- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 28th DECEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 28th DECEMBER 2024
28-12-2024

Brahmaputra River
Why in news?
- China has defended its plan to build the world's largest dam on the Brahmaputra River (Yarlung Zangbo) in Tibet, stating it won't harm lower riparian states like India and Bangladesh.
- Estimated at ₹137 billion, the dam is located in a seismically active Himalayan region, raising ecological and geopolitical concerns.
About Brahmaputra River:
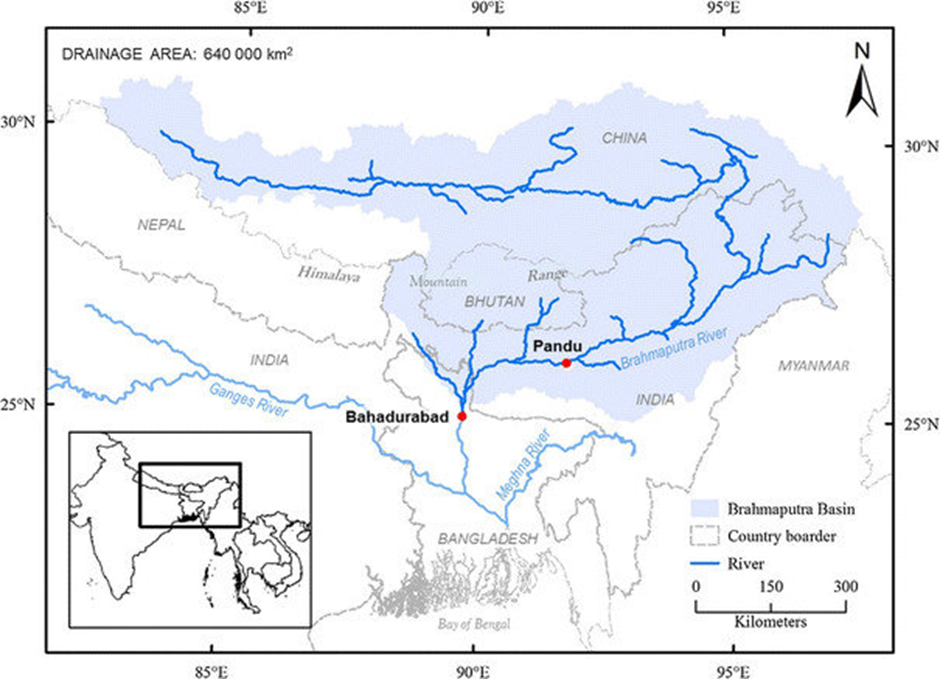
- Geography and Location:
- The Brahmaputra River originates in the Chemayungdung Glacier in the Tibetan Himalayas, flowing eastward as the Yarlung Zangbo River before making a dramatic U-turn at the Namcha Barwa mountain to enter Arunachal Pradesh, India.
- It then flows through Assam and Bangladesh, where it merges with the Ganges to form the Meghna River, eventually emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The river spans approximately 2,900 kilometres, making it one of the world's longest rivers.
- The Brahmaputra has numerous tributaries, contributing to its vast drainage system. Key tributaries in India include the Dibang, Lohit, and Subansiri Rivers in Arunachal Pradesh and the Manas and Teesta Rivers in Assam.
- Economic significance:
- The Brahmaputra supports agriculture and fisheries, which are vital for the livelihoods of millions in the region. The fertile alluvial plains, created by seasonal floods, make the valley a prime agricultural zone for crops like rice, jute, and tea.
- Additionally, its vast water resources facilitate inland navigation, connecting remote areas and supporting trade.
- The river is a powerhouse for hydroelectric energy. Several projects, like the Subansiri Lower Dam, aim to harness its potential for renewable energy. However, its flow through seismic zones and ecologically sensitive areas poses challenges to large-scale energy projects.
- Ecological importance:
- The Brahmaputra sustains a diverse flora and fauna. Its basin is home to grasslands, wetlands, and forests, which support species like the Indian rhinoceros, Bengal tiger, and Gangetic dolphin.
- Migratory birds also thrive in the region, making it a biodiversity hotspot. The wetlands and floodplains provide critical habitats for these species, despite threats from habitat loss and human activities.
- Concerns about Brahmaputra dam:
- The planned Brahmaputra dam in Tibet highlights its geographical and strategic importance. Located near a tectonic plate boundary, the dam is positioned in one of the most seismically active zones in the world. The region frequently experiences earthquakes, posing a significant challenge to the dam's structural integrity.
- The dam's location near the Indian border raises geopolitical concerns. China’s ability to regulate water flow could affect downstream nations like India and Bangladesh. In times of conflict, this control might be weaponised, leading to potential flooding or water shortages in border regions.
- Engineering challenges are amplified by the dam's scale and location. Building such a massive structure in a high-altitude region with harsh weather conditions requires advanced technology and extensive resources. The site's remote location also complicates logistics and increases costs.
- Ecological implications include threats to biodiversity and the disruption of natural river flow. Changes in sediment transport could impact fertile plains downstream, reducing agricultural productivity. The project might also affect fish migration and other aquatic life, further straining the river's ecosystem.
- In the Indian context, the dam could exacerbate regional tensions. It underscores the need for robust water-sharing agreements and effective dialogue between India and China. The Expert Level Mechanism (ELM), established in 2006 for trans-border river discussions, has facilitated data sharing, but more comprehensive measures are necessary to ensure equitable water distribution.
You Can Read Also: PLACES IN NEWS 27th DECEMBER 2024
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary in Odisha is set to receive a pair of tigers from Madhya Pradesh as part of a tiger relocation program to bolster its predator population and restore ecological balance.
About Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary:
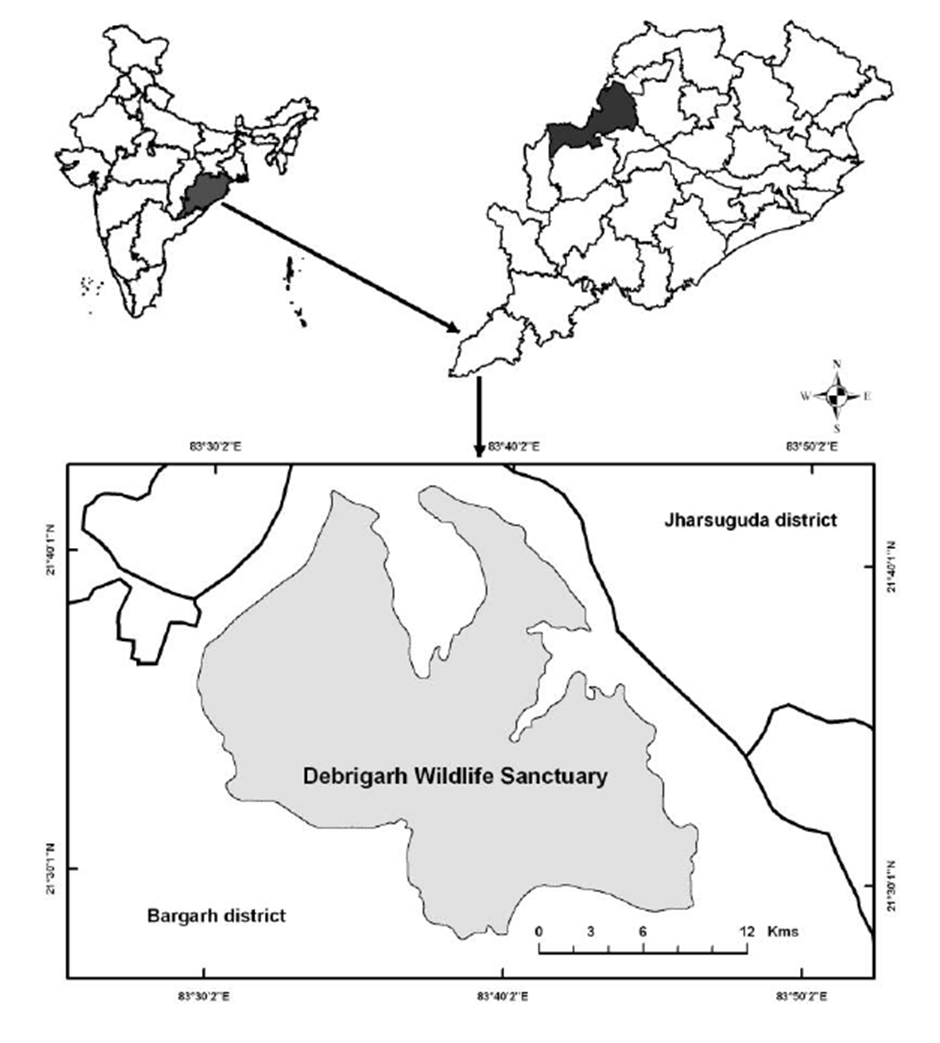
- Geography:
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Bargarh district of Odisha, nestled along the Hirakud Reservoir, one of the largest artificial lakes in Asia.
- It covers an area of approximately 347 square kilometres, offering a mix of rugged terrain, hills, and flatlands that create diverse habitats.
- The sanctuary's proximity to the Mahanadi River and its integration with the Hirakud Dam make it ecologically significant. It serves as a vital watershed area, supporting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary features dry deciduous forests dominated by species such as sal, teak, and neem. Seasonal vegetation adds to its ecological variety, supporting a range of wildlife.
