- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Successful Flight Test of India’s 1st long-Range Hypersonic Missile
Successful Flight Test of India’s 1st long-Range Hypersonic Missile
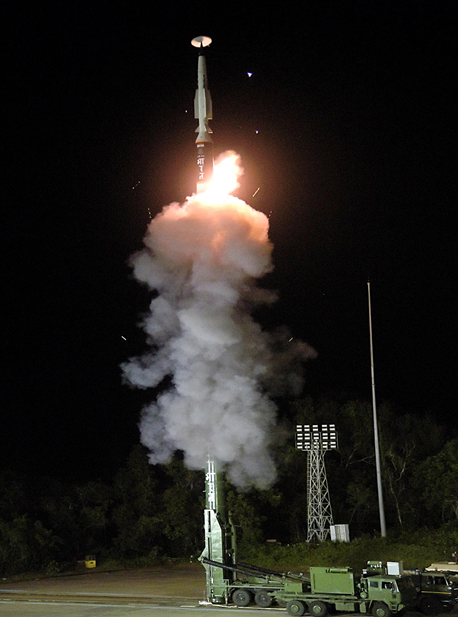

- India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted a flight test of its first long-range hypersonic missile on November 17 off the coast of Odisha.
- This milestone positions India among a select group of nations with the ability to develop and test such advanced military technology.
Significance of the Test
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh described the successful test as a historic moment, noting that it is a major step for India in the field of advanced military technologies.
- India now joins a small group of countries with the capability to develop hypersonic missiles.
- The missile was launched from Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Island, off the coast of Odisha, a site named after India’s former president and renowned missile scientist.
Key Features of the Hypersonic Missile
- Range: The missile has the ability to carry a range of payloads and can strike targets more than 1,500 km away.
- Indigenous Development: This missile was developed by multiple DRDO laboratories and industry partners, centered around the Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Missile Complex in Hyderabad.
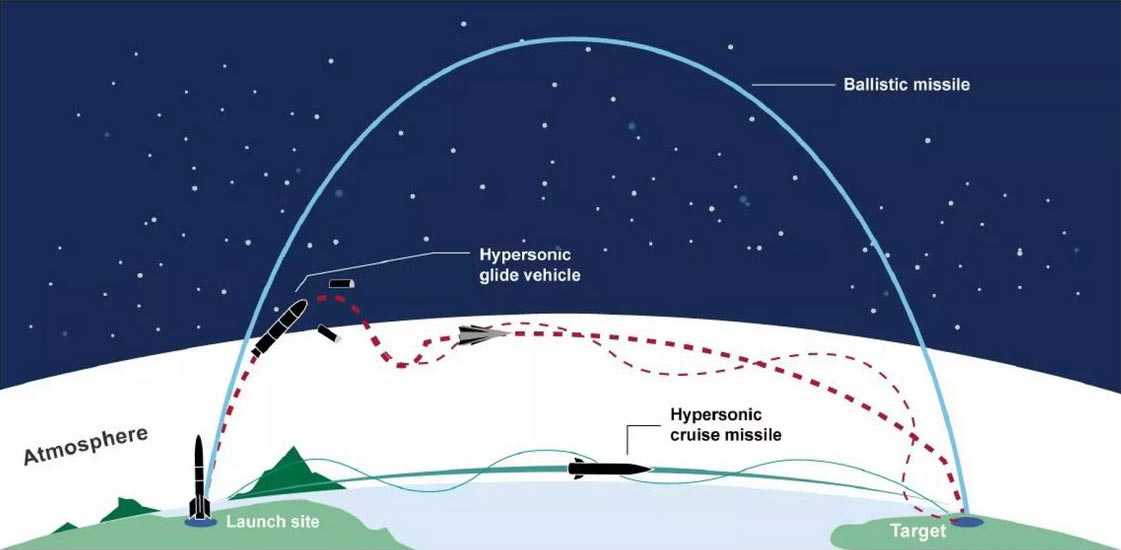
What is a Hypersonic Missile?
- A hypersonic missile is one that travels at speeds of at least Mach 5, which is five times the speed of sound or about 1 mile per second.
- Speed and Maneuverability: Hypersonic missiles are faster than traditional ballistic missiles and are also maneuverable, unlike ballistic missiles that follow a fixed trajectory.
There are two main types of hypersonic weapons:
- Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGV): These are launched from a rocket and glide to the target.
- Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCM): These are powered by scramjets (air-breathing engines), which keep the missile moving at high speeds after the initial launch.
Advantages of Hypersonic Missiles
- Long-Range Strike Options: Hypersonic missiles can hit distant targets, even those that are defended or time-sensitive, such as moving missiles or time-critical facilities.
- Difficult to Track: Due to their speed and low flight path compared to ballistic missiles, hypersonic missiles are harder to detect with surface-based sensors like traditional radar systems.
- Kinetic Energy: These missiles rely on kinetic energy (energy from motion) to destroy targets, including underground facilities or structures that are harder to penetrate using conventional weapons.
Challenges of Hypersonic Missiles
- Heat and Friction: The high speed creates extreme heat due to air resistance, making it challenging to develop materials that can withstand this heat during flight.
- Precision Maneuverability: Hypersonic missiles need to be incredibly precise in their manoeuvrability, making their design and operation complex.
- Communication Difficulties: Maintaining communication with operators during hypersonic flight is difficult due to the missile's high speed and altitude.
- Cost: Hypersonic missile systems are more expensive to develop and produce compared to traditional ballistic missiles.
Global Race in Hypersonic Technology
- Russia: Russia is one of the leading countries in hypersonic missile development. In 2022, it used a hypersonic missile for the first time during its conflict with Ukraine, targeting an underground warehouse in Ivano-Frankivsk.
- China: China is also a leading developer of hypersonic missile technology, with several successful tests of its own hypersonic missiles.
- United States: The US is actively pursuing hypersonic missile technology. In May 2023, the US Army awarded Lockheed Martin a $756 million contract for developing a ground-based hypersonic weapon system, the Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW).
- Other Countries: Several other nations are also pursuing hypersonic missile programs, including France, Germany, Australia, Japan, Iran, and Israel.
Ballistic Missiles vs. Hypersonic Missiles
|
Feature |
Ballistic Missiles |
Hypersonic Missiles |
|
|
||
|
Flight Path |
Arcing trajectory; follows a predictable path (sub-orbit or atmospheric) |
Unpredictable, maneuverable path within the atmosphere |
|
Speed |
Speed varies; re-entry can be very fast (Mach 20+), but not hypersonic during entire flight |
Mach 5+ (greater than five times the speed of sound) |
|
Maneuverability |
Generally non-maneuverable after launch |
Highly maneuverable during flight |
|
Targeting and Accuracy |
Very accurate with modern guidance (GPS, inertial) |
Highly precise, difficult to track due to maneuverability |
|
Launch Platforms |
Silos, submarines, mobile launchers |
Aircraft, land-based platforms, sea-based systems |
|
Range |
Varies (short-range, medium-range, ICBMs with intercontinental range) |
Medium to long-range, but depends on type (HGV or HCM) |
|
Defense Systems |
Defended by ABM systems like THAAD, Aegis |
Very challenging to intercept with current defenses |
|
Role and Usage |
Strategic deterrence (ICBMs, nuclear), conventional strikes |
Precision strikes, capable of defeating modern defenses |
|
Development Status |
Established for decades, widely deployed |
Emerging technology, still under development |
|
Cost and Complexity |
High cost but relatively mature technology |
Expensive, cutting-edge technology, still evolving |
|
Flight Environment |
Re-enters Earth's atmosphere from space (ICBMs) |
Entire flight is within the atmosphere |
|
Interception Difficulty |
Medium (depending on missile type, can be intercepted with ABM systems) |
Very high (due to speed and unpredictability) |
|
Example Countries |
U.S., Russia, China, North Korea, India, etc. |
U.S., Russia, China, India (in development stages) |
Conclusion
India’s successful flight test of the long-range hypersonic missile marks a significant step in strengthening its defence capabilities. The test confirms India’s position as a key player in the global race to develop advanced military technologies, specifically hypersonic weapons. While challenges remain in developing these weapons—particularly related to heat, precision, and communication—the advantages of speed, maneuverability, and long-range strike capabilities make hypersonic missiles a game-changing asset for national security.
With this achievement, India has further solidified its military strength and enhanced its technological standing in the field of hypersonic weapons.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus