- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 25 NOVEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 25 NOVEMBER 2024
25-11-2024
Kurram, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Why in news?
- Sectarian violence has escalated in Kurram, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan after the massacre of 45 Shia travellers on November 21, 2024.
- At least 64 people have been killed in three days of clashes between Shia and Sunni tribal groups.
- Kurram, bordering Afghanistan, is home to both Shia and Sunni Pashtuns, with Shia making up 45% of the population.
- The region has a history of sectarian violence due to tribal rivalries, poor governance, and external geopolitical factors, especially involving Saudi-Iranian rivalry.
- The Soviet-Afghan War and Pakistani policies in the 1980s exacerbated these tensions, leading to the rise of militias and armed groups.
- Clashes have continued for decades, fuelled by land disputes, lack of development, and the influence of militant groups like the Pakistani Taliban and ISIS.
- Security measures and restrictions have not been effective in curbing the violence.
About Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
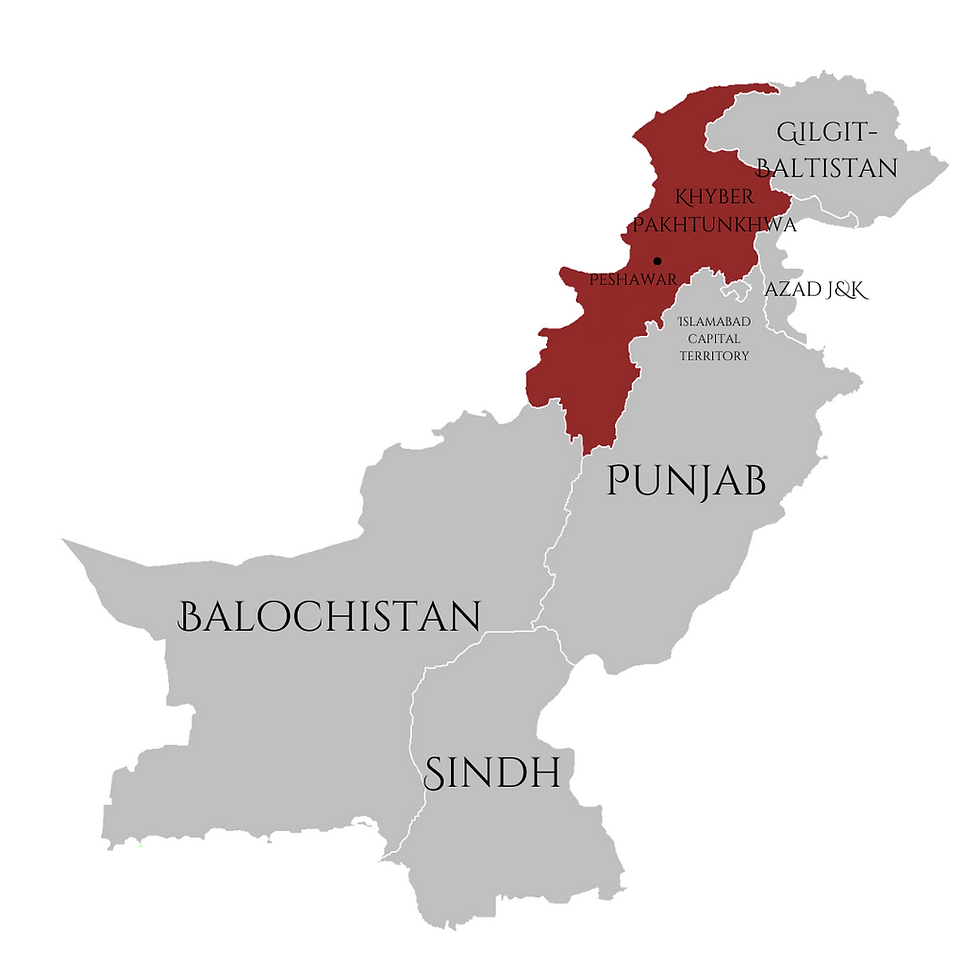
- Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) is located in the north-western region of Pakistan, bordered by Afghanistan to the west.
