- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Tripura dam didn’t cause Bangladesh floods: India
Tripura dam didn’t cause Bangladesh floods: India

Recently, severe flooding in Bangladesh has raised concerns about whether water from the Dambur Dam in Tripura, India, might be contributing to the problem. However, the Indian government has clarified that the flooding is due to heavy rainfall in the larger catchment areas of the Gumti River, which flows through both India and Bangladesh, rather than from the dam’s water release.
Gumti River and Dambur Dam
- Gumti River
- Overview: Also known as Gomti, Gumati, or Gomati, the Gumti River originates in Tripura, India, and flows through the Comilla district in Bangladesh.
- Tributaries:
- Right Bank: Kanchi Gang, Pitra Gang, San Gang, Mailak Chhara, and Surma Chhara.
- Left Bank: Ek Chhari, Maharani Chhara, and Ganga.
- Dambur Dam
- Location: Built on the Gumti River in Tripura.
- Specifications: Stands 30 meters high and contributes to power generation, with 40 megawatts of electricity supplied to Bangladesh.
- Purpose: Besides generating electricity, it supports local water needs and contributes to regional infrastructure.
- Dumboor Lake
- Location: Situated in Gandacherra, near Agartala, Tripura.
- Formation: Created by the confluence of the Raima and Sarma rivers.
- Significance: Known for its diverse fish species and the annual 'Poush Sankranti Mela' celebrated on January 14th.
Transboundary Rivers of India with Neighboring Countries
-
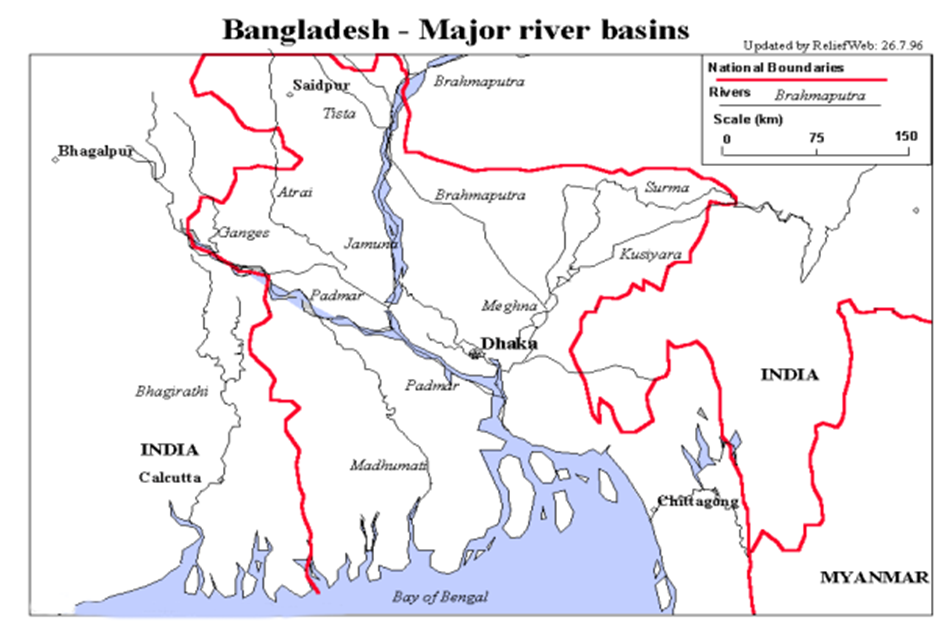
India-Bangladesh
- Shared Rivers: India and Bangladesh share 54 rivers. Key rivers include:
|
River |
Key Details |
|
Ganges (Padma in Bangladesh) |
|
|
Teesta |
|
|
Feni |
|
|
Kushiyara |
|
|
Brahmaputra (Jamuna in Bangladesh) |
|
|
Meghna |
|
-
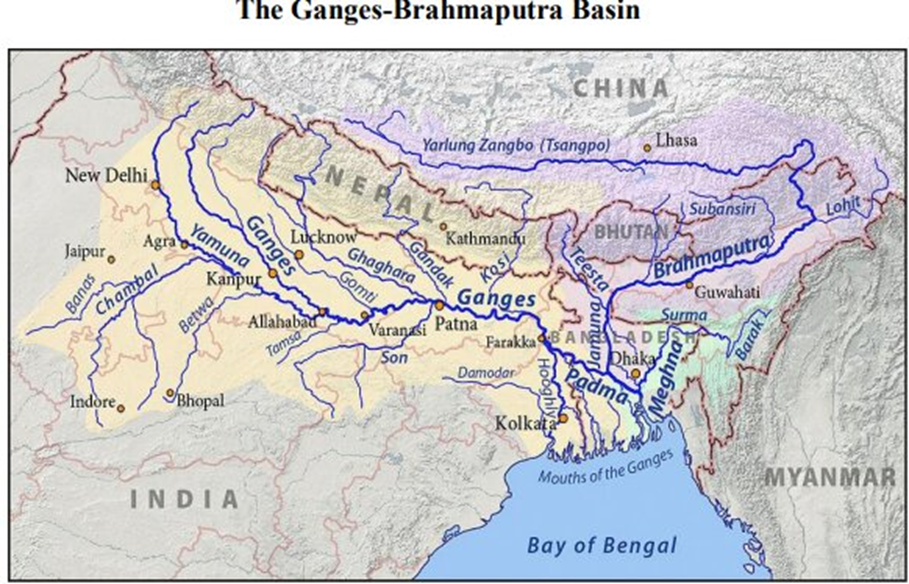
India-China
-
- Brahmaputra River System
- Path: Includes the Siang (Brahmaputra's main stream), originating in Tibet and flowing through Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tributaries: Subansiri and Lohit rivers.
- Indus River System
- Path: Includes the Indus and its tributaries like the Sutlej.
- Treaties: Two MoUs between India and China for sharing hydrological data on these rivers.
- Brahmaputra River System
-
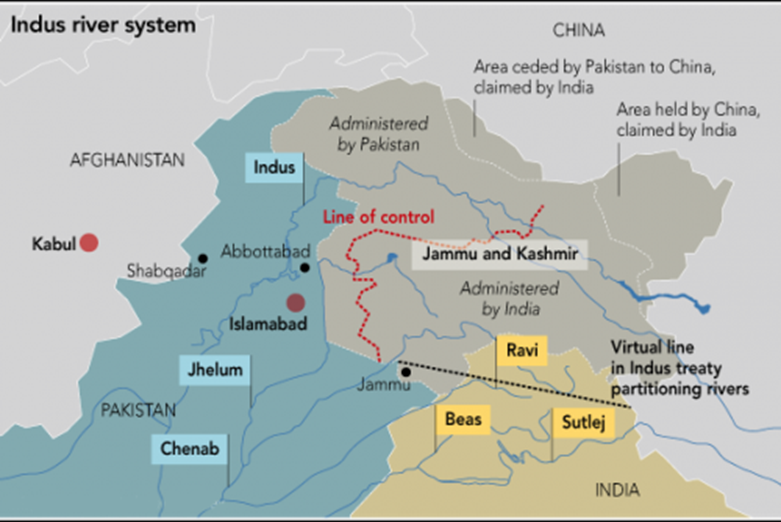
India-Pakistan
- Indus River
- Path: Originates in Tibet, flows through Kashmir, and continues south to the Arabian Sea.
- Controversy: Water-sharing issues have been significant since independence.
- Sutlej
- Path: Originates in Tibet, flows through Himachal Pradesh and Punjab, joining the Beas before merging with the Chenab to form the Panjnad River.
- Chenab
- Path: Originates in Himachal Pradesh, flows through Jammu and Kashmir, and into Pakistan.
- Confluence: Joins the Jhelum near Trimmu.
- Jhelum
- Path: Originates in Kashmir, flows through Jammu and Kashmir, and into Pakistan.
- Beas
- Path: Originates in Himachal Pradesh, flows through Punjab, and joins the Sutlej River.
- Ravi
- Path: Originates in Himachal Pradesh, flows through Punjab, and joins the Chenab River.
- Treaty: The 1960 Indus Waters Treaty allocates control of the Beas, Ravi, and Sutlej rivers to India, and the Indus, Chenab, and Jhelum rivers to Pakistan.
- Indus River
-
India-Nepal
- Kosi
- Path: A major tributary of the Ganges, originating in the Himalayas, flows through Nepal and Bihar.
- Characteristics: Known for its frequent course changes and flooding, earning the nickname "sorrow of Bihar."
- Gandak
- Path: Originates in Tibet, flows through Nepal and Bihar before merging with the Ganges.
- Tributaries: Includes Mayangadi, Bari, Trisuli, Panchand, Sarhad, and Budhi Gandak.
- Sharda/Kali/Mahakali River
- Path: Originates at Kalapani in Uttarakhand, flows along the India-Nepal border, and merges with the Ghaghra River.
- Project: The Pancheshwar Dam is a joint India-Nepal project for irrigation and hydroelectric power.
- Dispute: India and Nepal have historical disagreements over the interpretation of the Sugauli Treaty 1816, which affects the boundary along the Mahakali River.
- Kosi
Conclusion
Transboundary rivers are crucial for the economies and ecosystems of multiple countries, including India and its neighbors. These rivers facilitate vital water resources but also present complex challenges related to water sharing and management. India’s agreements with neighboring countries, such as the Indus Waters Treaty with Pakistan and the Ganges Water Treaty with Bangladesh, aim to address these issues. Despite the progress, ongoing disputes and environmental concerns require continued cooperation and effective management to ensure sustainable use and equitable distribution of these essential water resources.




