- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
RBI's Balance Sheet Grows Significantly in FY24
RBI's Balance Sheet Grows Significantly in FY24
01-06-2024
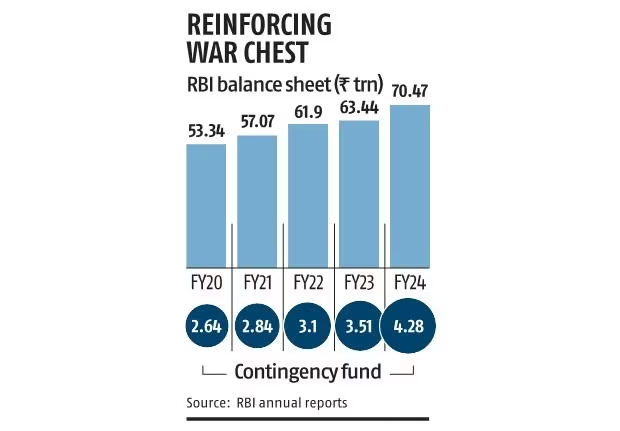
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reported a substantial 11.08% increase in its balance sheet size to ₹70.47 lakh crore for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024 (FY24).
- This growth is attributed to increased liquidity and foreign exchange operations, with notable increases in foreign investments, gold holdings, and loans and advances on the asset side.
- On the liability side, the expansion was driven by increased notes issued, deposits, and other liabilities.
How the RBI Generates Income:
The RBI employs various methods to generate income, including:
- Interest on Loans and Advances: Charging interest on loans provided to commercial banks and the government.
- Investments: Earning interest on investments in government securities and foreign assets.
- Foreign Exchange Operations: Profiting from buying and selling foreign currencies and managing foreign exchange reserves.
- Issue of Currency: Generating seigniorage, the profit made from issuing currency.
- Management of Government Accounts and Other Services: Charging fees and commissions for various services.
- Open Market Operations: Buying and selling government securities in the open market.
- Discount and Rediscount Operations: Providing liquidity to commercial banks and charging interest.
- Penalties and Fines: Imposing penalties on non-compliant financial institutions.
- Miscellaneous Income: Earning from subsidiary organisations and other financial services.
Key Highlights of RBI's Financial Performance in FY24
- The balance sheet size increased by 11.08% to ₹70.47 lakh crore, driven by increased liquidity and forex operations.
- The balance sheet size now represents 24.1% of India's GDP, normalising to pre-pandemic levels.
- Net income surged by 141.22% due to reduced expenditures and lower provisions.
- Expenditures declined by 56.29% to ₹64,694.33 crore, including a ₹42,819.91 crore provision transferred to the contingency fund.
- The surplus transferred to the central government increased to ₹2.1 trillion in FY24.
Overall, the RBI's financial performance in FY24 reflects its diverse income sources and active role in managing India’s monetary and financial systems.
Must Check: UPSC Coaching Institute In Delhi