Fiji
Why in the News?
- Prime Minister of Fiji Sitiveni Rabuka visited India (Aug 2025).
- India announced training, equipment, and capacity building support to upgrade Fiji’s maritime security.
- Both countries reaffirmed commitment to a free, open, inclusive, and prosperous Indo-Pacific.
- Key outcomes:
- Cooperation in UN peacekeeping, military medicine, White Shipping Information Exchange, and cybersecurity.
- Signing of 7 MoUs, including a super-specialty hospital in Fiji and a migration & mobility pact.
- Two ambulances gifted to Fijian military forces; India to open a Defence Wing in Suva.
- Planned Indian naval ship port call to Fiji to enhance maritime interoperability.
- Fiji had earlier opposed China’s reported plan for a naval base in the Pacific Islands.
About Fiji
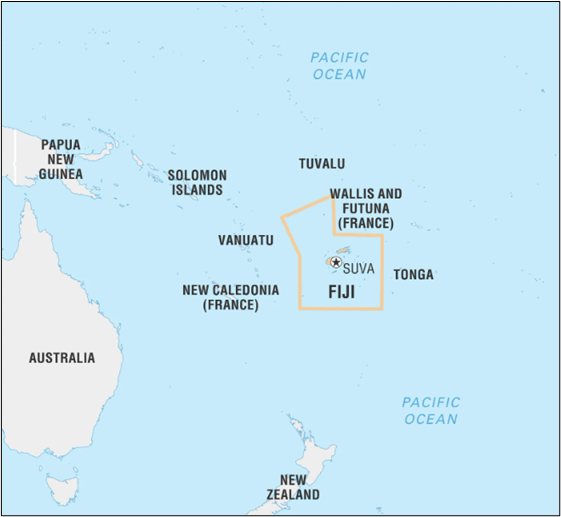
- Fiji is a sovereign island country located in Melanesia, Oceania, officially called the Republic of Fiji.
- It is strategically significant in the South Pacific and is rich in natural resources.
- Location:
- Situated in the South Pacific Ocean, about 2,000 km northeast of New Zealand.
- Bordered by the Koro Sea and forms part of Oceania’s wider Pacific archipelago.
- Capital: Suva, located on the island of Viti Levu.
- Key Features:
- Archipelago: Over 330 islands and 500 islets, with around 110 islands permanently inhabited.
- Major Islands: Viti Levu and Vanua Levu, together hosting nearly 87% of Fiji’s population.
- Geography: Volcanic in origin, with active geothermal regions on Vanua Levu and Taveuni.
- Demography: Population of mixed Austronesian and Melanesian heritage, with notable Polynesian influence.
- Currency: Fijian Dollar (FJD).
India–Fiji Relations
- Diplomatic relations were established in 1970, marking the beginning of a strong partnership.
- India has a High Commission in Suva, while Fiji maintains a High Commission in New Delhi, ensuring continuous engagement.
- Fiji plays an important role in Pacific geopolitics, and India leverages its Act East Policy and outreach to the Pacific Islands Forum to deepen ties.
- Areas of Cooperation:
- Defence & Security: Defence Cooperation MoU (2017), maritime security, capacity building.
- Trade & Economy: Bilateral trade reached USD 8.012 million (2022–23).
- India’s exports to Fiji: Pharmaceuticals, machinery, textiles, plastics, vehicles.
- Fiji’s exports to India: Wood, mineral water, and small volumes of precious stones.
- Space & Energy: MoU on space cooperation (2017) and cooperation in nuclear energy, oil, and gas.
- Education & Culture: Through ITEC, ICCR scholarships, and an IT Centre of Excellence, India supports student exchange, research, and innovation.
- Health: Agreement to build a super-specialty hospital in Fiji.
- Key Agreements Signed:
- Trade Agreement (1991)
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA, 2014)
- MoU on Defence Cooperation (2017)
- MoU on Space Cooperation (2017)
Sahel Region
Why in the News?
- The S. under President Donald Trump has reset ties with West Africa’s military regimes (Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger) on a “trade, not aid” basis.
- Washington offered counter-jihadist support in exchange for access to critical minerals like lithium, gold, and uranium.
- This marks a shift from the Biden era, when development and military aid were suspended after coups (2020–23).
- The move is part of U.S. efforts to counter Russia and China’s growing influence in the region.
- Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger welcome U.S. investment despite previously pivoting toward Russia’s Wagner/Africa Corps mercenaries.
- The Sahel remains strategically vital due to:
- Mali: Major producer of gold & lithium.
- Burkina Faso: Rich in gold reserves.
- Niger: Among top global exporters of uranium.
About Sahel Region
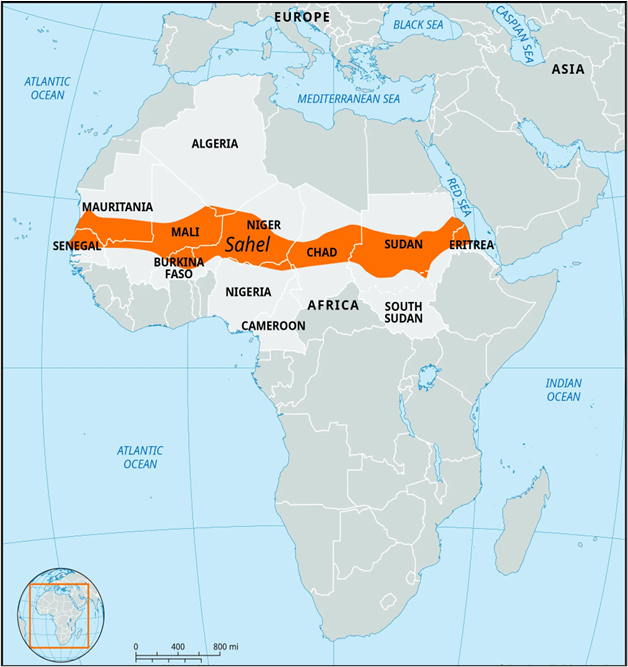
- The Sahel is a semi-arid zone located in western and north-central Africa.
- It forms a 5,000 km-long belt, extending from Africa’s Atlantic coast to the Red Sea.
- Geographically, it acts as a transition zone between:
- The arid Sahara Desert to the north, and
- The humid savannas to the south.
- Countries Covered:
- Parts of Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, and Eritrea fall within the Sahel.
- Vegetation:
- Characterised as a semi-arid steppe (dry grassland).
- Dominated by savanna-type vegetation with sparse cover.
- Features include short grasses, thorny shrubs, and scattered acacia and baobab trees.
- Socio-Political & Environmental Context:
- Since independence in the 1960s, Sahel nations have faced challenges of weak governance, economic decline, violent extremism, and climate change impacts.
- The region is also a major transit corridor for migrants moving from sub-Saharan Africa towards the Mediterranean and Europe.




