- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 9th APRIL 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 9th APRIL 2025
09-04-2025

Mount Kanlaon
Why in news?
- Mount Kanlaon, a highly active volcano in the Philippines, recently erupted dramatically, spewing a massive ash plume that soared 4,000 meters (2.5 miles) high into the atmosphere.
About Mount Kanlaon:
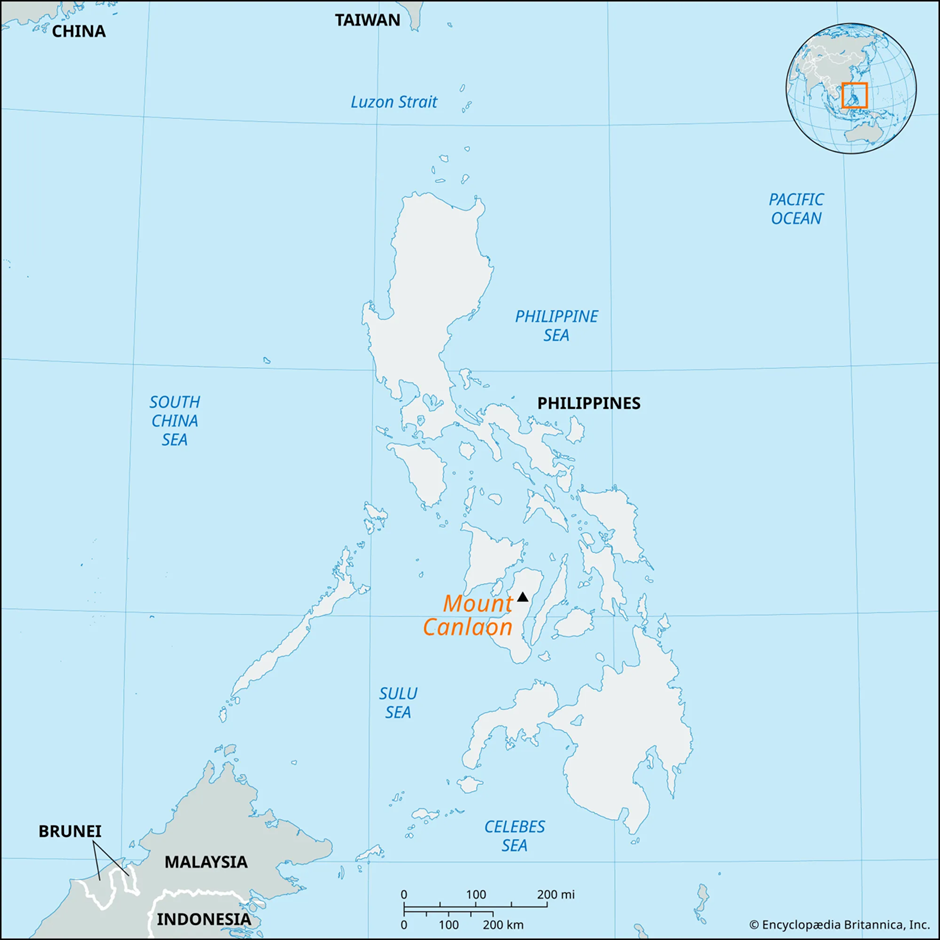
- Location:
- Mount Kanlaon is a stratovolcano situated in the north-central region of Negros Island, Philippines. It stands as the highest mountain on Negros and ranks as the 42nd tallest island peak in the world.
- It forms part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area known for frequent seismic and volcanic activity due to tectonic plate movements.
- Volcanic Features and Activity:
- Kanlaon’s structure includes multiple pyroclastic cones and craters. Its summit features a large northern caldera with a crater lake and a smaller, historically active southern crater.
- The volcano spans a base measuring 30 km by 14 km, underlain by layered volcanic deposits such as lava flows, lahar, airfall tephra, and pyroclastic materials.
- Its slopes support rich biodiversity and serve as critical watersheds for major river systems on Negros Island.
- Recorded eruptions since 1866 have mainly been phreatic explosions, typically moderate in scale, producing localised ashfall.
- Reason Behind Eruption:
- Kanlaon’s activity is primarily driven by subduction processes at the Philippine Mobile Belt, where tectonic plates collide, generating magma and pressure beneath the volcano.
- Phreatic eruptions, like the recent one, occur when groundwater interacts with hot volcanic materials, causing steam-driven explosions without new magma reaching the surface.
Mesopotamia Region
Why in news?
- In southern Mesopotamia's Eridu region, researchers have uncovered a vast, well-preserved network of ancient irrigation canals, shedding new light on the agricultural techniques of early civilizations.
About Mesopotamia Region:
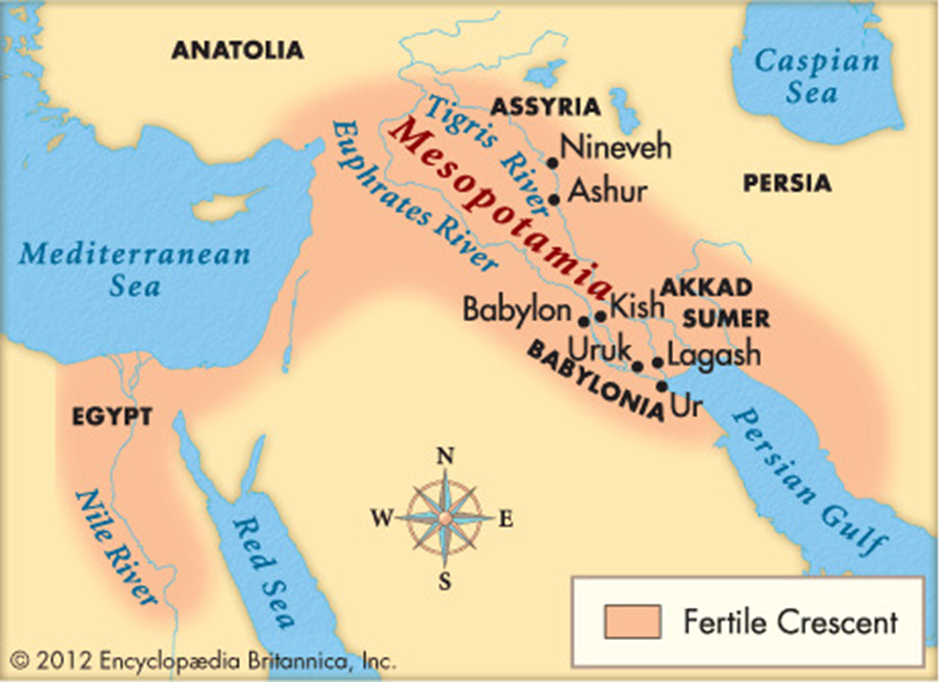
- Location and Historical Significance:
- Mesopotamia, meaning “land between rivers”, refers to the fertile region nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
- It forms part of the Fertile Crescent, stretching across modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Syria, and parts of Turkey, and is often referred to as the “Cradle of Civilisation”.
- The region witnessed the rise of ancient civilisations like Sumer, Assyria, and Babylonia, where early innovations such as settled agriculture, urban planning, and cuneiform writing took root.
- Flourishing for over three millennia, Mesopotamia remained a dominant force in the Near East until its decline following Cyrus the Great’s conquest in 539 BC and eventual cultural dissolution by the 1st century AD.
- Trade with the Indus Valley Civilisation:
- Mesopotamia maintained extensive trade relations with the Indus Valley Civilisation, often referred to as Meluhha in Mesopotamian texts.
- Archaeological and textual evidence confirms that goods like timber, ivory, beads, lapis lazuli, and textiles were exchanged.
- Mesopotamian cities such as Ur and Uruk received Indian goods via long-distance trade networks, possibly through the Persian Gulf, highlighting the maritime trade prowess of both civilisations.
- This inter-regional commerce not only facilitated material exchange but also enabled the transfer of ideas, technologies, and agricultural techniques.
- Recent Discovery of Irrigation Canals:
- A ground-breaking discovery in the Eridu region near Basra, Iraq, has revealed a well-preserved irrigation system dating back to the sixth century to early first millennium BC.
