- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Report on Compressed Bio-Gas plants
Report on Compressed Bio-Gas plants
07-08-2023
plants-1691499244067.png)
Latest Context:
Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee (PSC) submitted its report in the parliament regarding the review on implementation of Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) plants.
- In 2018, Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas launched Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) initiative.
- SATAT initiative aims to set up 5000 Compressed Biogas (CBG) plants for the production of atleast 15 Million Metric Ton (MMT) per annum of CBG by the year 2023-24.
Key highlights of the report are:
- PSC found that CBG projects are not being implemented at the desired rate, only around 40 CBG plants have been established so far.
- Need to provide financial support for the development of pipeline infrastructure for connecting CBG projects with the City Gas Distribution (CGD) network.
- Need to set up “Bio Fuel Infrastructure Fund” and to establish “Credit Guarantee Fund” to improve the availability of credit to CBG projects.
- It is necessary to develop a solid mechanism for coordination with other ministries and agencies.
About Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG)
- CBG also known as Bio-CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), is a type of renewable energy that is produced from organic waste materials through a process called “anaerobic digestion”.
- Anaerobic digestion involves the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen by bacteria and other microorganisms, leading to the production of biogas.
- Biogas primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), along with little amounts of other gases.
- It is produced from various organic feedstocks such as agricultural residues, food waste, sewage sludge, and other biodegradable materials.
- To convert biogas into CBG, it undergoes a purification process to remove impurities like CO2, water vapour, hydrogen sulfide and siloxanes, resulting in a gas that is primarily methane.
- The purified methane gas is then compressed to high pressures, similar to the compression process used for natural gas, which leads to the production of Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG).
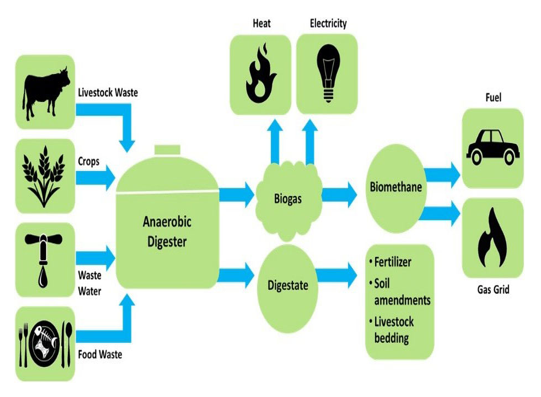
Applications of CBG are:
- Transportation: CBG can be used as a fuel for vehicles, especially in CNG vehicles. It offers a more environmentally friendly and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, as it reduces greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Cooking and Heating: CBG can be used for cooking and heating purposes, particularly in areas with limited access to traditional energy sources. It provides a cleaner and renewable option compared to traditional fuels like firewood or charcoal.
- Industrial Applications: CBG can be used in industrial processes that require heat or fuel, helping industries reduce their carbon footprint and reliance on non-renewable resources.
- Power Generation: In addition to being used directly as fuel, CBG can also be used in gas engines to generate electricity, providing a decentralized and cleaner energy source.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi



