- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman Spectroscopy
30-04-2024
The researchers used a non-invasive laser technique called Raman spectroscopy to identify the origin of the ivory.
- This technology enables law enforcement and customs agencies to differentiate between the ivory of extinct mammoths and living elephants.
What is Raman Spectroscopy?
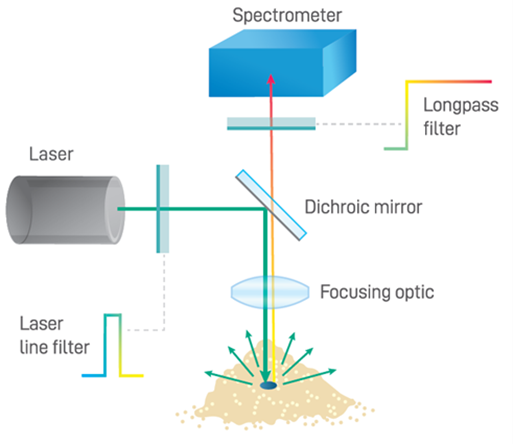
- A light-scattering technique: Raman spectroscopy analyzes how light scatters after interacting with the molecules of a sample. It provides information about the chemical composition, phase, crystallinity, and molecular interactions within the sample.
- Based on the Raman Effect: Discovered by Sir C.V. Raman, the effect describes how a small portion of light scatters at wavelengths different from the incident light source due to interactions with the molecule's vibrations.
How Raman Spectroscopy Works:
- Excitation: A laser beam (usually visible or near-infrared) is focused on the sample.
- Interaction: The laser light interacts with the molecules, causing them to vibrate.
- Scattering: Most of the light scatters at the same wavelength as the laser (Rayleigh scattering). However, a tiny fraction scatters at different wavelengths (Raman scattering).
- Detection: The scattered light is collected and passed through a spectrometer, which separates the light based on wavelength.
- Raman Spectrum: The spectrometer produces a Raman spectrum, a graph of the intensity of scattered light versus its energy difference from the laser source (expressed in wavenumbers, cm⁻¹).
Raman Spectroscopy's Role
- Vibrational Fingerprint: Raman spectroscopy focuses a laser on the ivory. Light scatters reveals information about the vibrational modes of the molecules present within the sample.
- Unique Spectroscopic Signature: Differences in the composition of mammoth and elephant ivory result in different Raman spectra for each type.
- Database Comparison: The researchers have created a database of known Raman spectra from both elephant and mammoth ivory. When an unknown ivory sample is analyzed, its spectrum is compared to this database.
- Detection Accuracy: This comparison allows a high degree of accuracy in classifying ivory as follows:
- Elephant: Indicating illegal poaching and trade of ivory from recently killed elephants.
- Mammoth: Indicating that the ivory is from an extinct species. Trade with mammoth ivory often has different legal regulations.
Advantages for Law Enforcement
- Non-destructive: Raman spectroscopy doesn't damage the valuable ivory sample.
- Portable: Handheld devices allow for rapid on-site analysis at customs checkpoints.
- Deterrent: This technology provides a strong tool to deter poaching and illegal wildlife trade.
Applications of Raman Spectroscopy:
Raman spectroscopy has a wide range of uses across industries and research:
- Material Identification: Used to identify unknown substances as each molecule has a unique Raman fingerprint.
- Pharmaceuticals: Analysis of drug purity, active ingredient distribution, and polymorphism.
- Art and Archaeology: Non-destructive analysis of pigments in paintings, inks, and historical artifacts.
- Medical Diagnostics: Potential for the detection of diseases like cancer based on changes in the Raman spectra of tissues and biofluids.
- Semiconductor Industry: Characterization of thin films, stress measurements, crystal defects, etc.
- Environmental Science: Identification and monitoring of pollutants and microplastics.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