- Led by geoarchaeologist Jaafar Jotheri, the team identified over 200 main canals and 4,000 smaller branches linked to more than 700 farms, using satellite imagery, drone photography, and field surveys.
- The canals, designed to divert water from the Euphrates, employed gravity-based systems and crevasse splays to distribute water across the floodplains.
- This find offers invaluable insights into the ingenuity of early Mesopotamian farmers and the evolution of agricultural management over centuries.
Bornadi Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- A Nature Camp was held at Bornadi Wildlife Sanctuary in Assam’s Udalguri district to promote conservation awareness and eco-education.
About Bornadi Wildlife Sanctuary:
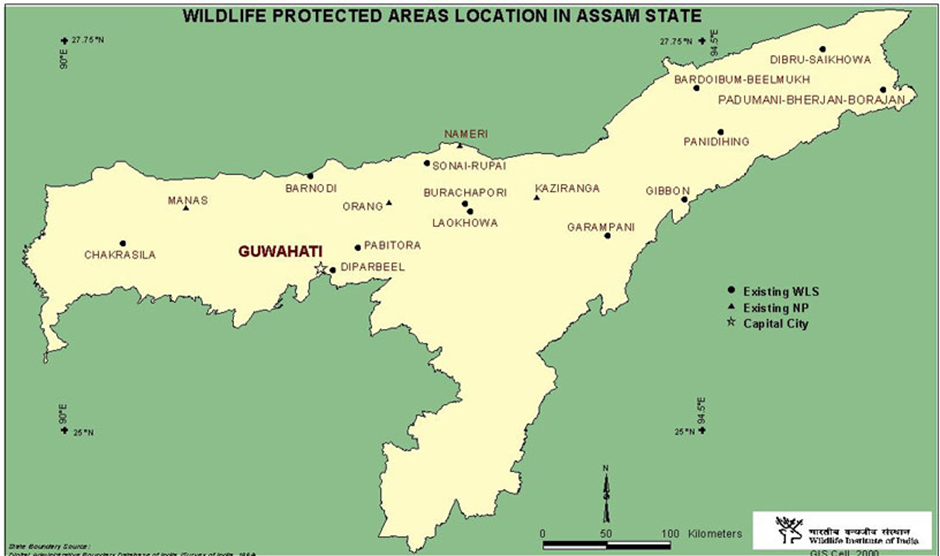
- Location and Geographical Features:
- Bornadi Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Udalguri and Baksa districts of Assam, India, along the foothills of the Himalayas, bordering Bhutan to the north.
- Spanning an area of 26.22 km², it is named after the Bornadi River, which flows along its western boundary.
- The sanctuary lies about 30 km from Tangla and 130 km from Guwahati.
- Established in 1980, it was primarily created to protect endangered species like the hispid hare and pygmy hog. The region experiences a generally warm climate.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Bornadi is rich in biodiversity, home to rare and endangered mammals such as the clouded leopard, golden langur, hoolock gibbon, and deer species.
- It also shelters a variety of bird species, including the white-capped redstart, blue magpie, peafowl, hornbill, Bengal florican, and several types of cormorants and herons.
- The sanctuary plays a vital role in wildlife conservation and supports a diverse ecosystem in the region.
Rocky Mountains
Why in news?
- A recent study reveals that snowpack in the Rocky Mountains is contaminated with mercury and other toxic metals, raising concerns about ecosystem and water quality impacts.
