- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Money Laundering and Its Prevention
Money Laundering and Its Prevention

Money Laundering and Its Prevention
What is Money laundering?
- Money laundering is the process of making illegally obtained funds (such as proceeds from criminal activity) appear legitimate or "clean" by channeling them through legitimate financial systems.
- This is typically done through a series of complex financial transactions that obscure the true source of the funds and make it difficult to trace them back to their illicit origins.
- Money laundering is often used by criminals to "launder" money obtained from activities such as drug trafficking, organized crime, and corruption.
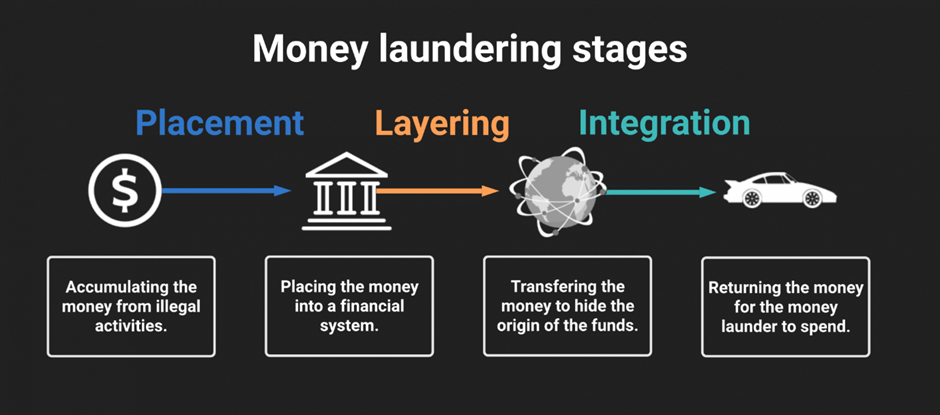
Process of money laundering
Money laundering typically involves three basic steps, which are often referred to as the "three stages" of money laundering. It include following processes:
- Placement: This stage involves placing the illegally obtained funds into the financial system, typically through depositing cash into bank accounts or purchasing assets such as real estate, art, or other valuable goods.
- Layering: Once the funds are in the financial system, the launderer will attempt to create a complex series of transactions and movements to obscure the true source of the funds. This may involve transferring the funds between different accounts, purchasing and selling various assets, and using financial instruments such as derivatives and options to create layers of complexity.
- Integration: In the final stage, the laundered funds are reintroduced into the legitimate economy, typically through investment in businesses or real estate, or by using the funds to purchase high-value goods that can be sold for a profit.
Ensure your Civil Services Dream Career
Click Here to Book your free Counseling
The Hawala System
- Within India, the system of money laundering is further complicated by the ancient underground form of banking known as Hawala. Hawala, which means providing a code, was established centuries before the financial systems of the West.
- Created as a means to facilitate the secure and convenient flow of funds, the system has become increasingly popular over the past few decades. Under the present-day Hawala system, a person wishing to transfer funds to another country deposits the money with a Hawala dealer. The depositor also gives the dealer a code, which must be given by anyone trying to access the funds.
- Through the use of corporate accounts, the dealer is able to move the funds to one of the dealer's agents in another country. Armed with the code, the intended recipient of the money is able to obtain it from the dealer's agent.
- With its lack of governmental supervision, the Hawala system allows individuals to make deposits and withdrawals through Hawala dealers rather than financial institutions.
Money laundering in India
- Over the years, money laundering in the banking system has become more frequent and sophisticated with the advent of internet-based banking leading to increase in the quantum of money involved in such cases.
- Much recently, in February 2022, India witnessed its biggest ever bank fraud of INR 22,842 crores (approx. USD 3 billion) that involved ABG Shipyard Ltd., a shipbuilding and repair company.
- During the fiscal years between 2012-13 to 2021-22, ED filed a total of 3,985 criminal complaints under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) and 24,893 under the civil law of FEMA.
Impacts of Money laundering
- Economic Distortion: Money laundering can distort the economy by inflating asset prices and causing misallocation of resources. For example, if a large amount of illegally obtained funds are invested in real estate, it can drive up prices and create an artificial bubble, which can burst and cause significant economic damage.
- Loss of Tax Revenue: Money laundering can result in the loss of tax revenue for the government, as illegal funds are not subject to taxation. This can have a significant impact on the government's ability to fund public services and infrastructure development.
- Corruption and Organized Crime: Money laundering is often associated with corruption and organized crime. The flow of illicit funds can undermine the rule of law and create a culture of corruption, which can have far-reaching negative impacts on society.
- Security Risks: Money laundering can also pose a security risk, as it can be used to fund terrorism and other illegal activities. For example, the 2008 Mumbai attacks were partly funded through money laundering.
- Reputation Damage: Money laundering can damage the reputation of banks, financial institutions, and countries, leading to a loss of investor confidence and reduced economic activity. For example, the recent money laundering scandal involving a major Indian bank has damaged its reputation and led to a loss of investor confidence.
- Other impacts: promotes cash based economy, Decreases human development, Misallocation of resources and Affects trust of local citizens in their domestic financial institutions.
Steps taken to prevent money laundering
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA): The PMLA was enacted in 2002 to prevent money laundering and to provide for confiscation of property derived from, or involved in, money laundering. The act defines money laundering as a criminal offence and provides for penalties for those found guilty of it.

- Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU): The Indian government has established the FIU to receive, analyze, and disseminate information related to money laundering. This helps to identify suspicious financial transactions and prevent money laundering.
- Powers to Enforcement Directorate (ED): ED is a law enforcement agency which is responsible for enforcing economic laws and countering economic crimes in India. An important function of ED is to Investigate cases of money laundering under PMLA.

- International Cooperation: The Indian government has signed several international agreements and conventions on money laundering, including the United Nations Convention against Corruption and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations. This helps to facilitate cooperation with other countries in preventing and investigating cases of money laundering.
International measures
- Vienna Convention: tries to creates an obligation for signatory states to criminalize the money laundering from illicit drug smuggling.
- The Financial Action Task Force: It has been set up by the governments of the G-7 countries. It gives rules and suggestions related to Money laundering and monitors member countries progress in applying these measures to counter Money Laundering.
How cryptocurrencies are related to money laundering?
Cryptocurrencies are related to money laundering because they can be used to facilitate anonymous and untraceable transactions. Unlike traditional financial systems, which are subject to Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations, cryptocurrencies operate outside of the traditional banking system, making it easier for criminals to launder money without detection.
Some ways in which cryptocurrencies can be used for money laundering:
- Mixing Services: Mixing services are online platforms that allow users to mix their cryptocurrency holdings with those of others, making it difficult to trace the source of funds. This can be used to conceal the origin of illegally obtained funds and to create a layer of anonymity.
- Anonymous Wallets: Some cryptocurrencies, such as Monero, are designed to be completely anonymous, with no traceable transaction records. This can make it easier for criminals to move funds without detection.
- Dark Web Markets: Cryptocurrencies are commonly used on the dark web to buy and sell illegal goods and services. This can include drugs, weapons, and stolen data. Criminals can use cryptocurrencies to receive payment for these goods and services, making it difficult for law enforcement to trace the money trail.
- Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs): ICOs are fundraising mechanisms used by startups to raise funds in cryptocurrencies. While ICOs can be a legitimate way for startups to raise funds, they can also be used as a means of laundering money. Criminals can create fake ICOs, raise funds in cryptocurrencies, and then move the funds through a series of transactions to conceal their origin.
Way forward
- Strengthening Regulation: The government can strengthen regulatory oversight of financial institutions and non-financial sectors that are susceptible to money laundering, such as real estate, gems and jewelry, and non-banking financial companies. This can involve regular audits, imposing stricter compliance standards, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Enhancing Enforcement: The government can enhance enforcement efforts to investigate and prosecute cases of money laundering. This can involve setting up specialized units to investigate money laundering cases, providing adequate resources to the investigating agencies, and ensuring that there is effective coordination between different agencies.
- Improving International Cooperation: The government can improve cooperation with other countries to investigate and prosecute cases of money laundering. This can involve sharing information and intelligence, extradition agreements, and mutual legal assistance treaties.
- Using Technology: The use of technology can help to prevent money laundering. This can involve the use of sophisticated software and algorithms to detect suspicious transactions, artificial intelligence to identify patterns of money laundering, and blockchain technology to create a transparent and tamper-proof ledger of financial transactions.
- Promoting Awareness: The government can promote awareness of money laundering among the public, businesses, and financial institutions. This can involve conducting workshops and training programs, disseminating information on best practices, and raising awareness of the consequences of money laundering.
- Big data and artificial intelligence are two examples of equally cutting-edge Anti-Money Laundering tools that must be used to combat the ever-evolving threats posed by money laundering and supported by cutting-edge technologies.
- Both worldwide and homegrown partners need to meet up by fortifying information sharing instruments among them to actually dispense with the issue of tax evasion.
Reducing money laundering in India requires a comprehensive approach that involves regulatory measures, enforcement, international cooperation, technology, and awareness.
It is important for the government to take proactive measures to combat this problem and protect the integrity of the financial system.
TO ACCESS ALL THE GENERAL STUDIES NOTES CLICK ON: https://ensureias.com/notes