- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 3rd JULY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 3rd JULY 2025
03-07-2025

1. SUDAN
Why in the News?
- Millions of people are suffering because of the war in Sudan.
- The United Nations World Food Programme (WFP) has warned that food aid is running out. If help does not come soon, many people may face hunger and even famine.
- A UN meeting is happening in Spain this week to ask countries for more help.
What are the Key Highlights?
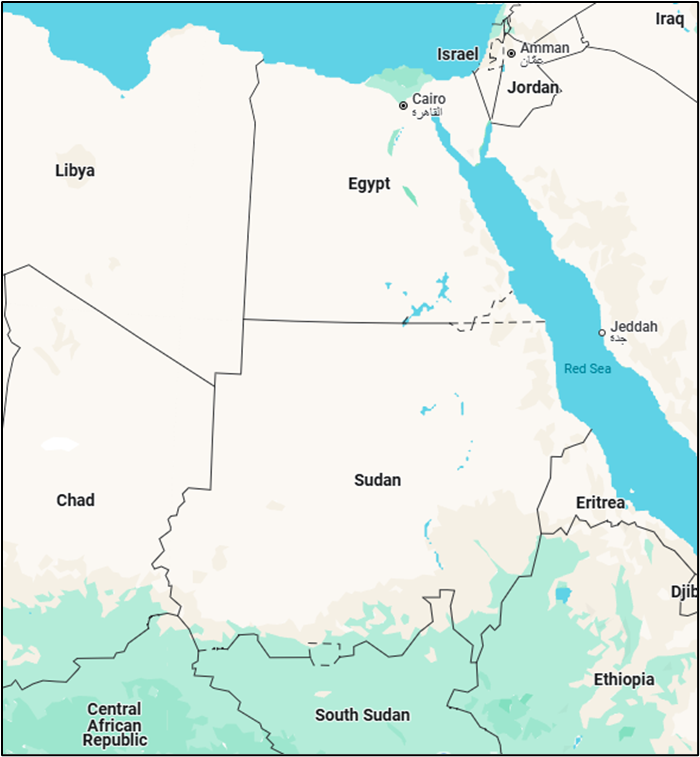
- Sudan, officially the Republic of Sudan, is located in Northeast Africa.
- Geographical Coordinates and Borders:
- Coordinates: Approximately centered at 15°N, 30°E.
- Borders:
- North: Egypt
- Northeast: Borders the Red Sea
- East: Eritrea and Ethiopia
- South: South Sudan
- Southwest: Central African Republic
- West: Chad
- Northwest: Libya
- Area: Approximately 1,861,484 km², making it the 15th largest country in the world by land area.
- Coastline: Sudan has a Red Sea coast (providing a coastline of about 853 km)
- Topography and Physical Features:
- Landscape: Sudan features diverse terrain:
- Deserts: The Nubian Desert in the northeast and parts of the Sahara Desert in the northwest dominate much of the country.
- Nile River: The White Nile and Blue Nile converge in Khartoum, the capital, forming the main Nile River, which is a lifeline for agriculture and settlement.
- Mountains: The Nuba Mountains in the south-central region and the Jebel Marra plateau in Darfur (western Sudan) are significant highland areas.
- Savanna and Grasslands: Southern and western regions transition into savanna, supporting agriculture and pastoralism.
- Landscape: Sudan features diverse terrain:
- Highest Point: Mount Kinyeti (3,187 meters) in the Imatong Mountains, though this is now in South Sudan after the 2011 split.
- Climate: Predominantly arid and semi-arid, with tropical climates in the south. Rainfall varies from nearly zero in the northern deserts to 500–1,000 mm annually in the south.
- Political and Administrative Divisions:
- Capital: Khartoum (though Giza has served as a temporary administrative capital during recent conflicts).
- States: Sudan is divided into 18 states (wilayat), including Khartoum, North Kordofan, South Darfur, and Red Sea, among others.
- Population and Demographics:
- Population: Approximately 47 million (based on recent estimates).
- Ethnic Groups: Diverse, including Sudanese Arabs, Nubians, Beja, Fur, Zaghawa, and others.
- Languages: Arabic (official), English (co-official), and numerous indigenous languages like Nubian, Beja, and Fur.
- Religion: Predominantly Sunni Islam, with small Christian and animist minorities.
- History and Political Context:
- Historical Background: Sudan was under Anglo-Egyptian rule until gaining independence in 1956.
- It has faced internal conflicts, notably the Darfur conflict and the civil war that led to South Sudan's secession in 2011.
- Recent Developments:
- Since April 2023, Sudan has been embroiled in a civil war between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), causing widespread displacement and a humanitarian crisis.
- Over 7.7 million people have been displaced, with 2.2 million fleeing to neighboring countries like Chad and Egypt.
- Economy
- Main Sectors: Agriculture (cotton, sorghum, millet), oil (though production declined after South Sudan’s secession), and livestock.
- Challenges: Economic instability due to conflict, sanctions, and reliance on agriculture in a largely arid environment.
- Currency: Sudanese Pound (SDG).
- Humanitarian Situation:
- Crisis: The ongoing conflict has led to severe food insecurity, with millions facing famine risks. Infrastructure, including hospitals and schools, has been heavily damaged.
- Refugees: Sudan hosts refugees from neighboring countries (e.g., Ethiopia, Eritrea) while also producing millions of internally displaced persons (IDPs) and refugees.
- Cultural and Historical Significance
- Archaeological Sites: Sudan is home to ancient Nubian and Kushite civilizations, with UNESCO sites like the Pyramids of Meroë and Jebel Barkal.
- Cultural Diversity: A blend of Arab, African, and indigenous traditions shapes Sudan’s music, dance, and cuisine.
- Geopolitical Importance:
- Strategic Location: Sudan’s Red Sea coast makes it a key player in regional trade and geopolitics, with Port Sudan serving as a vital hub.
- Regional Influence: Sudan is a member of the African Union, Arab League, and Organization of Islamic Cooperation, though its role has been limited by internal instability.
- Environmental Challenges:
- Desertification: Northern regions face encroaching desertification due to climate change.
- Water Resources: Dependence on the Nile River creates tensions with downstream countries like Egypt over water rights (e.g., disputes over Ethiopia’s Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam).
2. CUBA
Why in the News?
- Cuba is going through a very tough time. There are serious shortages of food, fuel, and medicines. People face long power cuts, and many parts of the country do not have working factories or services.
- In the past, Cuba often got help from Russia. But now, many of Russia’s promises have not been fulfilled.
- Instead, China has quietly started helping Cuba in important ways. In 2025, China is building 55 solar power plants in Cuba. One of them, a 21 MW solar park, has already started working near a small town called Jatibonico.
- This shows that China is becoming a strong partner for Cuba, especially through its Belt and Road Initiative.
What are the Key Highlights?
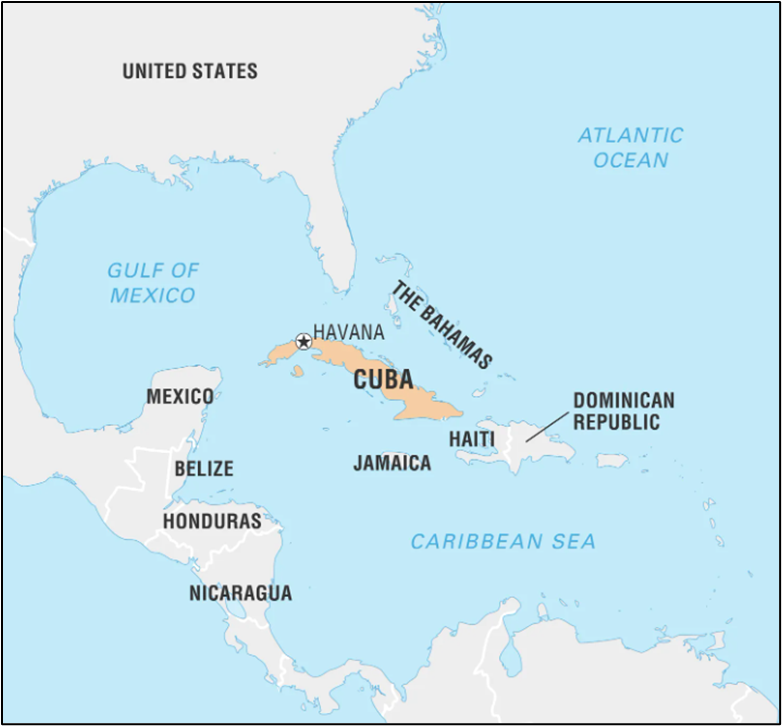
- Cuba, officially known as the Republic of Cuba, is an island nation located in the Caribbean, at the intersection of the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean.
- Geographical Coordinates and Location:
- Coordinates: Approximately 21.5°N latitude and 80°W longitude.
- Bordering Nations of Cuba:
- North: United States (Florida): Approximately 150 km (90 miles) across the Straits of Florida. The closest point is between Key West, Florida, and Havana, Cuba.
- West: Mexico: The Yucatán Peninsula is about 210 km (130 miles) from Cuba’s western tip across the Yucatán Channel.
- South: Jamaica: Roughly 140 km (87 miles) south of Cuba’s southern coast across the Caribbean Sea.
- Cayman Islands (United Kingdom territory): Approximately 150 km (93 miles) southwest of Cuba.
- East:
- Haiti: About 77 km (48 miles) east of Cuba’s eastern tip (near Guantanamo Bay) across the Windward Passage.
- Dominican Republic: Further east, beyond Haiti, sharing maritime boundaries indirectly via the Caribbean Sea.
- Northeast:
- The Bahamas: Approximately 100 km (62 miles) north of Cuba’s northern coast, particularly near the eastern provinces.
- Area: Total land area of approximately 109,884 km², including the main island and smaller islets like the Isle of Youth (Isla de la Juventud).
- Coastline: About 5,746 km, with numerous beaches, bays, and coral reefs.
- Topography and Physical Features:
- Landscape:
- Main Island: The island of Cuba is long and narrow, stretching about 1,250 km east to west and 191 km at its widest point.
- Mountains: The Sierra Maestra in the southeast is the highest range, with Pico Turquino (1,974 meters) as the highest peak.
- Other ranges include the Sierra de los Órganos in the west and the Escambray Mountains in the central region.
- Plains and Valleys: Fertile plains, such as the Cauto River Valley, support agriculture (e.g., sugarcane, tobacco).
- Coastal Features: Cuba has over 200 bays and 289 beaches, with notable areas like Varadero Beach and the Zapata Peninsula (a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve).
- Climate:
- Tropical, with a wet season (May–October) and a dry season (November–April).
- Average temperatures range from 21°C (70°F) in winter to 27°C (81°F) in summer.
- Cuba is prone to hurricanes, especially from August to November.
- Rivers: The Cauto River (343 km) is the longest, flowing through the eastern provinces.
- Landscape:
- Political and Administrative Divisions:
- Capital: Havana (La Habana), the largest city and economic hub.
- Provinces: Cuba is divided into 15 provinces and one special municipality (Isle of Youth).
- Key provinces include Havana, Santiago de Cuba, and Pinar del Río.
- Population and Demographics:
- Population: Approximately 11.2 million (based on recent estimates).
- Languages: Spanish (official).
- Religion: Predominantly Christian (Catholic and Protestant), with Afro-Cuban religions like Santería widely practiced.
- Cultural Significance:
- Cultural Heritage: Cuba is known for its vibrant music (salsa, son, rumba), dance (mambo, cha-cha), and literature.
- Landmarks: Old Havana (UNESCO site), Viñales Valley (UNESCO site), and the Che Guevara Mausoleum in Santa Clara.
- Cuisine: Features dishes like ropa vieja, arroz con pollo, and mojitos.
- Economy Main Sectors:
- Agriculture: Sugarcane, tobacco, coffee, and citrus fruits.
- Tourism: A major revenue source, with attractions like Havana’s historic district (a UNESCO World Heritage Site) and Varadero’s beaches.
- Other Industries: Biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and nickel mining (Cuba has one of the world’s largest nickel reserves).
- Environmental Issues:
- Environmental Challenges: Deforestation, soil degradation, and vulnerability to hurricanes and climate change (e.g., rising sea levels threaten coastal areas).