- It is characterized by a diverse geographical landscape, ranging from rugged mountainous terrains to fertile valleys.
- The province is part of the Hindukush mountain range, with peaks such as the Tirich Mir, the highest point in the range.
- The Khyber Pass, a historic route, connects the region to Afghanistan, playing a crucial role in trade and military movements.
- KP’s major rivers, including the Kabul River, irrigate its plains and valleys, supporting agriculture.
- The province has a semi-arid climate in the plains and colder temperatures in the mountainous areas.
- The diverse topography and proximity to Afghanistan have made KP a historically strategic region, often a centre of conflict and cultural exchange.
- Its tribal areas are also significant, housing various ethnic groups, including Pashtuns, whose traditions and language dominate the region.
- The region has natural resources such as timber, minerals, and agricultural land, contributing to its economy, though it faces challenges related to governance, security, and infrastructure.
Manila
Why in news?
- A massive fire in the Isla Puting Bato area of Tondo, Manila, on Sunday destroyed about 1,000 homes, leaving 2,000 families homeless.
- The blaze lasted for nearly eight hours, displacing around 8,000 people.
- No casualties have been reported, but residents fled on makeshift rafts or salvaged belongings as flames engulfed the densely packed slum.
- The fire's cause is under investigation, though electrical faults or gas canisters are often to blame in such areas.
About Manila:
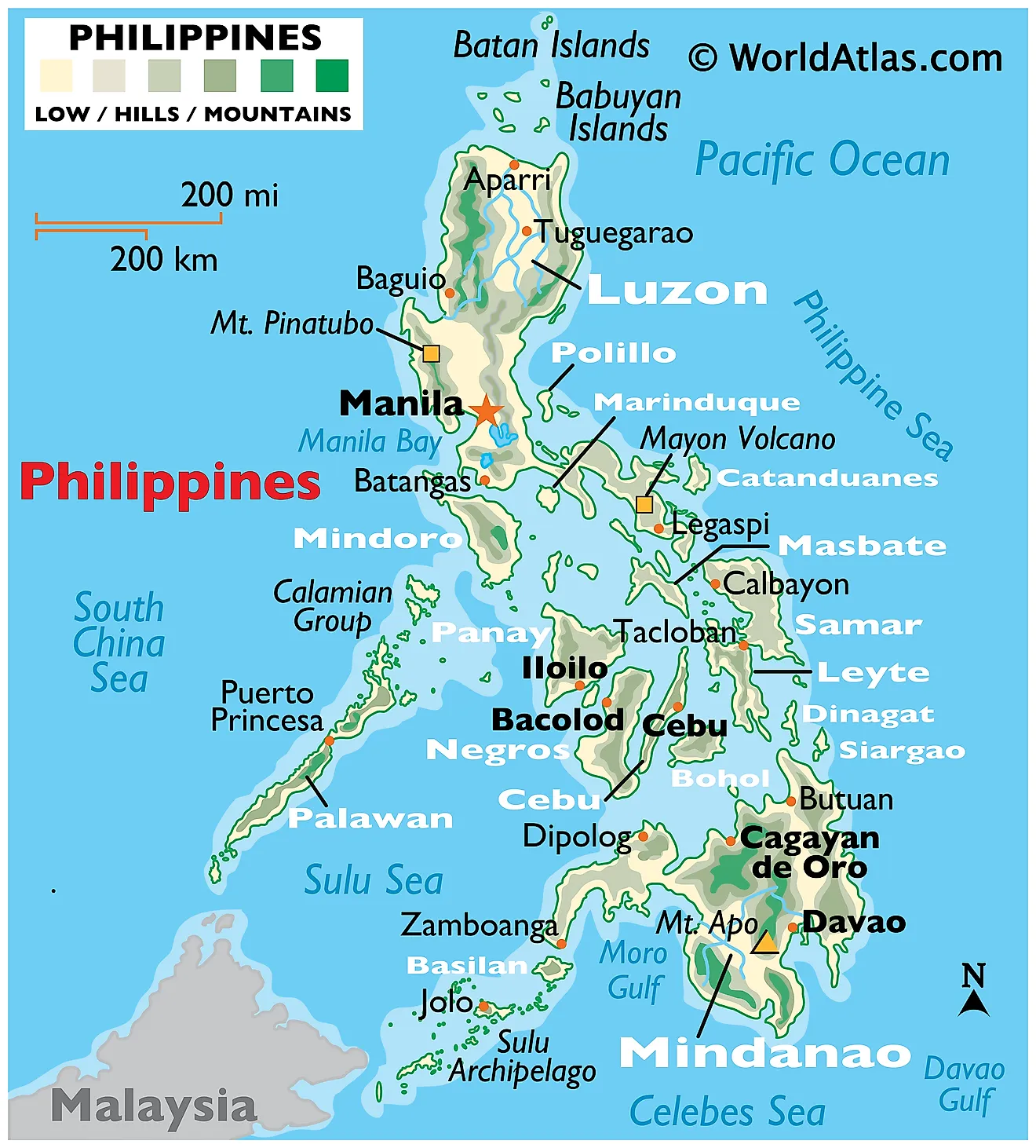
- Manila, the capital of the Philippines, is located on the western coast of Luzon, along the shores of Manila Bay.
- The city is strategically positioned with a coastline that has historically made it a key trading hub.
- Its geographic layout includes a mix of urban areas, slums, and waterfront zones. Manila’s climate is tropical, experiencing distinct wet and dry seasons, which influences its agriculture and urban infrastructure.
- Manila is traversed by several rivers, with the Pasig River being the most significant. The Pasig River flows through the heart of the city, connecting Laguna de Bay to Manila Bay.
- Economically, Manila is the financial and commercial centre of the country. It houses major industries, including trade, manufacturing, retail, and services. The Port of Manila, one of the busiest ports in Asia, plays a critical role in international trade, linking the Philippines to global markets.
- The city is also home to key financial districts, such as Makati, where many multinational companies are based.
- The city’s economic geography reflects significant disparities in wealth, with affluent areas like Makati and Bonifacio Global City contrasting with densely populated, poverty-stricken districts like Tondo and Quiapo.
- Manila also faces challenges such as overpopulation, traffic congestion, and environmental degradation, which affect both its quality of life and economic development.
Ukraine
Why in news?
- Ukraine has launched U.S.-supplied Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) at Russian territory for the first time, targeting the Bryansk region.
- The Russian defence ministry reported five missiles were intercepted, with one causing minor damage, though U.S. officials stated only two of eight missiles were intercepted.
- Russia condemned the strike as an escalation, accusing the U.S. of direct involvement, while Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov warned of potential retaliation.
- Concurrently, Russia updated its nuclear doctrine, treating non-nuclear attacks backed by nuclear powers as joint assaults, escalating nuclear tensions.
Regions affected due to Russia-Ukraine war:
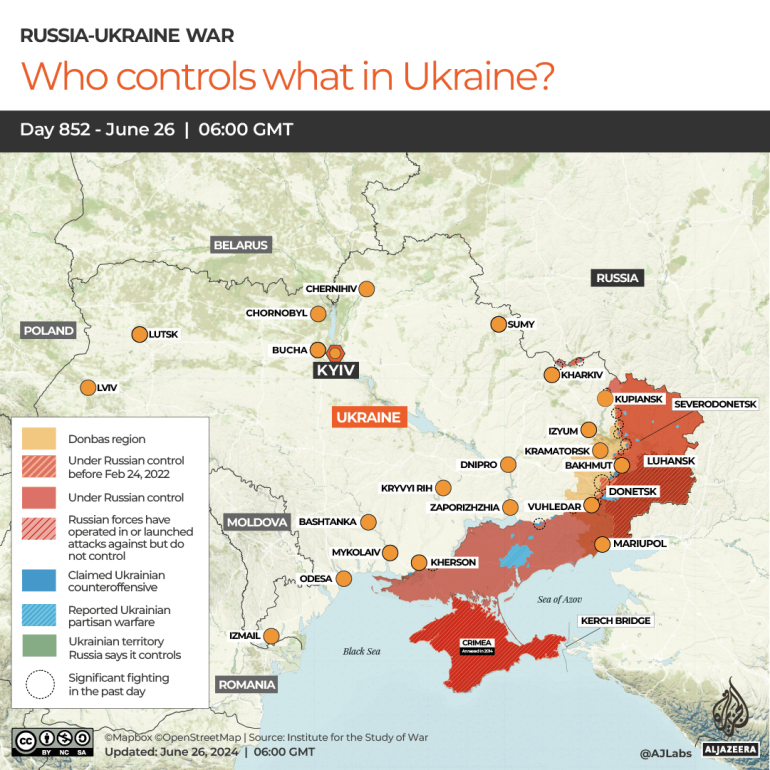
- The Russia-Ukraine war remains intense, with active conflict in several regions.
- Ukraine continues its counteroffensive, focusing on regaining Russian-occupied territories in the eastern Donetsk and southern Zaporizhzhia regions.
- The use of long-range missiles, including U.S.-supplied ATACMS, has enabled deeper strikes into Russian-occupied areas, impacting Russian supply chains and logistics.
- Russia, in turn, has ramped up its attacks on Ukrainian cities and critical infrastructure, targeting energy and water supplies. The areas around Kharkiv, Dnipro, and Kyiv remain under frequent missile and drone attacks.
- Ukraine’s Black Sea ports, essential for grain exports, are also under threat, impacting global food supply chains.
- In occupied territories, including Crimea and eastern Ukraine, local resistance and insurgent activities continue. Civilians face dire conditions, with reports of forced conscriptions and evacuations. The humanitarian toll remains severe, with millions displaced and facing hardships as winter approaches.
Japan
Why in news?
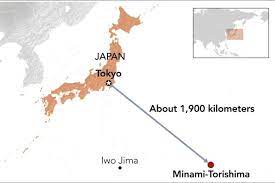
- Japanese researchers have discovered 230 million tons of manganese deposits near Minami-Torishima Island, 1,200 miles from Tokyo.
- This underwater resource includes 740,000 metric tons of nickel and 610,000 metric tons of cobalt, sufficient for Japan's needs for 11 and 75 years, respectively.
- These metals are essential for renewable energy storage, electric vehicle batteries, consumer electronics, and semiconductor production, marking a significant boost to Japan's push for resource independence and its supply chain security in critical technologies.
About Japan:
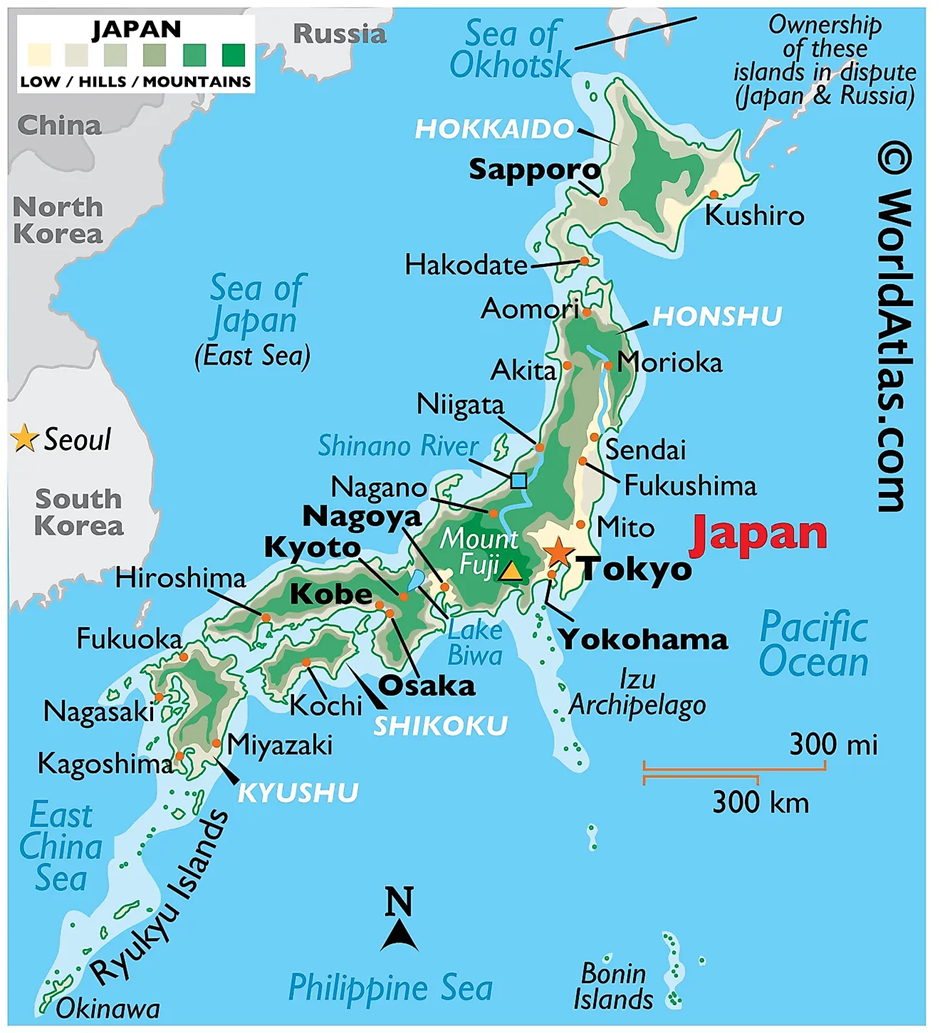
- Japan is an archipelago of over 6,800 islands in the Pacific Ocean, stretching along the eastern edge of Asia. Its four main islands—Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku—constitute most of its landmass.
- The country lies on the Pacific Ring of Fire, making it seismically active with frequent earthquakes and numerous volcanoes.
- Mount Fuji, an iconic stratovolcano, symbolizes its geophysical landscape. The terrain is predominantly mountainous, with limited arable plains like the Kanto and Kansai regions.
- Japan's economic geography is influenced by its natural features. The coastal plains host densely populated urban centres such as Tokyo, Osaka, and Yokohama, which are economic powerhouses.
- Despite limited natural resources, Japan thrives on advanced technology, manufacturing, and trade. Its proximity to key shipping routes facilitates its export-oriented economy, particularly in automobiles, electronics, and machinery.
- Fisheries and agriculture, including rice and tea cultivation, are vital in rural areas, although constrained by limited flatlands. Its fishing sites include notable areas like the Hokkaido coast, known for salmon and crab; the Pacific coast around Honshu, which yields tuna, mackerel, and sardines; and the Sea of Japan, rich in squid and shellfish. Ocean currents play a significant role in its marine resources, including the warm Kuroshio Current and the cold Oyashio Current, which create nutrient-rich fishing zones through their interactions.
- Rich in geothermal energy, Japan utilizes hot springs and volcanic activity for tourism and potential renewable energy. Geothermal energy is harnessed from sites such as Beppu and Kusatsu, known for hot springs, and areas around Kyushu and Tohoku, rich in volcanic activity.
- Japan's major mineral resources are limited, with some domestic production of gold, silver, copper, and limestone. Offshore exploration has identified rich deposits of rare earth elements and manganese nodules, particularly near Minami-Torishima Island, which hold potential for supporting advanced technology industries.




