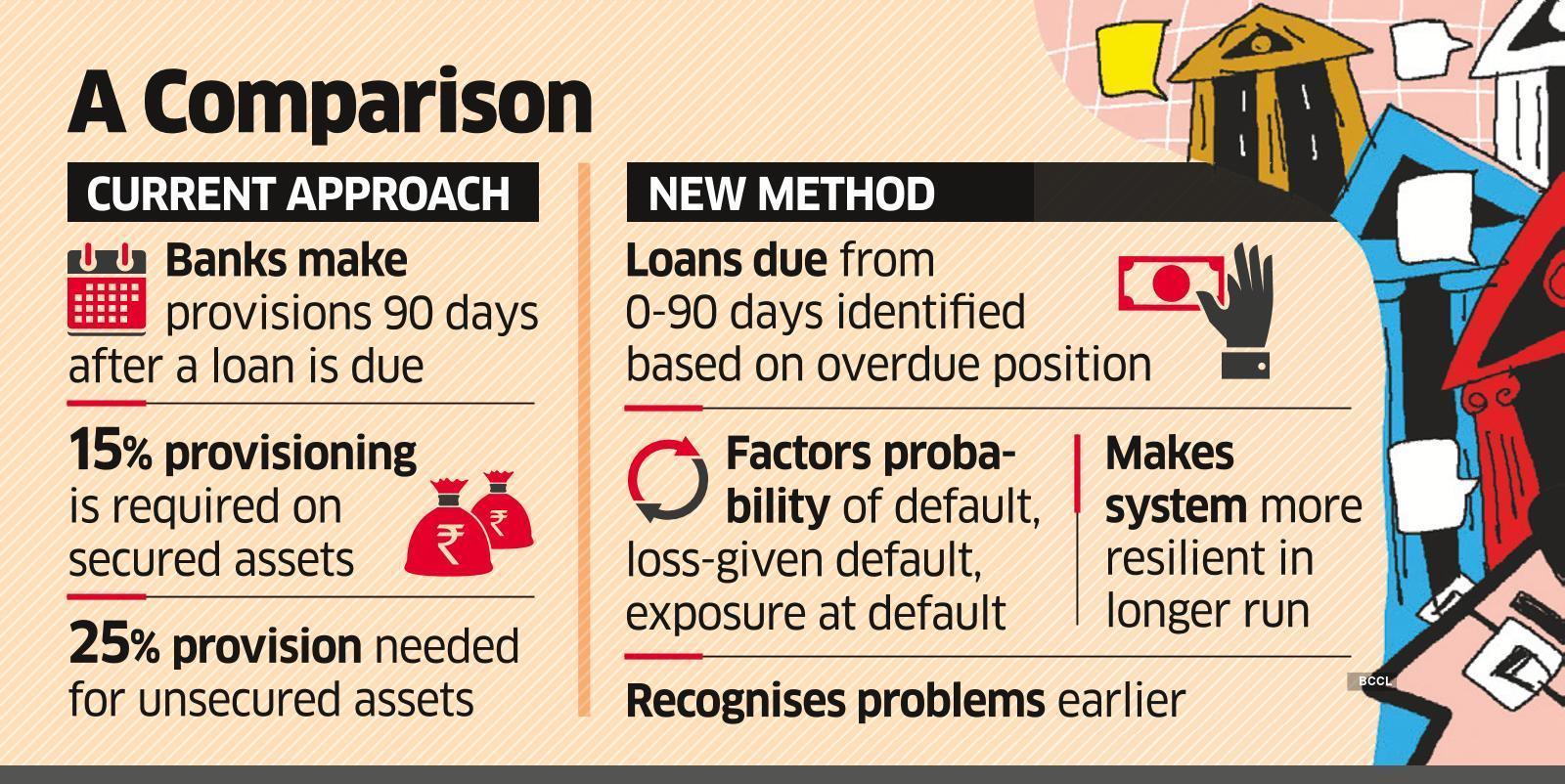
ECL-based Loan Loss Provisioning Framework
-
Background
- The Central Bank has recently released a proposal to adopt the ECL approach used in International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS9). It released a discussion paper titled “Expected Credit Loss” model for loan provisioning by commercial banks in India.
- Currently, Banks are making provisions for the assets which are identified as non-performing as per the regulator which is too little. Hence, there is scope for improvement. Therefore, RBI’s objective is to formulate principle-based guidelines supplemented by regulatory backstops to fulfil the gap. It would be based on the current internal risk estimate of potential future credit loss.
-
ECL Framework: It is the bank’s internal estimate of the anticipated future loss on the credit supplied by it due to its exposure to the default expected to take place during the normal course of business. It is an integral component of credit risk estimation. Under the new accounting standard, three stages namely Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3 have been specified to determine the amount of impairment to be recognised as ECL at each reporting date.
Expected Credit Loss Model Versus Incurred Loss Model
|
Incurred Loss Model |
Expected Cross Model |
|
It requires an entity to recognise an impairment loss if a “credit loss has been incurred”. It assumes that all loans are repaid until evidence that is contrary is identified. |
Under this model, banks are required to recognize the ECLs at all times taking into account past events, current conditions, and forecast information and to update the amount of ECLs recognised at each reporting date to reflect the change in an asset’s credit risk. |
|
The main drawback of this model is that it ignores the expected losses which are implicit in the initial measurement of a loan asset but the subsequent reporting ignores changes in expected losses “until a loss is incurred”. |
Contrary to IL Model, it will ensure timely recognition of ECLs. It classifies assets into three categories namely, Stage 1, Stage 2, Stage 3. |
Transitional Agreement
In order to avoid a capital shock, the Central Bank proposed a transitional agreement for the introduction of ECL norms. Step-to-step implementation will support the banks to absorb any additional provisions without getting affected by the introduction of these provisions that could adversely impact their profitability.
Loan Loss Provisioning
- As per RBI, a loan loss provision is an expense that banks keep aside for defaulted loans. In other words, it is a cash reserve that banks keep separately to cover the losses incurred from defaulted loans.
- According to RBI, Non-performing Assets are the ones that are overdue for more than 90 days. It will help banks to assess the exact value of their loan portfolio and assess their overall risk exposure.
Indian Bank Association
It is a voluntary association of banks in India that was formed on 26th September 1946 with the aim of promoting and coordinating the interests of the Indian banking industry. Its members are as follows:
- Public Sector Banks.
- Private Sector Banks.
- Foreign Banks having offices in India.
- Co-operative Banks.
- Regional Rural Banks.
- All India Financial Institution.

SUPREME COURT UPHOLDS LAWS ALLOWING JALLIKATTU

Latest Context
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) upheld the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (Tamil Nadu Amendment) Act of 2017, and Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Rules, 2017 and allowed the traditional bull-taming sport Jallikattu which is also known as "Eruthazhuvuthal". It is played in Tamil Nadu as a part of the Pongal festival.
Supreme Court Judgement
-
Latest Judgement: In its judgement, The Top Court stated that the state amendments (Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (Tamil Nadu Amendment) Act of 2017 and Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Rules of 2017) did not infringe the Constitution and the 2014 ruling of Supreme Court regarding the banning Jallikattu.
- The court said the Amendment Act “substantially reduced pain and cruelty” to the participating animals. The judgment holds that the 2017 Amendment Act and Rules on Jallikattu are in line with Entry 17 (prevention of cruelty to animals) of the Concurrent List, Article 51A(g) (compassion to loving creatures) of the Constitution.
-
The Ruling of 2014: In the Animal Welfare Board of India vs A. Nagaraja case, the Supreme Court banned Jallikattu through a judgment in May 2014 on the basis of cruelty to animals. It states that Act was also not “relatable” to Article 48 of the Constitution stating the duty of a State to “organise agriculture and animal husbandry”. It ruled that any violation of the law in the name of cultural tradition would be punishable. According to the Supreme Court to decide the Jallikattu's cultural heritage status is the right of the State's legislative assembly and not a court of law.

Jallikattu
-
Introduction: It is a very popular sport played on the harvest of the Pongal festival in Tamil Nadu. In this sport, a wild bull is released into a crowd of people, and the participants try to grab the bull's hump and ride it as maximum as possible time and try to bring him under control.
-
Note: A traditional buffalo race known as Kambala takes place in coastal Karnataka (Udupi and Dakshina Kannada) from November to March in paddy fields filled with slush and mud.
Arguments in Favour of Practice
- It is both a religious and cultural event in Tamil Nadu, celebrated by people irrespective of their caste or creed.
- Due to its cultural significance, the State government argues that it should be regulated and reformed instead of completely banning this centuries-old practice.
- It will be considered as an attack on the culture and sentiments of the community if Jallikattu gets banned.
- As per the government, Jallikattu plays an important role in conserving a valuable indigenous breed of livestock. Hence, it should not be termed inhumane and cruel against living creatures.
- State Government was of the view that it should be taught in high school curricula to ensure its preservation for future generations.
Arguments in Opposition
- According to the Constitution of India, all living beings comprising even animals, possess inherent liberty.
- It resulted in many deaths and high injuries to both humans and bulls in various districts of the State.
- More often than not, tamers often act aggressively towards the bulls, causing them extreme cruelty.
- Critics compared it with the practices like sati and dowry. Though, they were part of culture but were abolished by legislation.
Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960
- This Act is meant to “prevent the infliction of unnecessary pain or suffering on animals”.
- Under Section 4 of the Act the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) was established in 1962
- It provides punishment for committing unnecessary cruelty and suffering against animals. The Act defines animals and their different forms.
- It points out the different forms of cruelty, exceptions, and killing of a suffering animal in case of any cruelty has been committed against it to relieve it from further suffering.
- It also defines the guidelines relating to experimentation on animals for scientific purposes.
- It includes the provisions relating to the exhibition of the performing animals, and offences committed against the performing animals.
- It also provides for a limitation period of three months beyond which no prosecution shall lie for any offences under this Act.
![]()
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2014)
1. Animal Welfare Board of India is established under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
2. National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body.
3. National Ganga River Basin Authority is chaired by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the challenges to our cultural practices in the name of Secularism? (2019)


Greater Flamingo
- Recently, a Greater Flamingo which is known as the state bird of Gujarat was rescued from the Najafgarh Wetland that shares a border with Haryana.
- These birds are found in South and Southwest Asia, the Middle East region comprising the countries like Iran, Turkey, Dubai, and Oman. They are found especially in shallow waters of lagoons, lakes, estuaries, and muddy beaches.
- There are six species of Flamingos in the world. Out of which two are found in India. These are – The Greater Flamingo and The Lesser Flamingo. These birds are tall and black-tipped with light pinkish beaks, yellowish eyes, and pink-whitish body colour. They are classified as “Least Concern” in the ICUN Red List of Threatened Species.
Production-Linked Incentive Scheme
-
Recently, the Government of India is providing a modified Production-linked Scheme (PLI) for electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced chemistry cell batteries for attracting the investors like Tesla. A similar approach will also be applicable to other sectors like telecom products and IT Hardware.
- PLI is an integral component of Self-Reliant India. The objective of PLI is to boost the domestic manufacturing sector to create global champions in strategic sectors. Another objective of PLI is to encourage foreign companies to set up their units in India.
- Under this scheme, companies receive incentives on incremental sales from the products manufactured in India compared to a base year. On the basis of their potential for generating revenue and employment, fourteen sectors like telecom, solar PV modules, and textile products have been selected and 1.97 lakh crore have been allocated under the Union Budget 2021-22.
- Its objective is to transform India into a Global hub and to promote self-reliance.
Connection between COVID-19 and Climate
Though the World Metrological Organisation (WMO) suggested that there is cooler and drier weather may facilitate the transmission of COVID-19 but there are many evidences that contradict this conclusion. The final Report suggested that there is a
- Negative relationship between temperature and COVID-19 transmission which indicates that lower the temperature higher the COVID-19 transmission.
- In the same way, humidity is also connected to COVID-19 transmission. Drier condition facilitates the spread of COVID-19.
WMO is an international body comprising 192 members countries and territories. It originated from International Meteorological Organisation (IMO) which was established after the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress. It is headquartered at Geneva.
Baobab Tree
-
Recently, MP High Court ordered the State Government to stop cutting off the Baobab tree for any purposes whatsoever it may be. This decision is based on the protest of the tribal communities. Dhar district consists of approximately 1000 Baobab trees which are century old and have historical value.
- These trees have come under the Biological Diversity Act 2002. These trees are native to Africa and are popularly known as “World Tree” in Africa. These trees have high longevity and provide food, livestock fodder, and raw materials.
Heat Waves
-
Currently, Heat Waves are impacting areas like east and north India, Bangladesh, Laos, Thailand. According to Indian Meteorological Organisation (IMO). When the temperature of any station crossed 40oC then it will be called the Heat Wave condition.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi


