- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 20th June 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 20th June 2025
20-06-2025

1. Armenia
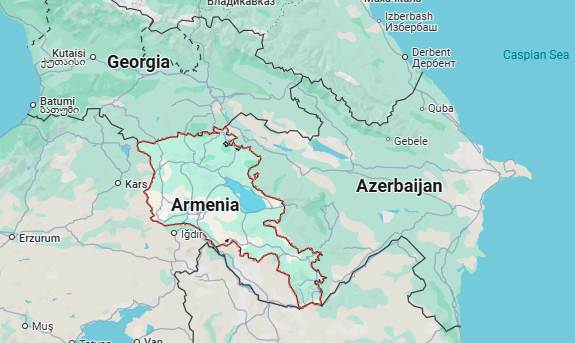
Why in the News?
- India’s Ministry of External Affairs carried out Operation Sindu to bring back Indian students and citizens from Tehran.
- They were safely evacuated through Armenia.
- This was done because of increasing tensions between Israel and Iran.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Location & Borders
- Continent: Asia (Transcaucasia / South Caucasus)
- Coordinates: 40° N latitude and 45° E longitude
- Landlocked Country
- Borders:
- North: Georgia
- East: Azerbaijan
- South: Iran
- West: Turkey
- Area & Size
- Total Area: 29,743 sq. km (slightly smaller than Belgium)
- Strategic Location: Between Europe and Asia, part of the historical Silk Road
- Topography
- Highly mountainous: over 90% of Armenia lies above 1,000 meters
- Dominated by the Lesser Caucasus Mountains
- Key features:
- Mount Aragats: Highest point (4,090 meters)
- Ararat Valley: Most fertile and densely populated region
- Lake Sevan: One of the largest freshwater, high-altitude lakes in the world (Approximate 1,900 m above sea level)
- Climate
- Continental climate: Hot summers, cold winters
- Influenced by elevation and topography
- Low precipitation: Especially in plains and valleys
- Snowfall common in winter, especially in highlands
- Rivers & Lakes
- Key rivers:
- Hrazdan River
- Aras River (forms border with Turkey and Iran)
- Major Lake:
- Lake Sevan (covers ~5% of Armenia's area)
- Key rivers:
- Natural Resources
- Copper, molybdenum, gold
- Small deposits of zinc, aluminum, and other minerals
- Forests cover approximately 11% of the land
- Environmental Issues
- Deforestation
- Water pollution (especially Lake Sevan)
- Soil erosion due to overgrazing
- Earthquake-prone region (e.g., 1988 Spitak earthquake)
- Geopolitical Importance
- Situated at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia
- Close to major regional powers: Turkey, Iran, Russia
- Disputes with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh region
- Urban Geography
- Capital: Yerevan (in Ararat Valley)
- Other cities: Gyumri, Vanadzor
- Most urban settlements located in western and central Armenia
- Geographical Challenges
- Landlocked: Hinders trade and connectivity
- Hostile borders: Closed borders with Turkey and Azerbaijan
- Earthquakes: Seismic zone
- Rugged terrain: Limits agriculture and infrastructure development
2. Croatia
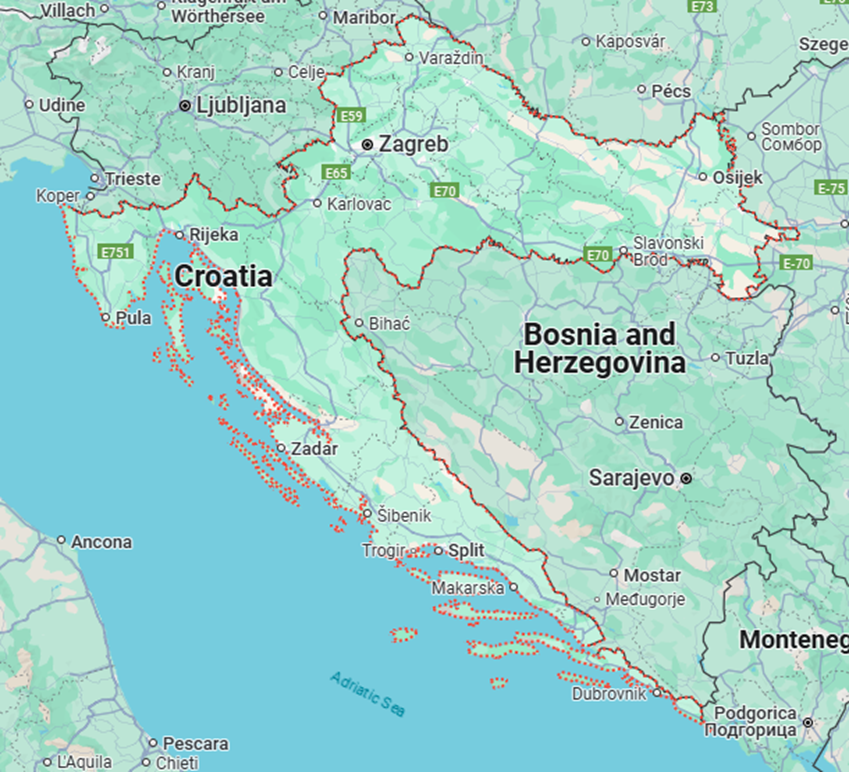
Why in the News?
- The Prime Minister of India reached Croatia. He is the first Indian Prime Minister to visit the country. This visit is part of his tour to three countries.
- He came after attending the G7 Summit in Canada.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Location & Borders
- Continent: Europe (Southeastern Europe, part of the Balkans)
- Latitude & Longitude: 45°N, 16°E
- Strategic Location: Along the Adriatic Sea, gateway between Central Europe and the Mediterranean
- Borders:
- North: Slovenia and Hungary
- East: Serbia
- South: Bosnia & Herzegovina and Montenegro
- West: Adriatic Sea (opposite Italy)
- Area & Size
- Total Area: ~56,594 sq. km
- Slightly smaller than West Bengal
- Coastline: ~1,800 km (including over 1,000 islands and islets)
- Topography
- Three main geographic zones:
- Pannonian Plain (North & East):
- Flat, fertile land — agriculture dominant
- Pannonian Plain (North & East):
- Dinaric Alps (Central region):
- Mountainous and rugged
- Dinara Peak: Highest point (1,831 meters)
- Adriatic Coast (West):
- Narrow coastal strip with limestone cliffs and karst topography
- Scenic, highly indented coastline with many islands
- Three main geographic zones:
- Climate
- Diverse climate due to varied topography:
- Continental Climate: In Pannonian region (cold winters, hot summers)
- Mediterranean Climate: Along Adriatic coast (mild, wet winters; hot, dry summers)
- Mountain Climate: In Dinaric Alps (snowfall common)
- Diverse climate due to varied topography:
- Rivers & Lakes
- Major Rivers:
- Sava River: Flows through capital Zagreb
- Drava River: Northern border
- Danube River: Eastern border with Serbia
- Kupa River
- Plitvice Lakes: UNESCO World Heritage site, known for cascading lakes and waterfalls
- Major Rivers:
- Natural Resources
- Bauxite, oil, natural gas, coal, limestone, salt
- Fertile soil in eastern plains
- Rich biodiversity, especially in karst regions
- Environmental Features
- Karst Topography:
- Limestone landscapes with sinkholes, caves, and underground rivers
- Covers over half of Croatia
- National Parks:
- Plitvice Lakes, Krka, Paklenica, and others
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Part of the Dinaric Alps and Mediterranean bioregions.
- Seismic Activity
- Croatia is located in a moderate seismic zone
- Earthquakes occasionally affect Zagreb and coastal areas
- Karst Topography:
- Urban Geography
- Capital: Zagreb (northwest, inland, on the Sava River)
- Other major cities:
- Split (coastal, Dalmatia region)
- Rijeka (main seaport)
- Dubrovnik (historic coastal city)
- Urbanization is concentrated along the coast and in river valleys
- Geopolitical Importance
- Member of EU and NATO
- Gateway to the Balkans
- Maritime significance: Important ports on the Adriatic Sea
- Proximity to Italy, Austria, and Central Europe increases trade potential



