The Delhi Forest and Wildlife Department is setting up a tissue culture lab in the Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary. This lab will generate saplings of endangered and rare native trees found in the city.
- The department has identified around 10 such species – hingot, khair, bistendu, siris, palash, chamrod, doodhi, dhau, desi babool, and kulu
- The aim is to help grow endangered native Delhi trees in a controlled environment, and to regenerate saplings whose seeds are not readily available in large quantities
- Asola-Bhati Wildlife Sanctuary covering 32.71 km² area on the Southern Delhi Ridge of Aravalli hill range on Delhi-Haryana border lies in Southern Delhi as well as northern parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts of Haryana state.
Objective:
The aim is to cultivate threatened indigenous trees in a controlled environment and produce saplings for species that are facing regeneration challenges.
Tissue Culture:
- Tissue culture involves growing cells or tissues in an artificial environment.
- It’s commonly known as micropropagation and serves as a valuable research tool for studying plant biology and conserving endangered species.
Animal Tissue Culture:
- Animal tissue culture is a biological technique that involves maintaining and propagating animal cells in an artificial environment.
- The process involves taking tissue from an animal specimen and growing and maintaining cells in an In Vitro Environment.
-
- In Vitro Environment: occur in a laboratory vessel or other controlled experimental environment rather than within a living organism
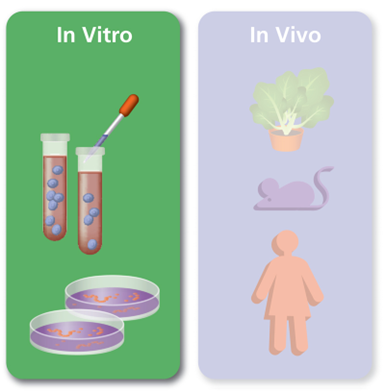
In Vivo: |
In Vitro: |
| In vivo research is performed within a living organism. This can range from microorganisms, plants, animals, to human beings. | Contrarily, in vitro studies take place outside of a living organism, typically in a controlled environment like a test tube or petri dish. |
 |
|
Plant Tissue Culture:
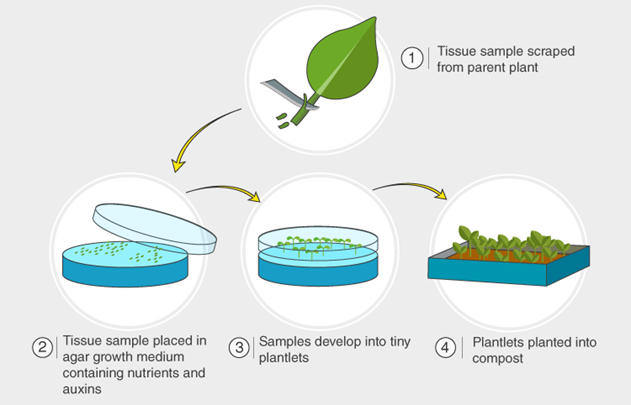
Plant tissue culture, also known as micropropagation, is a collection of techniques for growing plant cells, tissues, or organs in a controlled environment using nutrient solutions. This technique is used to produce clones of a plant, and can help with:
- Producing exact copies of plants: This may be useful for plants with desirable characteristics such as flowers or fruits.
- Producing mature plants quickly
- Producing many plants in a small space
- Producing plants without seeds or pollinators
- Regenerating whole plants from genetically modified cells
- Producing plants from seeds that have low germination rates






