- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Wayanad Wildlife Sanctury
Wayanad Wildlife Sanctury
10-01-2023
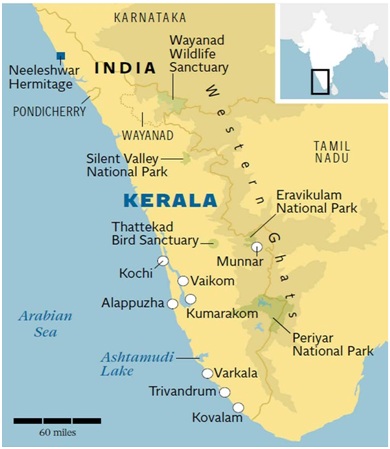
Wayanad Wildlife Sanctury
Why in News?
Recently, in a Human-Animal Conflict, a local man was attacked by an Elephant and a herd of elephants raided a field, near Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Kerala.
About the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Located in Kerala, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (WWS) is an integral part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. It was established in 1973.
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve was the first from India to be included in the UNESCO designated World Network of Biosphere Reserves (designated in 2012).
- Other wildlife parks within the Reserve are:
Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
Bandipur National Park
Nagarhole National Park
Mukurthi National Park
Silent Valley
- It is spread over 344.44 sq km, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary is contiguous to the tiger reserves of Nagerhole and Bandipur of Karnataka and Mudumalai of Tamil Nadu.
- Kabini river (a tributary of Cauvery River) flows through the sanctuary.
- The forest types include South Indian Moist Deciduous forests, West coast semi-evergreen forests and plantations of teak, eucalyptus and Grewelia.
- Elephant, Gaur, Tiger, Panther,Sambar, Spotted deer, Barking deer, Wild boar, Sloth bear, Nilgiri langur, Bonnet macaque, Common langur, Wild dog, common otter, Malabar giant squirrel etc are the major mammals.
What is Human-Animal Conflict?
- These conflicts arise out of the struggles, due to the direct threat of presence or behaviour of wildlife to human interests or needs.
- These often lead to disagreements between groups of people and negative impacts on people and/or wildlife.
- Human-animal conflict has become a serious wildlife management problem in Kerala in the last few years. People living on the fringes of reserve forests and sanctuaries have a heightened sense of insecurity now.
Causes of Human Animal Conflict:
- Human population expansion
- Habitat degradation and fragmentation
- Land use transformation
- Rising densities of livestock in protected areas
What is the Conservation Status of Elephants?
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of threatened species:
- African Forest Elephant- Critically Endangered
- African Savanna Elephant- Endangered
- Asian Elephant- Endangered
- Convention of the Migratory species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching in Delhi



