- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Caenorhabditis elegans
Caenorhabditis elegans
24-10-2024
- In Oct 2024, Molecular biologist Gary Ruvkun praised the tiny worm Caenorhabditis elegans while accepting the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2024.
- This small worm has played a key role in improving our understanding of biology and human health.
About Caenorhabditis elegans:
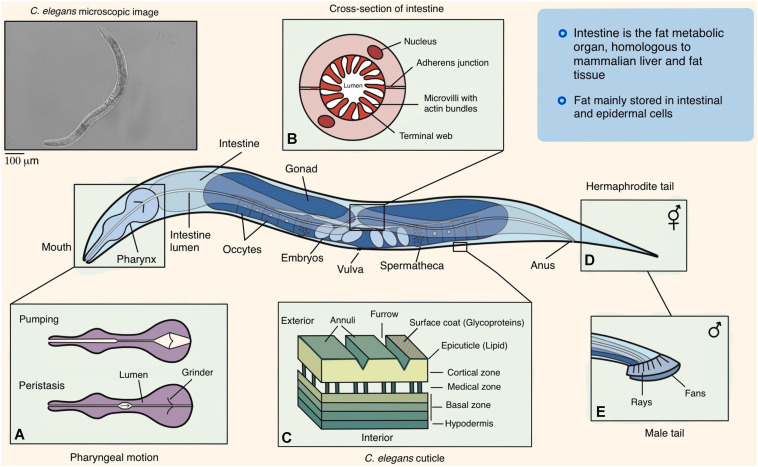
- Type: C. elegans is a nematode worm, part of the phylum Nematoda.
- Life Cycle:
- It grows from a fertilized egg to a one-millimeter-long adult in just 3-5 days.
- C. elegans has two sexes: a hermaphrodite that can reproduce with itself and a male.
- Its body mainly consists of a tube structure that includes an outer layer (cuticle), mouth (pharynx), gut, and reproductive system.
- It ages over time, gradually losing strength and eventually dying.
- Studying these processes helps scientists learn about genetics and behavior.
- Research Importance:
- C. elegans was the first multicellular organism to have its entire genome sequenced (the complete set of its genes) and its nerve connections mapped.
- It is widely used to study nerve functions and cell biology, leading to important discoveries about health and disease.
What are Nematodes?
- Nematodes are worms that belong to the phylum Nematoda, known for their variety and many habitats.
- Habitat:
- Nematodes are among the most common animals on Earth, found in many places, including soil, fresh water, and oceans, as well as extreme environments (like deep cracks in the Earth).
- They can live freely or be parasites that affect plants and animals.
- These worms have smooth skin, are not divided into segments, and have a long, tube-like shape that narrows at both ends.
- They can live freely in nature or as parasites and can be found in water and on land.
What is Molecular Biology?
- Molecular biology is the study of the tiny parts of cells, such as DNA and proteins, that are crucial for how cells work and stay alive.
- Relevance: Understanding how these parts interact helps scientists learn about diseases, genetic functions, and how cells behave, which is important for medical research and developing new treatments.
Conclusion
The recognition of Caenorhabditis elegans in scientific research highlights its important role in studying cell biology and genetics. Its simple structure and fast life cycle make it an ideal model organism, contributing to significant advancements in our understanding of complex biological systems.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus



