- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Chile’s Atacama Salt Flat Sinking Due To Lithium Mining
Chile’s Atacama Salt Flat Sinking Due To Lithium Mining
03-09-2024
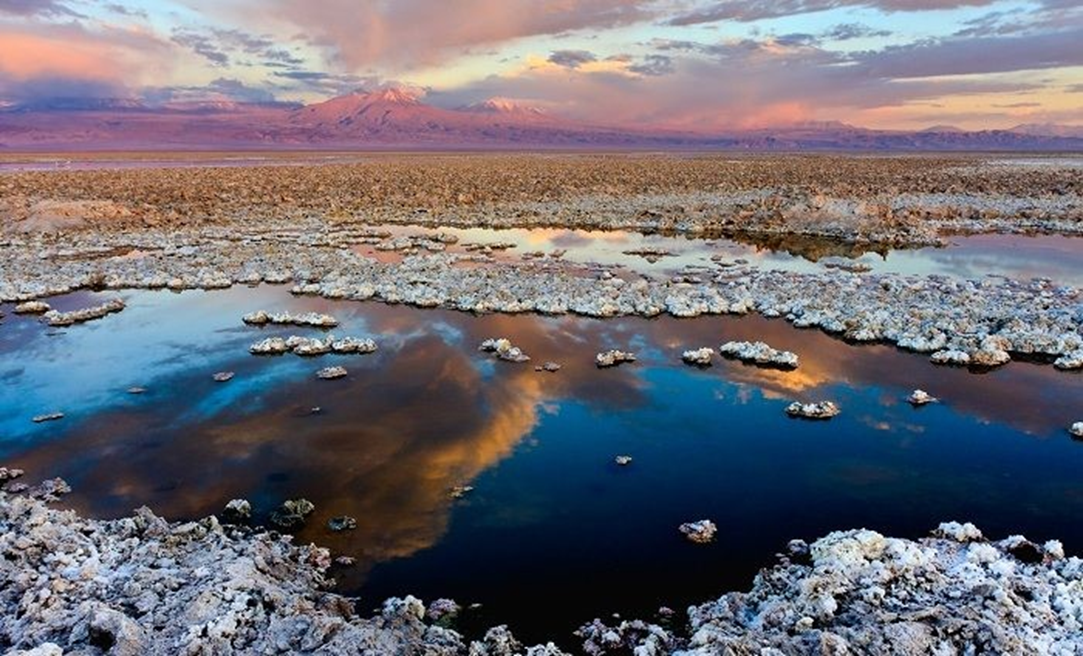

Study in Chile: A new study reveals land subsidence in Chile's Atacama salt flat due to lithium mining, with the land sinking at 1 to 2 centimeters per year.
Key Issues and Environmental Impact
- Land Subsidence:
- Cause: Lithium brine extraction, which involves pumping brine to the surface and evaporating it to obtain lithium, is depleting underground aquifers faster than they can naturally recharge. This process causes the ground to sink.
- Water Usage:
- High Consumption: Producing one ton of lithium requires about 2,000 tons of water, exacerbating water scarcity in the Atacama Desert, which is already an arid region.
- Chemical Contamination:
- Pollution: The use of chemicals like sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide in lithium extraction contaminates soil and water. This pollution harms local ecosystems and wildlife.
- Impact on Wildlife:
- Flamingo Decline: Reduced water levels in the Atacama have led to a decline in flamingo populations, affecting their breeding and survival.
- Potential Effects in Reasi (J&K):
- Water Crisis: Water-intensive lithium mining could worsen existing water scarcity issues in Reasi, where villages are already struggling due to dried-up streams.
- Biodiversity Threat: Mining could damage habitats in the biodiversity-rich Himalayan region, affecting species such as migratory birds and causing food insecurity.
- Pollution Risks: Mining could pollute water sources in the Himalayas, impacting the riparian ecosystems that are crucial for local rivers.
Key Facts about Lithium
- Properties:
- Description: Lithium is a soft, silvery metal with the lowest density among metals. It is highly reactive and has excellent electrochemical properties.
- Ores: Major ores include Petalite, Lepidolite, and Spodumene. Often referred to as "white gold."
- Applications:
- Batteries: Primarily used in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras, and electric vehicles.
- Other Uses: Includes applications in non-rechargeable batteries, magnesium-lithium alloys for armor plating, air conditioning systems, and lubricants.
- Global Reserves:
- Chile: Holds the largest reserves of lithium (36% of global reserves) and is the second-largest producer (32% of global supply). Chile is part of the "lithium triangle" with Argentina and Bolivia.
- Other Producers: Australia and China are the largest and third-largest global producers, respectively.
About the Atacama Desert
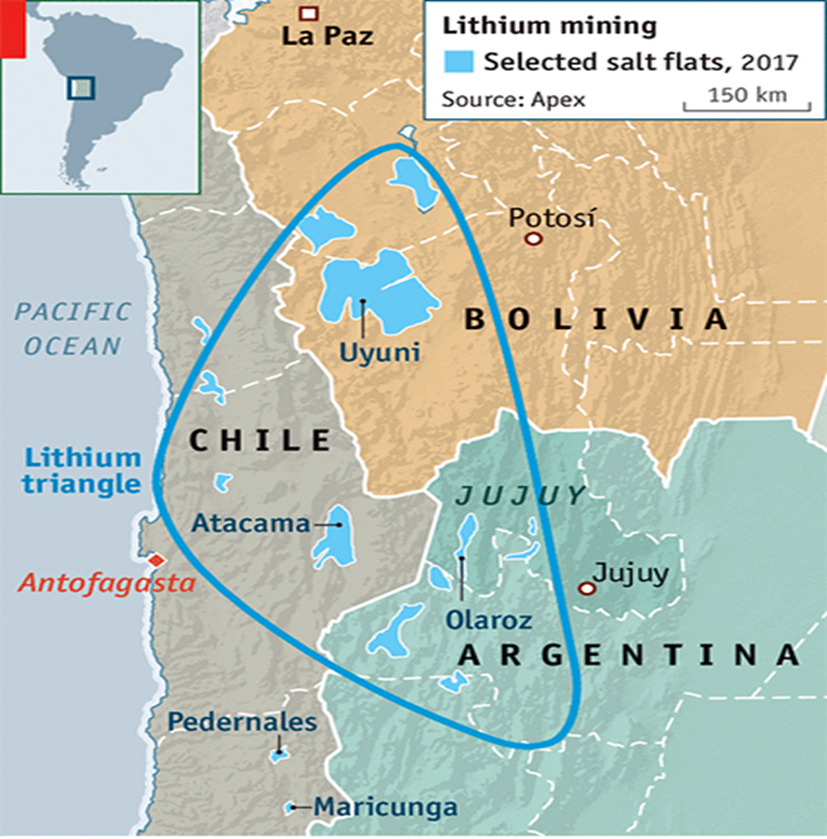
- Location: Situated in northern Chile between the Andes Mountains and the Cordillera de la Costa.
- Climate: Extremely arid, shielded from rain by the Andes and influenced by cold ocean currents that inhibit cloud formation.
- Temperature: Mild average temperature of around 18°C due to the temperate climate.
- Mineral Resources:
- Salt Deposits: Rich in thick salt deposits.
- Other Minerals: Contains significant amounts of lithium, copper, and iodine.
- Protected Areas: Includes Pan de Azúcar National Park, one of the few large protected areas in the desert.
The adverse effects of lithium mining, particularly in sensitive environments like the Atacama Desert, underscore the need for more sustainable practices to balance resource extraction with environmental preservation.




