- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
China’s Military Expansion Near Pangong Lake
China’s Military Expansion Near Pangong Lake
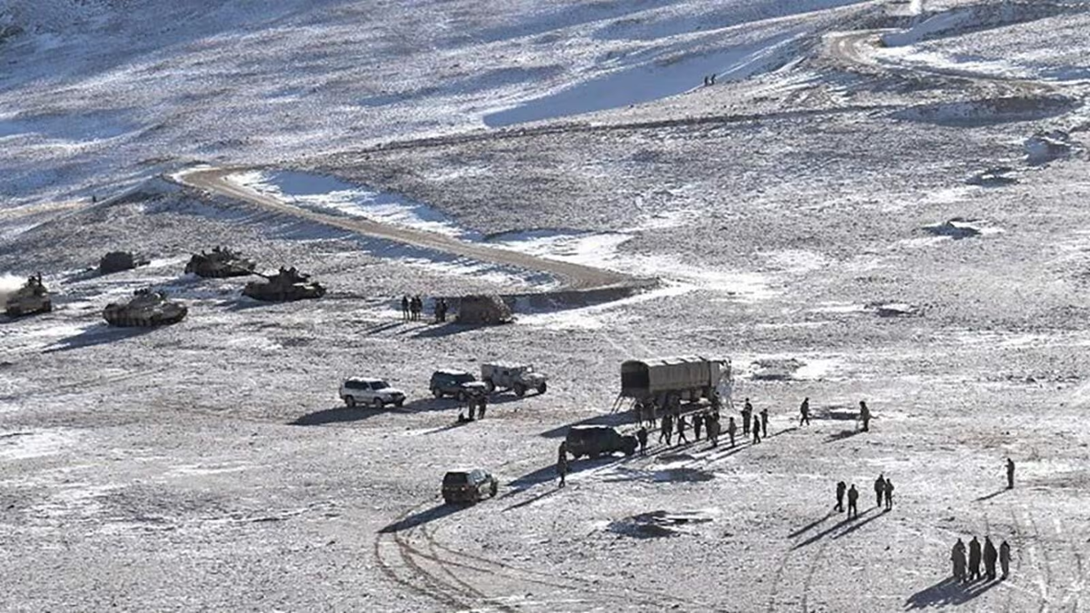

Recent satellite imagery has disclosed a notable military escalation by China near Pangong Lake in eastern Ladakh, close to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with India. This has sparked concerns regarding China’s motives and the implications for India’s national security.
Key Developments
-
Subterranean Bunkers and Hardened Shelters:
- China has constructed underground bunkers for weapon and fuel storage, as well as fortified shelters for armored vehicles at a significant regional base. These bunkers are designed to withstand air strikes and are equipped with precision-guided weapons.
-
PLA Post at Sirjap:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) post at Sirjap, on the northern bank of Pangong Lake, serves as the headquarters for Chinese forces around the lake. This post, located about 5 km from the LAC, is in an area claimed by India.
-
Increased Military Activity:
- Satellite images indicate heightened Chinese military activity at the Shigatse air base, a dual-use high-altitude airport in Tibet’s second-largest city, and at the disputed Doklam tri-junction.
-
Deployment of Stealth Fighter Jets:
- China has stationed its advanced stealth fighter, the Chengdu J-20, at the Shigatse air base. This is seen as a strategic shift aimed at countering the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Rafale jets.
-
Infrastructure Development:
- India has been enhancing its border infrastructure, including roads, bridges, tunnels, airfields, and helipads, to improve military mobility and logistics.
-
Border Roads Organisation (BRO) Projects:
- The BRO has completed 125 infrastructure projects worth ₹3,611 crore, such as the Sela tunnel in Arunachal Pradesh, to boost connectivity and facilitate military movement.
Pangong Lake
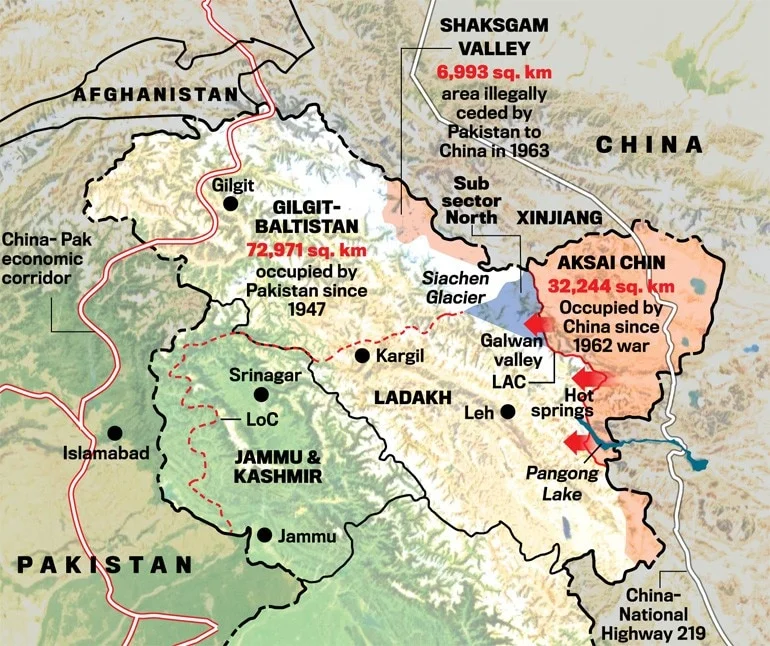
Introduction:
- Pangong Lake, also known as Pangong Tso, is an endorheic lake in the Himalayas, situated at an altitude of about 4,350 meters (14,270 feet).
- The name derives from the Tibetan “Pangong Tso,” meaning “high grassland lake.”
Location and Geography:
- The lake is approximately 140 km from Leh in Jammu and Kashmir.
- It spans 134 km (83 miles) in length, extending from India to China, with about 60% of its length in China.
- At its widest, the lake is 5 km (3.1 miles) and covers an area of 604 sq. km.
Unique Features:
- It is one of the world’s highest brackish water lakes, known for its color-changing water, shifting from blue to red and green.
- Despite being saline, the lake freezes completely in winter.
Significance:
- Pangong Lake is not part of the Indus River basin and is geographically a separate land-locked river basin.
- The lake lies in disputed territory, with the LAC passing through it.
Dispute and Line of Actual Control (LAC)
- The LAC demarcates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory.
- It is divided into three sectors: the eastern sector (Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim), the middle sector (Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh), and the western sector (Ladakh).
- India claims the LAC to be 3,488 km long, while China asserts it is around 2,000 km.
Implications
- Escalation of Tensions:
- China’s military build-up near Pangong Lake has heightened concerns about escalating tensions between India and China.
- National Security:
- This development impacts India’s national security, especially amid the ongoing border dispute.
- Regional Balance of Power:
- China’s deployment of stealth fighters represents a significant shift in regional power dynamics, with potential far-reaching consequences for India’s security.
- Diplomatic Efforts:
- The situation underscores the need for diplomatic measures to resolve the border dispute and mitigate regional tensions.
- Military Modernization:
- It highlights the necessity for India to modernize its military and enhance its capabilities to counter China’s growing military prowess.
Analysis
- China’s Intentions:
- The military build-up suggests China is preparing for a prolonged presence in the region, which is concerning for India.
- India’s Response:
- India’s infrastructure development around its borders is a reaction to China’s military actions, though its sufficiency remains uncertain.
- Regional Implications:
- This development affects the regional balance of power and could further escalate tensions.
- International Community:
- China’s military assertiveness in the region may also have broader implications for the international community.
Conclusion
China’s military expansion near Pangong Lake poses a significant concern for India’s national security. The situation highlights the urgent need for diplomatic efforts to resolve the border dispute and ease regional tensions. While India’s infrastructure development is a strategic response, it remains to be seen if it will be enough to counter China’s military strength. This development underscores the importance of India modernizing its military capabilities.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi