1. Lothal
Why in the News?
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi will visit Lothal, Gujarat on 20th September 2025 to review the progress of the National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC).
- He will inspect completed works and hold review meetings with officials regarding ongoing projects.
About Lothal
- Historical and Geographical Context
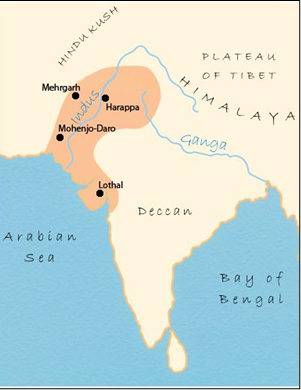
- Located on the Bhogava River, in the Gulf of Khambhat (Gujarat).
- Flourished between 2400–1600 BCE as part of the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC).
- Name derived from Gujarati words Loth (mound) + thal (dead) = “mound of the dead.”
- Excavated in 1954 by S.R. Rao (ASI).
- Southernmost major site of the IVC, with links to Sindh, Saurashtra, Mesopotamia, and Africa.
- Urban Planning and Architecture
- Town Planning: Divided into Citadel (Upper Town) and Lower Town.
- Citadel: Built on 4m high mud-brick platforms. Contained a warehouse for storage.
- Lower Town: Residential settlement, bead-making factory, and dockyard.
- Flood Protection: Entire settlement enclosed by a brick fortification wall.
- Advanced Engineering: Use of mud-brick platforms, drains, and tidal dock system.
- Maritime Trade and Dockyard
- Dockyard:
- World’s earliest known tidal dockyard (~200m × 35m).
- Equipped with sluice gate and spill channel to regulate water levels.
- Strategic Location: Situated near ancient Sabarmati River course, ensuring sea access.
- Trade Networks: Connected with Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Africa.
- Exports: Beads, ornaments, gems, semi-precious stones, cotton, rice.
- Imports: Marine shells, stone anchors, seals (including from Persian Gulf).
- Economic Role: Functioned as a major emporium of Harappan trade.
- Dockyard:
- Archaeological Findings
- Crafts and Industry:
- Bead-making, shell-working, metallurgy, ornaments.
- Famous for agate, carnelian, jasper, steatite micro-beads.
- Crafts and Industry:
- Used Cire Perdue (lost-wax technique) for metal casting.
- Science & Technology:
- Discovery of a compass (for navigation and astronomy).
- Ivory scale with smallest decimal divisions in IVC.
- Seals & Pottery:
- 3rd largest collection of seals among IVC sites.
- Seals show bulls, tigers, goats, composite animals with inscriptions.
- Pottery: Redware (common use) and Blackware (decorative/finer use).
- Terracotta & Toys: Figurines, wheeled animal toys, gaming pieces (like chess).
- Religion & Burials:
- Fire altars suggest worship of a fire god.
- Animal worship was evident, unlike other IVC sites where Mother Goddess was dominant.
- Burials lined with burnt bricks, including twin burials and pot burials.
- Significance and Legacy
- Economic Importance: Acted as a hub of maritime trade and craft specialization.
- Cultural Diversity: Differences in religious practices show regional variation in IVC beliefs.
- Agricultural Significance: Excavations revealed earliest rice cultivation evidence in South Asia.
- Engineering Marvel: Dockyard proves advanced hydrological knowledge and maritime technology.
- Modern Relevance: Site for the upcoming National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC)—set to be the world’s largest maritime museum.
2. Chabahar Port
Why in the News?
- The S. Trump administration has announced the revocation of sanctions waiver for Iran’s Chabahar Port, ending the special exemption granted to India in 2018.
- This decision threatens to hamper India’s regional connectivity plans, particularly its trade routes to Afghanistan and Central Asia, bypassing Pakistan.
- India has invested heavily in the port, and the sanctions could significantly affect its economic and strategic interests.
About Chabahar Port
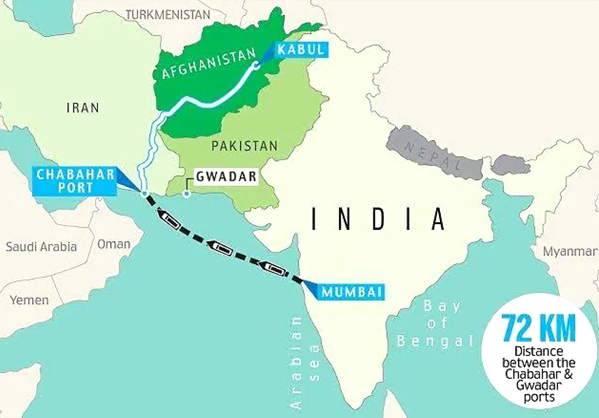
- Location: Situated in southeastern Iran, along the Gulf of Oman, outside the Strait of Hormuz.
- Structure: Includes the Shahid Beheshti Terminal, where India is involved in development.
- Strategic Importance for India: Provides an alternative route to Afghanistan and Central Asia by bypassing Pakistan.
- Connectivity Projects: Linked to the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) and other regional connectivity initiatives.
- India’s Investment: India signed a 10-year lease agreement in May 2024 and has already spent about ₹200 crore out of ₹400 crore allocated for its development.
- Operational Growth: The port saw a 43% rise in vessel traffic and a 34% increase in container traffic in 2023-24.
- Geopolitical Value: Considered a counterbalance to Pakistan’s Gwadar Port, which is developed by China.
- Challenges:S. sanctions under the Iran Freedom and Counter-Proliferation Act (IFCA) may now deter operators and investors, impacting India’s role in the project.