- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Atal Bhujal Yojana & Ground Water Management
Atal Bhujal Yojana & Ground Water Management
28-10-2023
Context
- On 28 October, 2023 fifth meeting of the National Level Steering Committee (NLSC) of Atal Bhujal Yojana and the Wrap up of the World Bank held in New Delhi.
- The meeting was chaired by Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR), Ministry of Jal Shakti.
Atal Bhujal Yojna

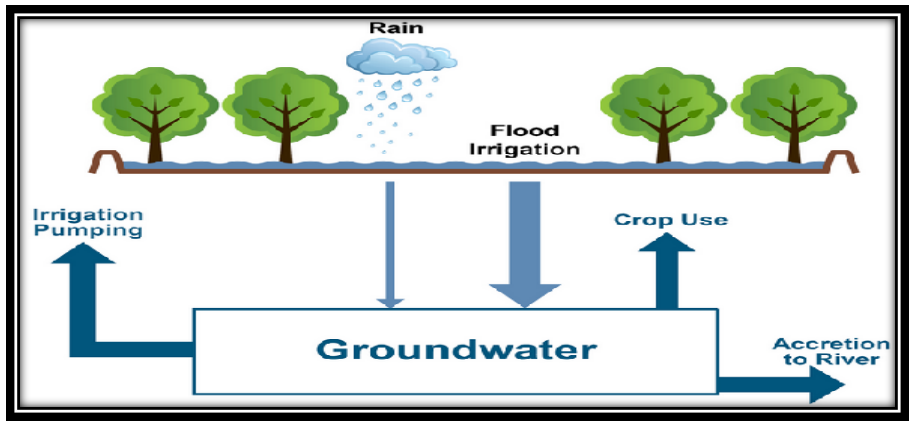
Status of Groundwater Depletion in India
- Groundwater Depletion in India is a major concern because it is the primary source of drinking water.
- Some of the main causes of groundwater depletion in India include over-extraction of groundwater for irrigation, Urbanisation, and Climate Change.
- India is the world’s largest user of groundwater, exceeding the use of the United States and China combined according to recent UN report.
- India is the world’s largest user of groundwater, exceeding the use of the United States and China combined according to recent UN report.
- According to the Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) of India, approximately 70% of the total water used in India is from groundwater sources.
- However, the CGWB also estimates that around 25% of the country's total groundwater extraction is unsustainable, meaning that it is being extracted at a faster rate than it can be replenished.
- Overall, groundwater depletion in India is a serious problem that needs to be addressed through sustainable water management practices, such as improved irrigation techniques and conservation efforts.
Major Causes of Groundwater Depletion in India
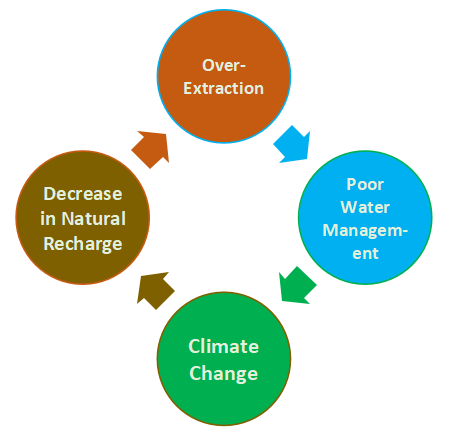
- About 80% of the total water use in India is used for irrigation, and most of this water is sourced from groundwater.
- As the demand for food increases, more and more groundwater is being extracted for irrigation, leading to shortages.
- According to the UN's Interconnected Disaster Risk Report 2023, 78% of wells in Punjab are considered overexploited, and the entire northwestern region is projected to experience critically low groundwater availability by 2025.
- Inefficient use of water, leaky pipes, and inadequate infrastructure for capturing and storing rainwater can all contribute to groundwater depletion.
- Rising temperatures and Changing Precipitation Patterns can alter the recharge rates of Groundwater Aquifers, making them more vulnerable to depletion.
- Droughts, flash floods, and Disrupted Monsoon Events are recent examples of climate change events that are placing pressure on India's groundwater resources.
- The natural recharge of groundwater aquifers can be decreased by factors such as Deforestation, which can lead to Soil Erosion and reduce the amount of water that is able to seep into the ground and replenish the aquifers.
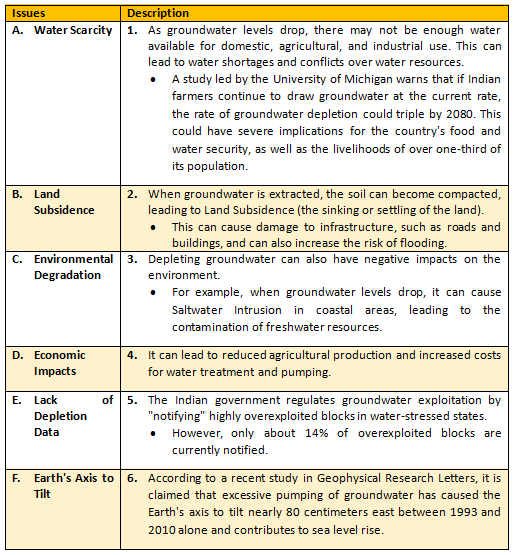
Issues Associated with Depleting Ground Water
Initiatives Related to Groundwater Conservation
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan- Catch the Rain Campaign
- Aquifer Mapping and Management Programme
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
Way Forward
- MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES: Embrace comprehensive and sustainable water management strategies that address both immediate needs and long-term challenges.
- ENGAGEMENT: Foster meaningful engagement with local communities, incorporating their perspectives and knowledge in water management decisions.
- INVESTMENTS: Prioritize investments in water infrastructure and capacity-building programs to build resilience against future water crises.
- ASSESSMENT: Establish robust monitoring and evaluation frameworks to assess the effectiveness and impact of water management initiatives.