- News :Researchers have recently established the first government-supported national biobank (repository that collects and manages biological samples (like blood and DNA) and health-related data) dedicated to rare diseases known as Lysosomal Storage Disorders.
- What Are Lysosomal Storage Disorders: Lysosomal Storage Disorders are rare genetic diseases in which toxic materials build up inside the body’s cells.
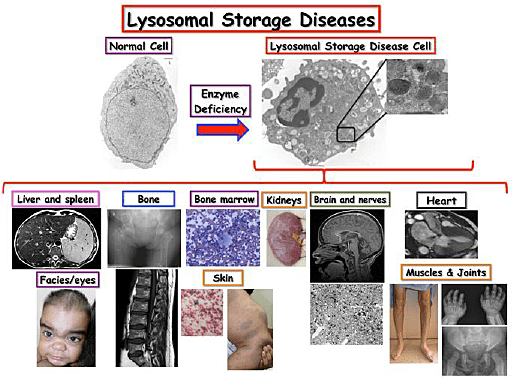
- Why does this happen: Because lysosome cells do not work properly. A lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosome function is to:Break down worn-out cell parts,Digest fats, sugars, and complex substances.
- What Goes Wrong in LSDs: In people with LSDs: Certain enzymes of Lysosome are missing or defective or substances that help these enzymes function are absent
- As a result: The body cannot break down fats, sugars, and other materials. These substances accumulate inside cells. Over time, this damages organs such as the brain, liver, heart, bones, and muscles
- Genetic Inheritance : Most LSDs require both parents to carry the abnormal/faulty gene.
- Examples of LSDs: Gaucher disease, Pompe disease, MPS I & MPS II (Hunter syndrome) .
- Symptoms and Treatment:
- Symptoms usually appear during pregnancy or shortly after birth; however, they can rarely develop in adults.
- There is currently no permanent cure for LSDs. Treatments focus on managing symptoms and reducing damage to vital organs and tissues.