About Rocky Mountains:
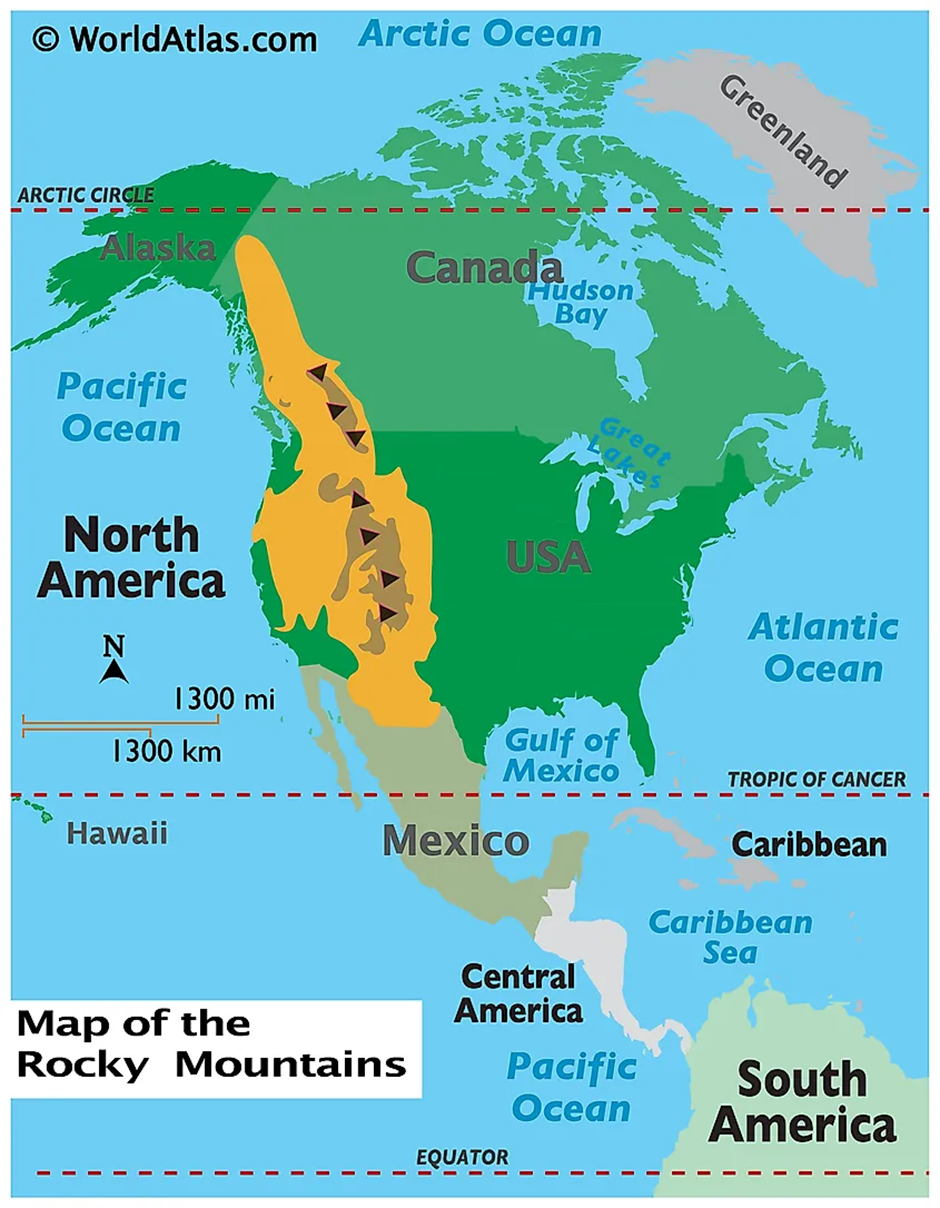
- Location and Geography:
- The Rocky Mountains, often called the Rockies, stretch over 4,800 kilometres from northern British Columbia in Canada through the western United States, including states like Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, and New Mexico.
- These majestic mountain ranges are characterised by rugged peaks, deep valleys, alpine meadows, and extensive forests.
- The range plays a critical role in shaping the geography and hydrology of western North America, acting as a major watershed divide for rivers flowing to both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
- Climate and Regional Impact:
- The Rockies have a diverse climate due to their vast latitudinal range and elevation. In general, they experience cold winters with heavy snowfall and mild summers.
- The range significantly influences regional weather patterns. One notable phenomenon is the Chinook winds—warm, dry winds that descend the eastern slopes of the Rockies, rapidly increasing temperatures and melting snow.
- These winds impact agriculture, wildlife behaviour, and water availability in regions like Alberta and Montana.
- Snowpack Contamination and Causes:
- A recent study published in Environmental Pollution has revealed that the snowpack in the Rocky Mountains is contaminated with mercury and other toxic metals like zinc, cadmium, and antimony.
- Researchers from the Desert Research Institute (DRI) and other institutions collected snow samples from 48 sites across the range during the spring of 2018.
- They found the highest contamination levels in the northern Rockies, particularly in Montana, Idaho, and northern Wyoming.
- The contaminants were traced to atmospheric deposition originating from current and historical mining operations in the Pacific Northwest and Rocky Mountain states.
- Storm systems carried dust and pollutants into the mountain range, depositing them onto the snowpack.
- Though metal levels were within EPA safety guidelines, their presence is significant because dust and contaminants can reduce snow reflectivity, leading to faster snowmelt and altering water availability.
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary generated ₹5 crore revenue in 2024–25 and introduced new SOPs to boost eco-tourism and strengthen conservation efforts.
About Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary:
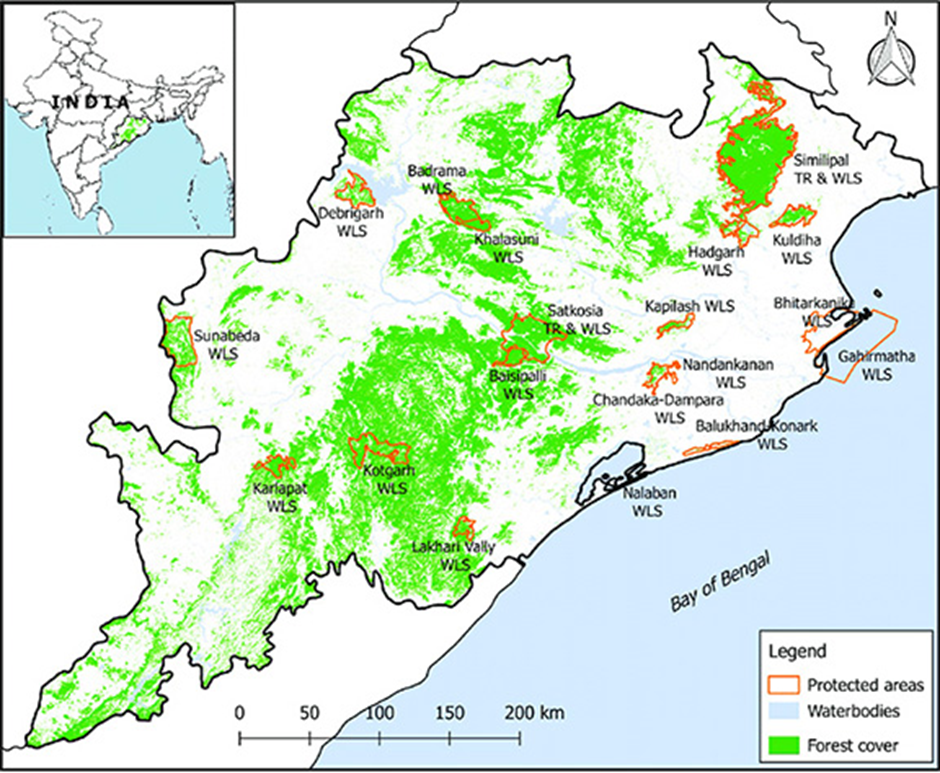
- Location and Geography:
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Bargarh district of Odisha, covering an area of 346.91 km².
- It lies close to Hirakud Dam, near Sambalpur city, and is bordered on the east and north by the vast Hirakud reservoir.
- This strategic location makes Debrigarh one of the few sanctuaries in Odisha that support both terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity.
- Recognised as an eco-sensitive zone, the area is protected from industrial activities to preserve its rich ecological value.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary is home to over 250 plant species, many of which hold medicinal and ethnobotanical importance.
- It supports a rich variety of wildlife, including more than 40 species of mammals, 200 species of birds, 40 reptiles, 12 amphibians, 42 fish species, 85 butterflies, 39 odonates, and 38 spiders.
- Key animals found here include cheetal, sambar deer, gaur, wild boar, leopard, Indian wild dog, langur, bear, and chowsingha.
|
Also Read |
|
| NCERT Books For UPSC | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Best IAS Coaching in Delhi |