- Debrigarh is a haven for fauna, housing species like leopards, wild boars, sloth bears, and Indian bison (gaur). The sanctuary is also home to numerous herbivores, such as spotted deer and sambar, which sustain its predator population.
- The avian diversity is remarkable, with over 250 bird species, including migratory birds like the great crested grebe and egrets. Wetlands formed by the Hirakud Reservoir attract numerous waterfowl and waders.
- Aquatic ecosystems thrive in the Hirakud backwaters, harbouring fish species that support both local biodiversity and livelihoods. Crocodiles and turtles add to the sanctuary's aquatic richness.
- The sanctuary is an important site for conservation efforts, particularly for species like tigers and elephants. The planned relocation of tigers from Madhya Pradesh aims to restore predator-prey dynamics.
- Its unique blend of forest and water ecosystems makes Debrigarh an ideal destination for ecotourism, attracting visitors with its scenic landscapes and wildlife safaris.
You Can Read Also: PLACES IN NEWS 26th DECEMBER 2024
South Africa
Why in news?
- South Africa’s mining crisis is intensifying as Zama Zamas—illegal miners—engage in violent clashes with authorities.
- Operating in abandoned mines, these miners often work in hazardous conditions, driven by poverty and unemployment.
- Recent confrontations have highlighted escalating tensions, with authorities cracking down on illegal mining activities linked to organized crime and environmental damage.
About South Africa:
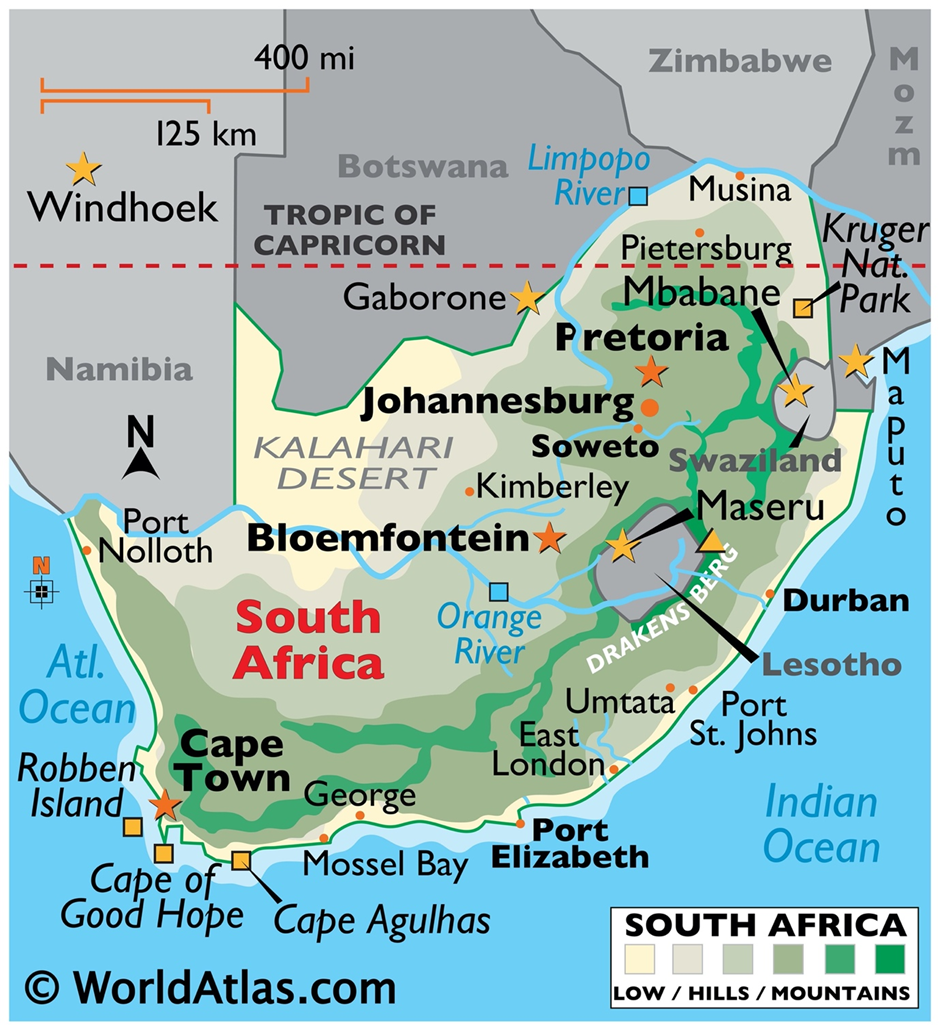
- Geography:
- South Africa is located at the southern tip of the African continent, bordered by the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. It shares land borders with Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and Eswatini and entirely surrounds Lesotho. Its geographic diversity includes vast plateaus, mountain ranges such as the Drakensberg, and coastal plains.
- The climate varies from Mediterranean along the Cape coast to subtropical in the northeast and semi-arid in the interior.
- This climatic variation supports diverse ecosystems, including savannas, grasslands, and fynbos vegetation, which is unique to the Cape Floral Region.
- Natural Resources:
- South Africa is rich in natural resources, particularly minerals. It is a global leader in the production of gold, platinum, and diamonds, alongside significant reserves of coal, manganese, and chromium.
- The country's mineral wealth has historically driven its economy but also contributed to socio-economic disparities.
- Colonial History:
- The colonial history of South Africa began with Portuguese explorers in the late 15th century, followed by Dutch colonisation in 1652 when the Dutch East India Company established a settlement in Cape Town. The British later seized control in the early 19th century, leading to conflicts with indigenous groups and Dutch settlers (Boers).
- The discovery of gold and diamonds in the 19th century transformed South Africa's economy and increased its strategic importance. This led to the Anglo-Boer Wars (1880–81, 1899–1902) between the British and Boers, resulting in British dominance and the eventual establishment of the Union of South Africa in 1910.
- South Africa's historical geography played a key role in its apartheid system, which institutionalised racial segregation and inequality from 1948 to 1994. Geographical segregation shaped urban planning and resource allocation, creating lasting disparities.
- The end of apartheid in 1994 marked a historic turning point, with Nelson Mandela becoming the first Black president. However, the legacy of apartheid persists, reflected in unequal land distribution, economic disparities, and urban-rural divides.
- Existing issues:
- The country faces existing issues such as high unemployment, poverty, and crime. Inequality remains a critical challenge, exacerbated by corruption and inefficiencies in governance. The mining sector, once a cornerstone of the economy, has seen declining productivity due to strikes, regulatory challenges, and illegal mining activities.
- Environmental degradation is another pressing issue. Decades of mining have left behind abandoned mines, polluted water systems, and degraded landscapes. The illegal mining crisis, fuelled by poverty and organised crime, further exacerbates these challenges.
- South Africa's water scarcity is a growing concern, worsened by climate change and mismanagement. Urban areas like Cape Town have experienced severe droughts, prompting measures to improve water conservation and infrastructure.
- Despite these challenges, South Africa retains its historical importance as a cultural and economic hub in Africa. Its strategic location facilitates trade, while its cultural diversity—evident in its 11 official languages—reflects its rich heritage.
Croatia
Why in news?
- Croatia’s left-leaning President Zoran Milanovic, a vocal critic of Western military support for Ukraine, seeks re-election against seven contenders, including Dragan Primorac, backed by the conservative Croatian Democratic Union.
About Croatia:

- Geography:
- Croatia is located in southeastern Europe, bordered by Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the west.
- It has a diverse geography, featuring coastal regions, mountain ranges like the Dinaric Alps, and plains in its interior. The country’s long coastline along the Adriatic Sea includes over 1,200 islands, making it a popular tourist destination.
- The climate varies from Mediterranean along the coast to continental in the interior, supporting diverse ecosystems and agricultural activities. The Adriatic coast, with its clear waters and mild winters, is particularly significant for tourism and maritime industries.
- Natural resources:
- Croatia is endowed with natural resources, including limestone, bauxite, and clay, which are used in construction and manufacturing. The country has fertile agricultural land, producing crops such as wheat, corn, and grapes.
- The Adriatic Sea supports fisheries, and Croatia is known for its olive oil and wine production. Additionally, the nation possesses modest reserves of oil and natural gas, contributing to its energy sector.
- Political status:
- Politically, Croatia operates as a parliamentary democracy. Its political system includes a largely ceremonial presidency and an active parliamentary structure led by the prime minister.
- Croatia joined the European Union (EU) in 2013, becoming its newest member state, and has embraced EU standards in governance, trade, and law.
- International participation:
- Croatia actively participates in international organizations. It became a member of NATO in 2009, aligning itself with Western military and security frameworks. NATO membership strengthens Croatia's defence capabilities and allows it to contribute to collective security measures. The country also participates in UN peacekeeping missions, underscoring its commitment to global stability.
- Croatia is a member of the United Nations (UN), the World Trade Organisation (WTO), and the Council of Europe. These affiliations reflect its engagement in global economic, political, and cultural discussions. Its role in regional initiatives, such as the Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA), emphasises its strategic importance in southeastern Europe.
- The nation has faced challenges stemming from its Yugoslav Wars history in the 1990s, but it has made significant strides in reconciliation and rebuilding. Joining NATO and the EU has marked its integration into Western institutions, enhancing economic opportunities and political stability.
UPSC CSE PYQQ1. Which of the following is/are tributary/tributaries of Brahmaputra?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (2016)
Answer: Option DQ. consider the following pairs:
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched? (2019)
|
|
Also Read |
|



