1. Arctic Sea
Why in the News?
- The Arctic Sea ice is melting rapidly due to rising global temperatures, reaching record lows in recent years.
- Melting ice is affecting global weather patterns, including monsoons and rainfall variability in regions like India.
- Changes in the Arctic are being studied for their impact on sea levels, ocean currents, and extreme climate events worldwide.
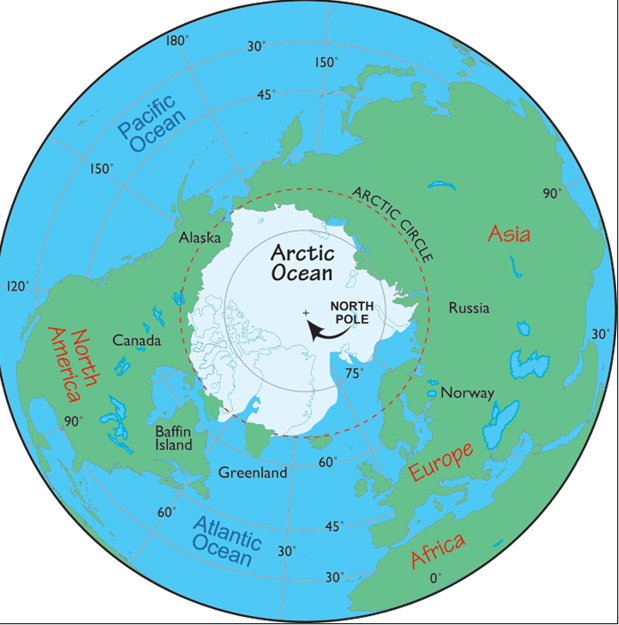
About Arctic Region
- The Arctic is a geographic region surrounding the North Pole.
- It includes the northern parts of Canada, the United States (Alaska), Russia, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Iceland, and Greenland.
- The Arctic Ocean lies at its center.
- The Arctic Circle (66°33’N) roughly marks the boundary of the Arctic based on solar radiation and daylight patterns.
- Geography and Climate
- The region mainly consists of flat tundras with some mountainous areas.
- Much of the ground is permanently frozen (permafrost), with only the surface thawing in summer.
- Greenland is largely covered by a permanent ice sheet.
- Daylight: The North Pole experiences six months of darkness and six months of daylight, while areas farther south have shorter extremes.
- Temperature: Winters are extremely cold (up to −68°C inland), while summers are mild (around 10°C).
- Coastal regions receive heavier snowfall compared to inland areas.
- Flora and Fauna
- Plants: Trees are scarce, limited to southern Arctic regions; tundras support lichens, mosses, grasses, and small flowering plants.
- Animals: Includes polar bears, caribou, Arctic foxes, Arctic hares, gray wolves, seals, walruses, whales, and many fish species.
- Birds: Some, like the snowy owl, stay year-round, while many migrate in summer.
- Human Presence
- Indigenous Peoples: Groups like the Nenets, Sakha, Evenk, Chukchi, Sami, Inuit, and Aleuts traditionally inhabit the region in small settlements, often practicing reindeer herding, hunting, and fishing.
- Settlers: Industrial activities like mining and oil drilling in the 20th century brought European settlers, leading to larger towns and resource-based communities.
2. Mediterranean Sea
Why in the News?
- The Mediterranean Sea region is the origin of western disturbances, which influence rainfall in northern India.
- Changes in the Mediterranean climate and temperature can affect the frequency and intensity of storms reaching India.
- It is strategically important for monitoring climate patterns and weather systems that impact agriculture and water resources in Asia.
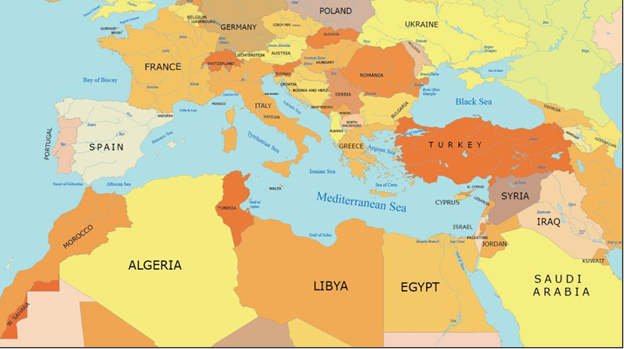
About Mediterranean Sea
- Location
- The Mediterranean Sea is an intercontinental sea, bordered by Europe (north), Asia (east), and Africa (south).
- It connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar in the west.
- In the northeast, it connects to the Black Sea via the Dardanelles Strait, Sea of Marmara, and Bosporus Strait.
- In the southeast, it connects to the Red Sea through the Suez Canal.
- Historical Significance
- The Mediterranean has been the cradle of Western civilization.
- Ancient civilizations like the Phoenicians, Greeks, and Romans flourished along its coasts.
- It played a central role in trade, culture, and maritime exploration for centuries.
- Bordering Countries and Geography
- Europe: Spain, France, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece.
- West Asia/Middle East: Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine (Gaza), Cyprus.
- North Africa: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt.
- Coastline stretches approximately 46,000 km, including 15 marginal seas such as the Adriatic, Balearic, Levantine, and Ionian Seas.
- Average depth is about 1,500 m, with the Calypso Deep (Ionian Sea) reaching 5,267 m.
- Rivers and Islands
- Major rivers draining into the Mediterranean include Ebro, Rhone, Po, Nile, and Tiber.
- Large islands include Sicily (largest), Corsica, Crete, Cyprus, Mallorca, Rhodes, Sardinia, Lesbos, Chios, Euboea.
- Climate and Oceanography
- The region has a Mediterranean climate: mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
- Mediterranean waters are more saline than the Atlantic.
- There is a continuous exchange of water with the Atlantic through the Strait of Gibraltar, influencing currents and salinity.
|
Also Read |
|
| UPSC Foundation Course | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |
| Free MCQs for UPSC Prelims | UPSC Test Series |
| ENSURE IAS NOTES | Our Booklist |