- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
What is Thirty Meter Telescope and Why is it Significant for India?
What is Thirty Meter Telescope and Why is it Significant for India?
13-07-2024

The Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) is an ambitious international project involving India, the United States, Canada, China, and Japan that aims to significantly advance our understanding of the universe.
Key Points:
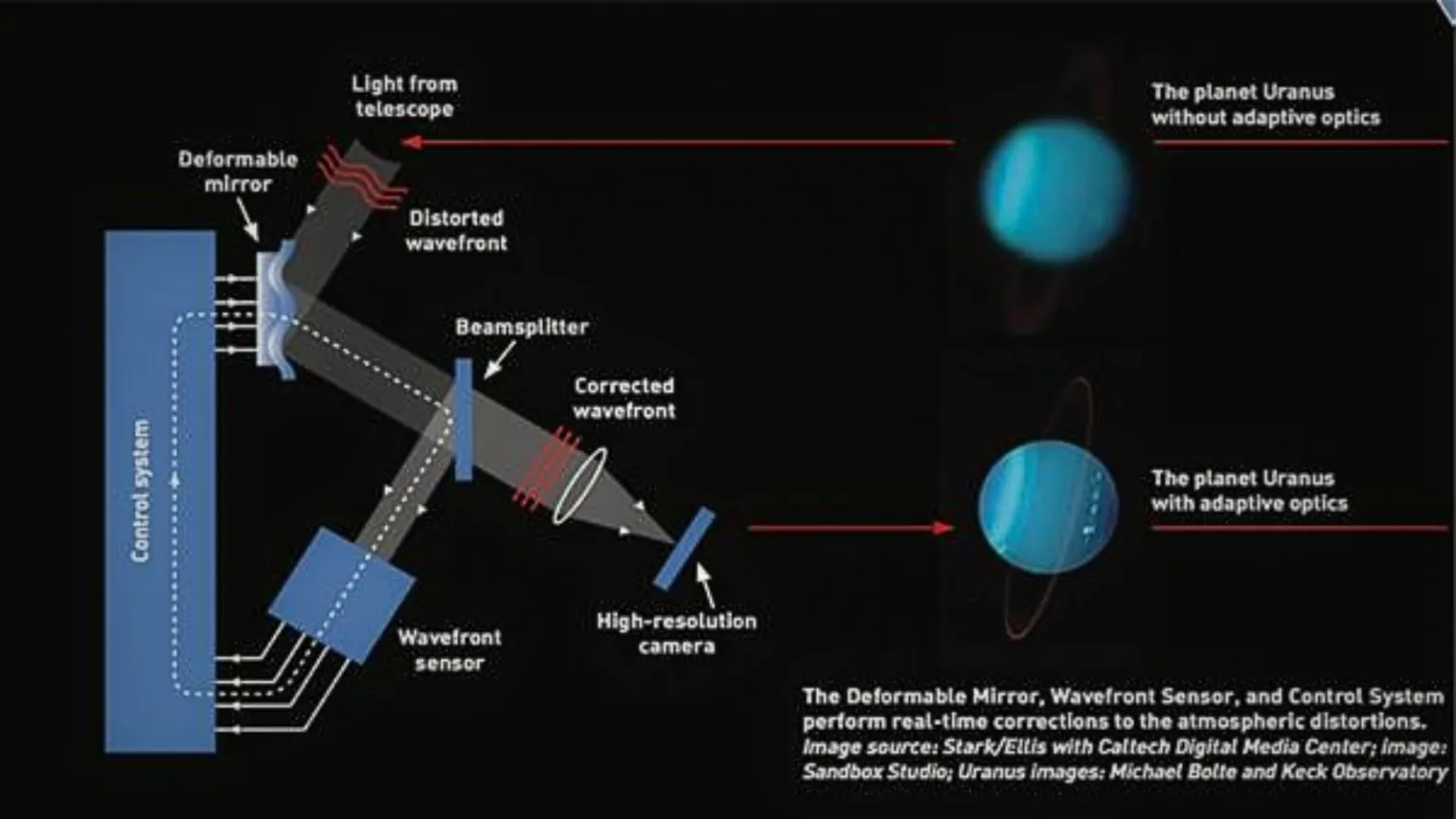
- TMT Project: The TMT is a next-generation astronomical observatory designed to provide unprecedented resolution and sensitivity with its massive 30-meter primary mirror, advanced adaptive optics system, and state-of-the-art instruments.
- Primary Goals: The primary goals of the TMT are to study the early universe, investigate the formation and evolution of galaxies, study the relationship between supermassive black holes and their host galaxies, investigate the formation of stars and planetary systems, and characterize exoplanets and study their atmospheres.
- Preferred Site: The preferred site for the TMT is Mauna Kea, Hawaii, one of the world's premier astronomical sites. However, due to conflicts with indigenous Hawaiians who consider the site sacred, alternative locations such as the Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos (ORM) on La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain, are being explored.
- Mirror System:
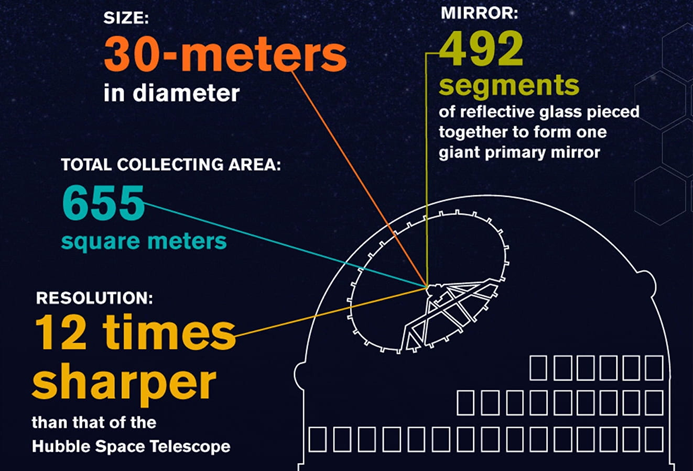
-
- Primary Mirror: 30 meters in diameter, composed of 492 hexagonal segments.
- Secondary Mirror: Composed of 118 smaller hexagonal segments.
- Tertiary Mirror: 3.5 meters by 2.5 meters, positioned centrally within the primary mirror.
- Adaptive Optics System: The TMT's Adaptive Optics System (AOS) uses deformable mirrors and laser guide stars to correct atmospheric turbulence, enhancing image resolution. Indian scientists have developed a tool to generate a comprehensive all-sky catalogue of NIR stars for this system.
- Scientific Instruments: The TMT will feature instruments like the Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (IRIS) and the Wide-Field Optical Spectrograph (WFOS) for various observations.
- Indian Contribution: India is seen as a major contributor to the TMT project, providing hardware, instrumentation, software, and funding worth $200 million.
- Significance for India: The new tool developed by Indian researchers will help mitigate atmospheric distortions by creating an all-sky NIR star catalogue, ensuring high-quality images from the TMT.
- Indian Institutes Involved: The Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Bengaluru, the Inter-University Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune, and the Aryabhatta Research Institute for Observational Sciences (ARIES), Nainital, are involved in the TMT project.
- Automated Code: Researchers at the IIA in Bengaluru, led by Dr. Sarang Shah, have developed an automated code to generate the all-sky NIR star catalogue, essential for the NFIRAOS to function optimally.
Benefits:
- Advancing Our Understanding of the Universe: The TMT will significantly advance our understanding of the universe, enabling us to explore deeper into space and observe cosmic objects with unparalleled sensitivity.
- Indian Contribution: India's contribution to the TMT project will enhance its reputation as a major player in international scientific collaborations.
- Development of New Technologies: The TMT project will drive the development of new technologies, including advanced adaptive optics systems and sophisticated instrumentation.
- Enhancing Scientific Capabilities: The TMT will enhance scientific capabilities, enabling researchers to study the universe in unprecedented detail.
- International Cooperation: The TMT project demonstrates the power of international cooperation in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding.
Analysis:
- International Cooperation: The TMT project highlights the importance of international cooperation in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding.
- Indian Scientific Capabilities: The project showcases India's scientific capabilities and its ability to contribute to cutting-edge research and development.
- Technological Advancements: The TMT project will drive technological advancements, including the development of new materials, instruments, and software.
- Enhancing Global Understanding: The project will enhance global understanding of the universe, enabling us to better understand the mysteries of the cosmos.
Conclusion:
The Thirty Meter Telescope project is a significant milestone in the advancement of our understanding of the universe. India's contribution to the project will enhance its reputation as a major player in international scientific collaborations and drive technological advancements. The project will also enhance global understanding of the universe, enabling us to better understand the mysteries of the cosmos.



